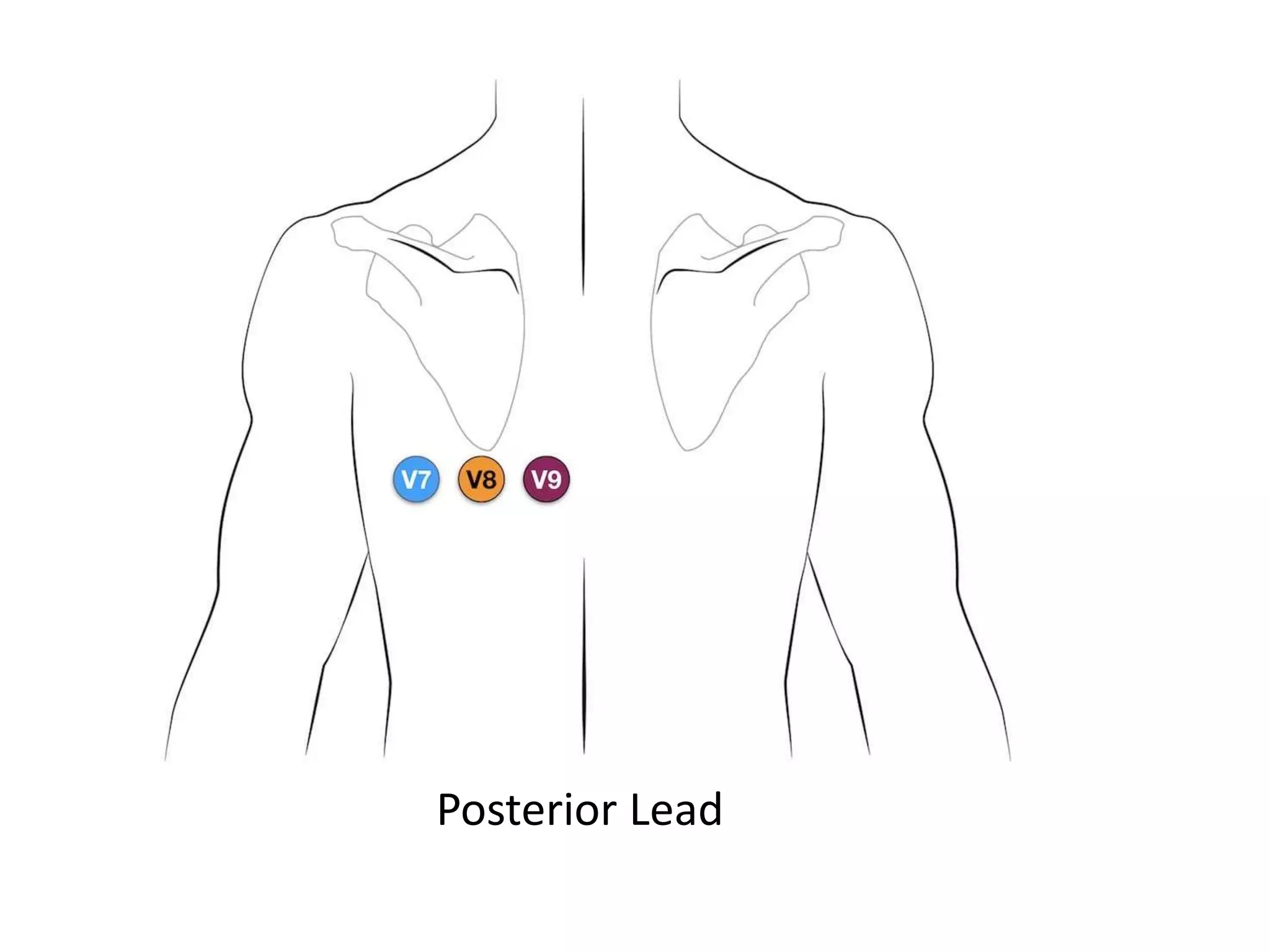
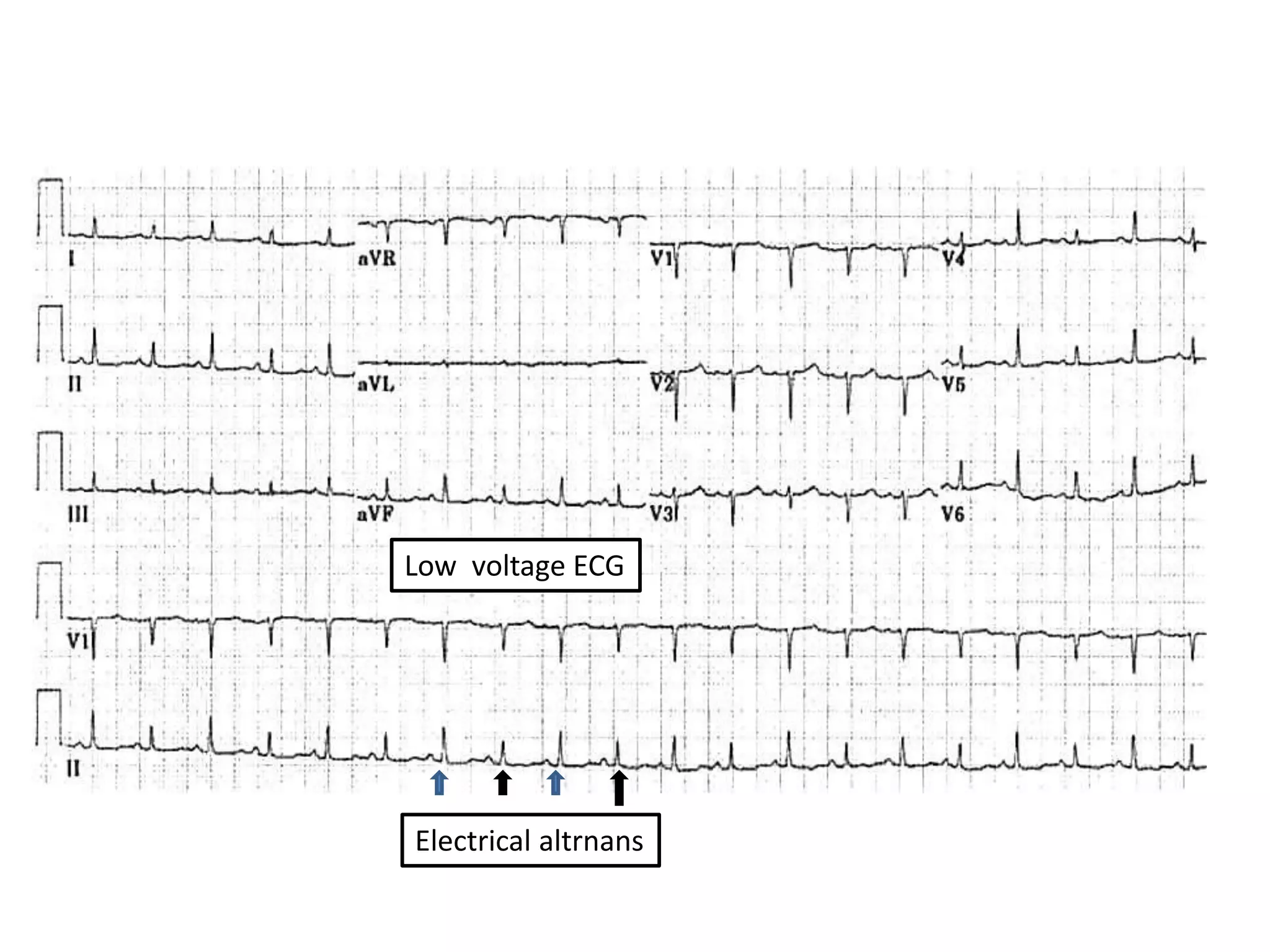
