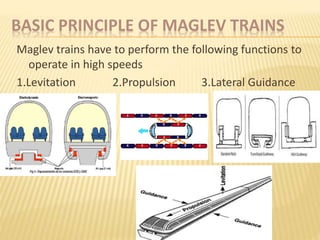
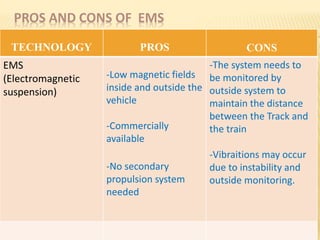
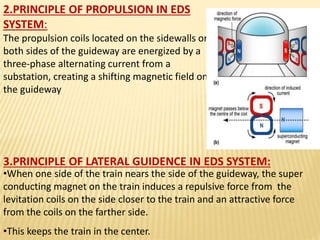
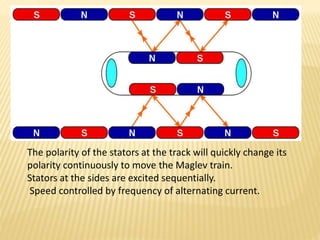
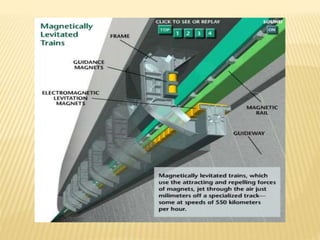
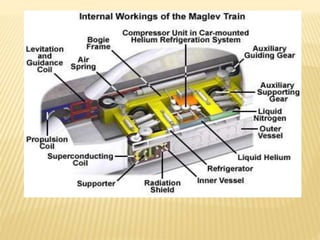
Maglev trains use magnetic levitation to lift and propel trains at high speeds without friction. There are two main types - electromagnetic suspension (EMS) which uses attractive forces, and electrodynamic suspension (EDS) which uses repulsive forces. EMS systems require external monitoring to maintain levitation distance while EDS uses superconducting magnets but requires cryogenic cooling. Both have benefits for high-capacity, high-speed transportation but EDS currently achieves the highest speeds of 581 km/h. Maglev technology has potential applications for space travel and mining in addition to passenger transit.