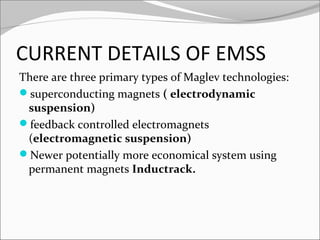
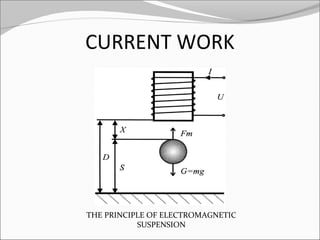
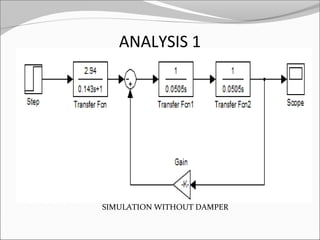
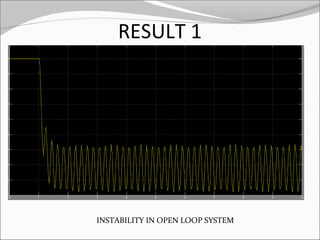
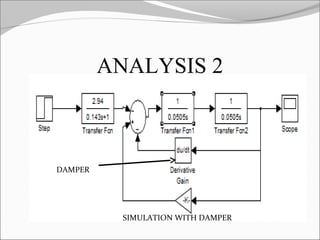
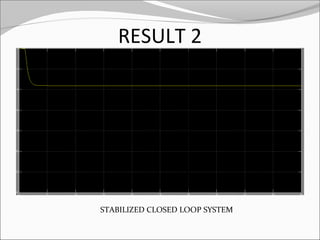
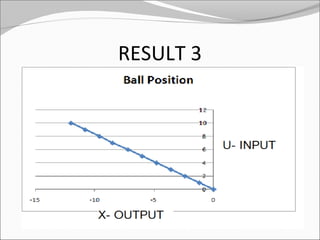
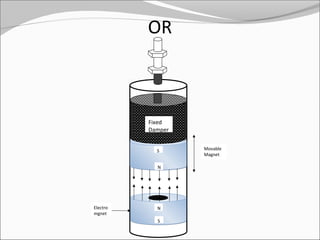
This document discusses the design and analysis of a magnetic suspension system prototype. It provides background on early magnetic suspension systems from 1966. The major components of electromagnetic suspension systems are described as linear motors, electromagnets, thrust bearings and frames. There are three primary types of maglev technologies: superconducting magnets, feedback controlled electromagnets, and newer permanent magnet systems. The research aim is to design, analyze and compare a magnetic suspension system prototype to other suspension systems. Various analyses are presented on simulation of the system without and with a damper to stabilize the system. Results and comments on the modeling and a conclusion are also provided.