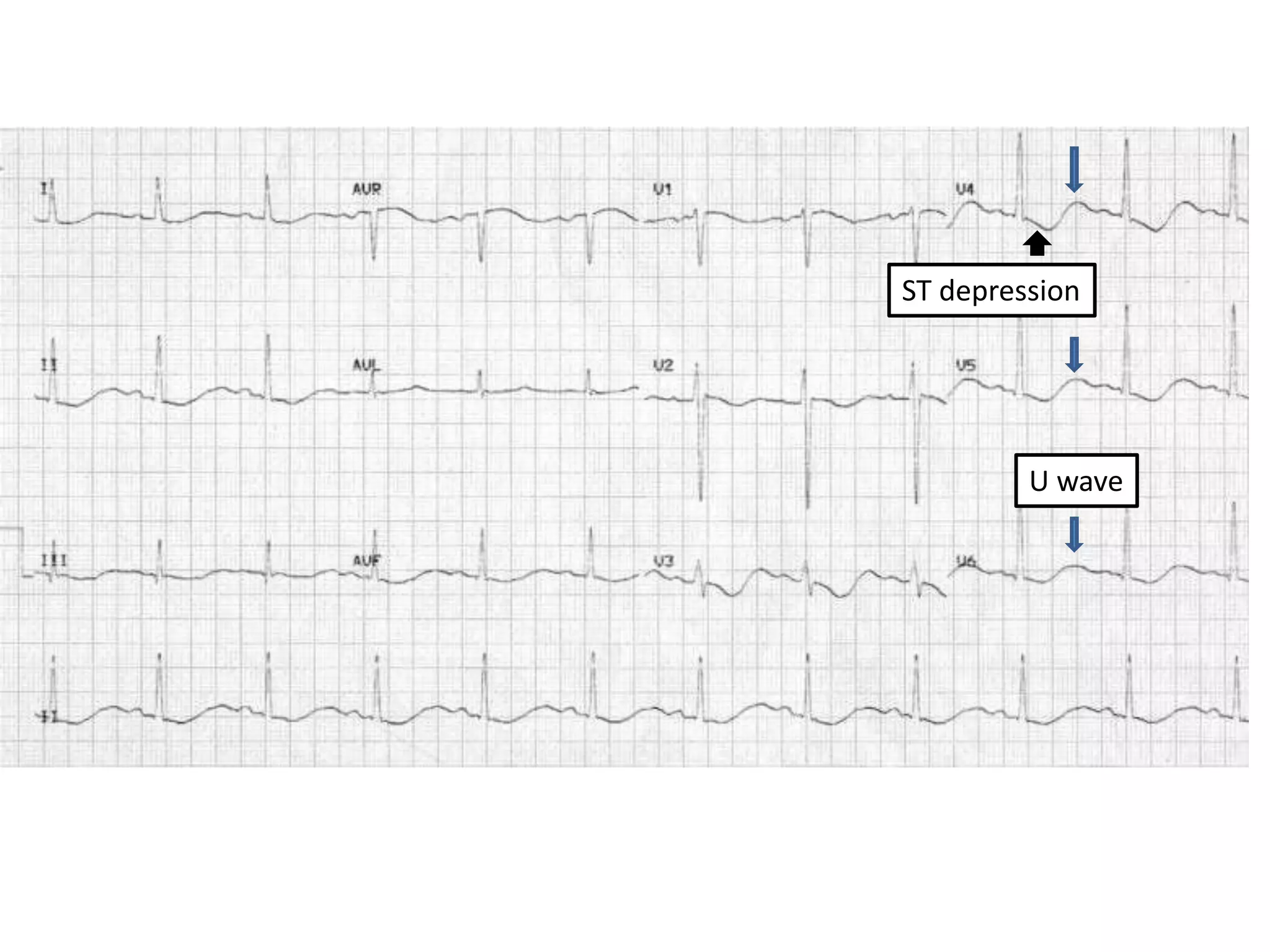
This document provides an overview of ECG interpretation including:
