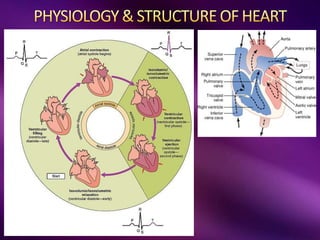
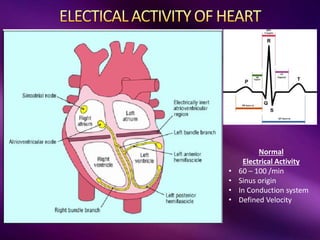
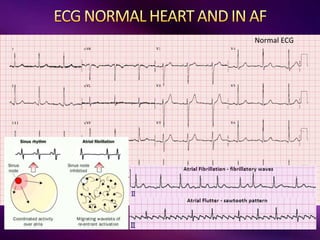
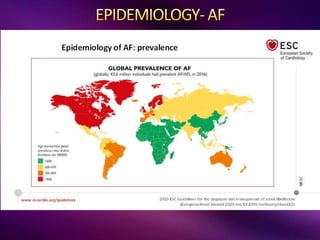
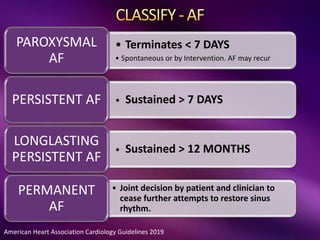
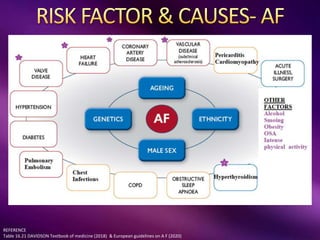
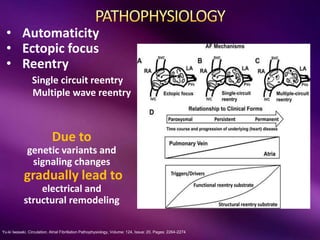
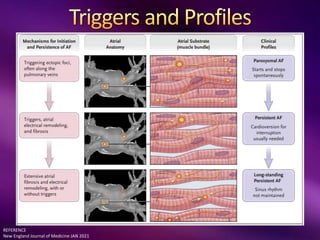
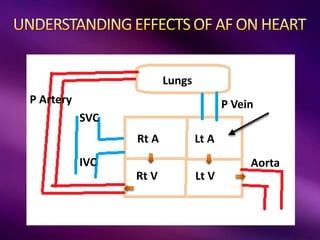
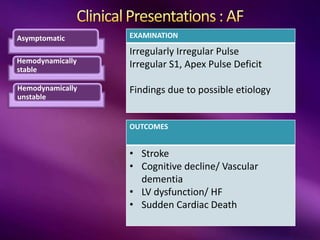
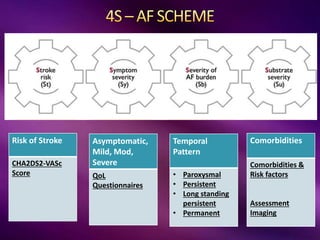
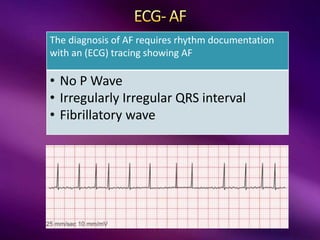
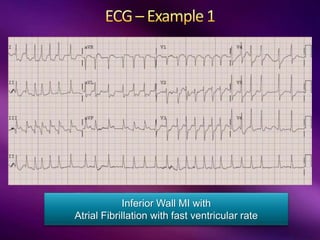
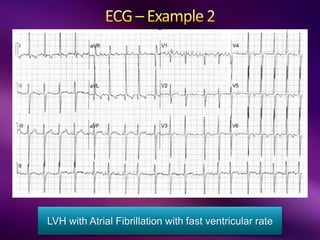
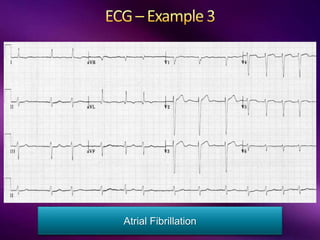
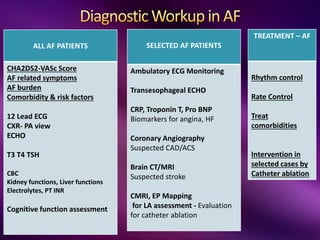
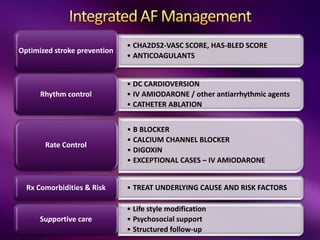
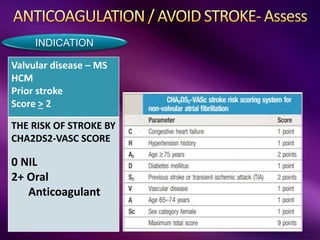
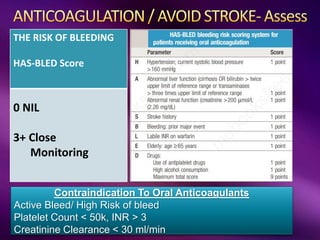
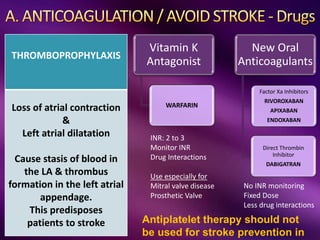
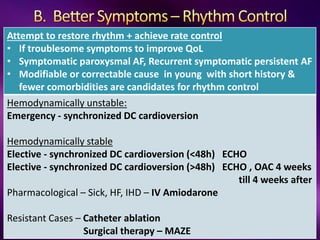
