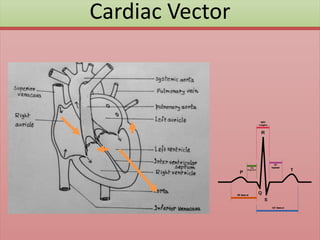
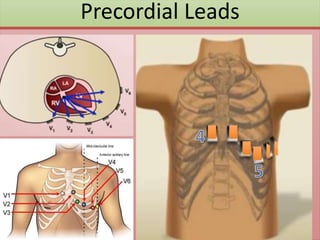
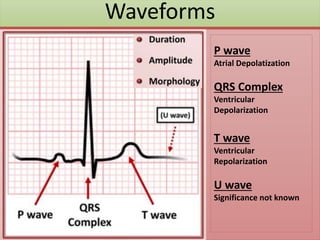
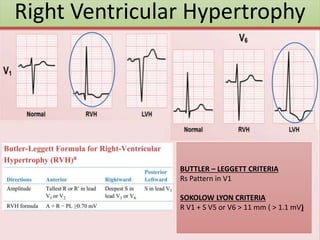
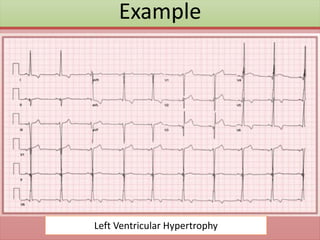
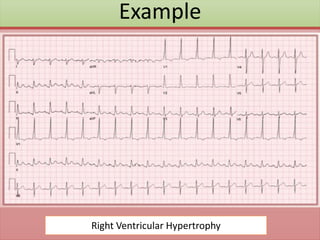
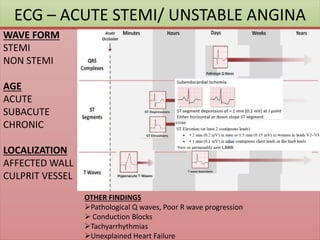
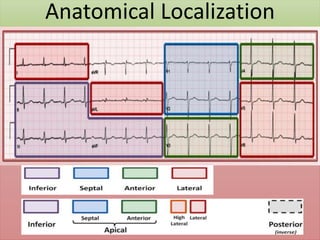
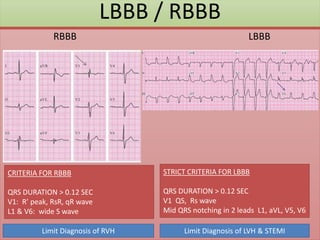
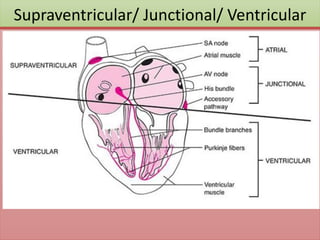
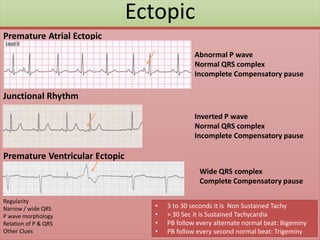
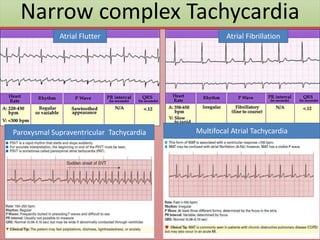
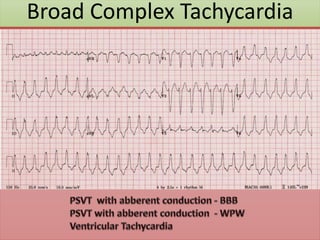
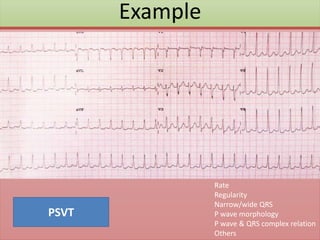
The document provides an extensive overview of ECG analysis, detailing the function and behavior of myocardial cells, conduction pathways, and the significance of various waveforms. It explores ECG abnormalities, criteria for conditions like left and right ventricular hypertrophy, and methods for reading ECGs to identify arrhythmias. Additionally, it discusses the anatomical localization of affected areas and different tachyarrhythmias along with their characteristics.