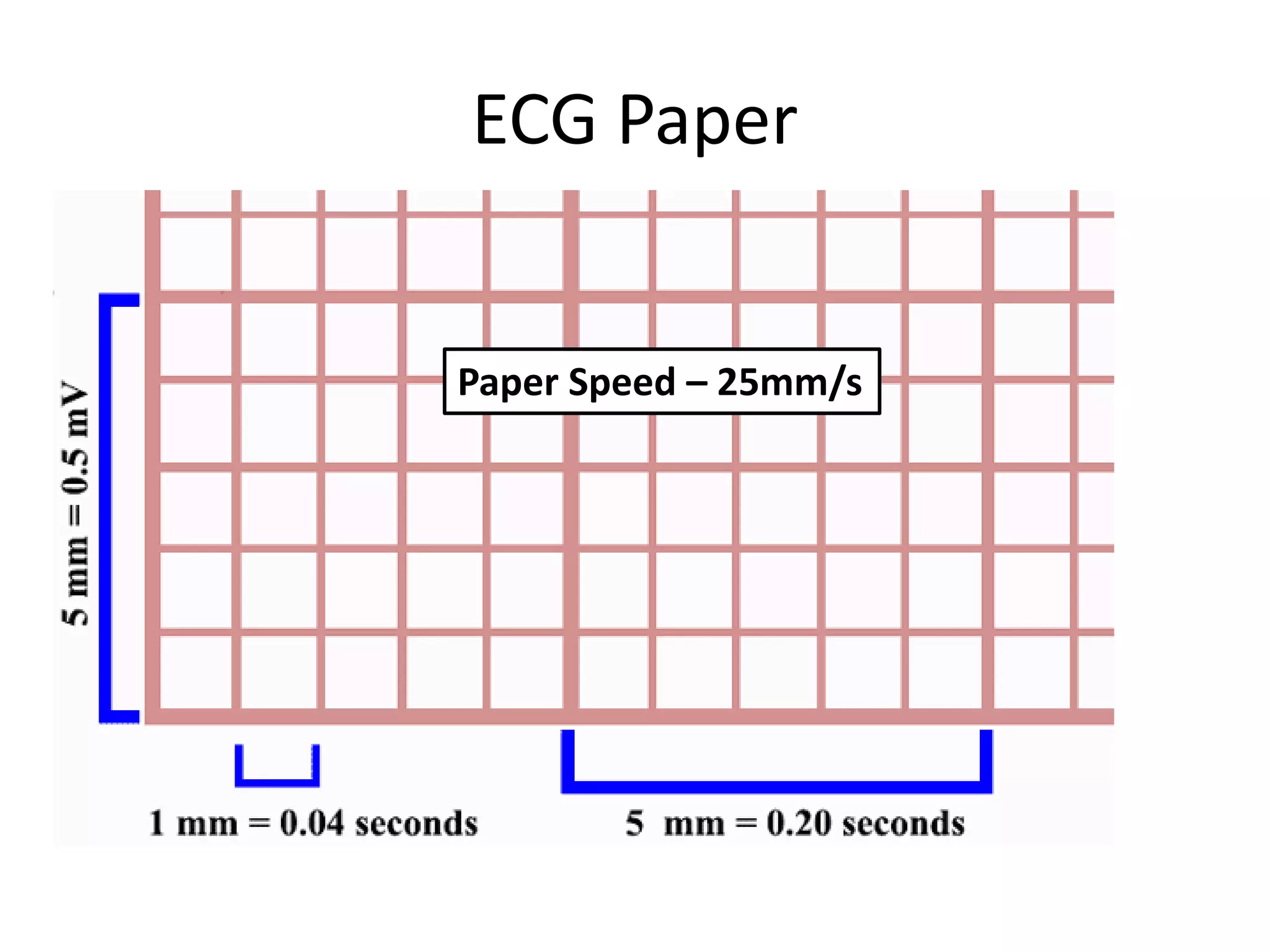
1. The conductive system of the heart and waves seen on ECG such as P, QRS, T.