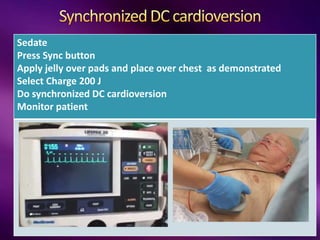
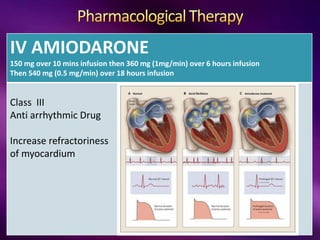
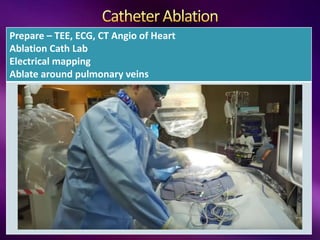
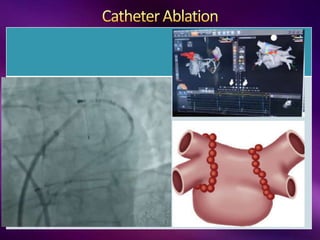
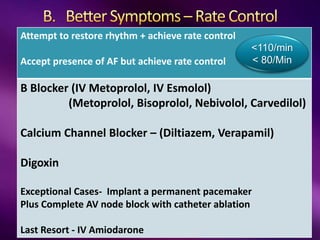
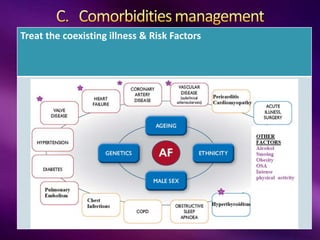
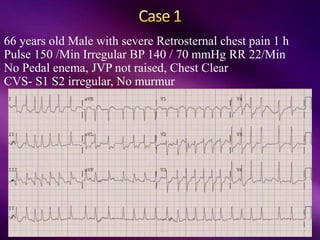
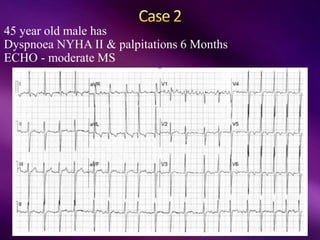
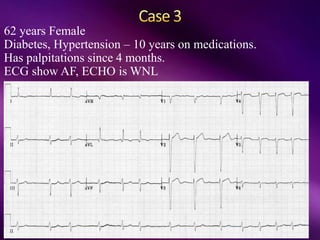
The document outlines the clinical aspects of atrial fibrillation (AF), including its pathophysiology, classifications, symptoms, and management guidelines. It discusses various forms of AF and their presentations, as well as diagnostic tools and treatment options like rhythm and rate control strategies. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of stroke risk assessment using CHADS2-VASc and HAS-BLED scores to guide anticoagulation therapy.