2. Approaches to ECG interpretation including assessing rate, rhythm and characteristics of waves.
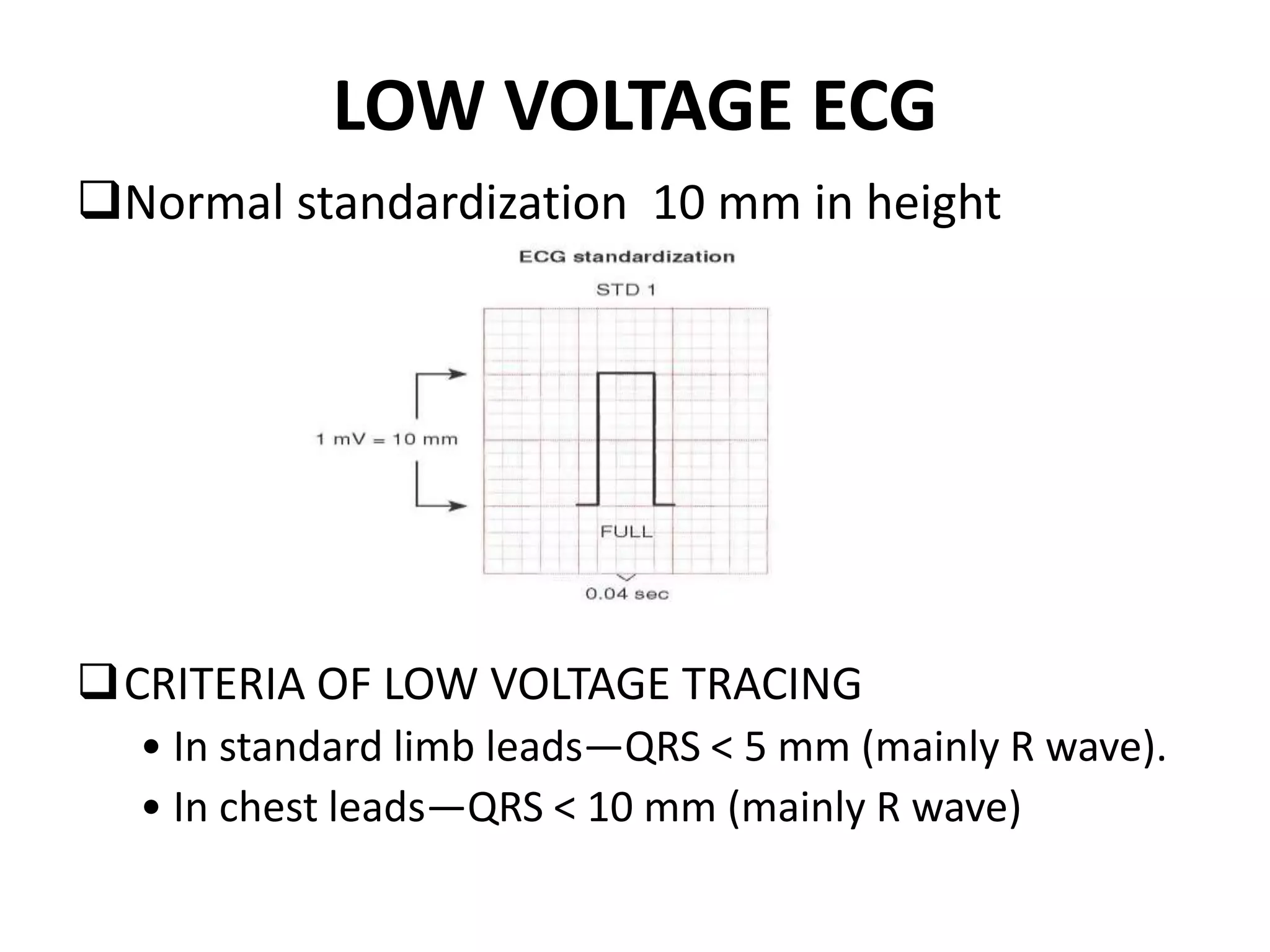
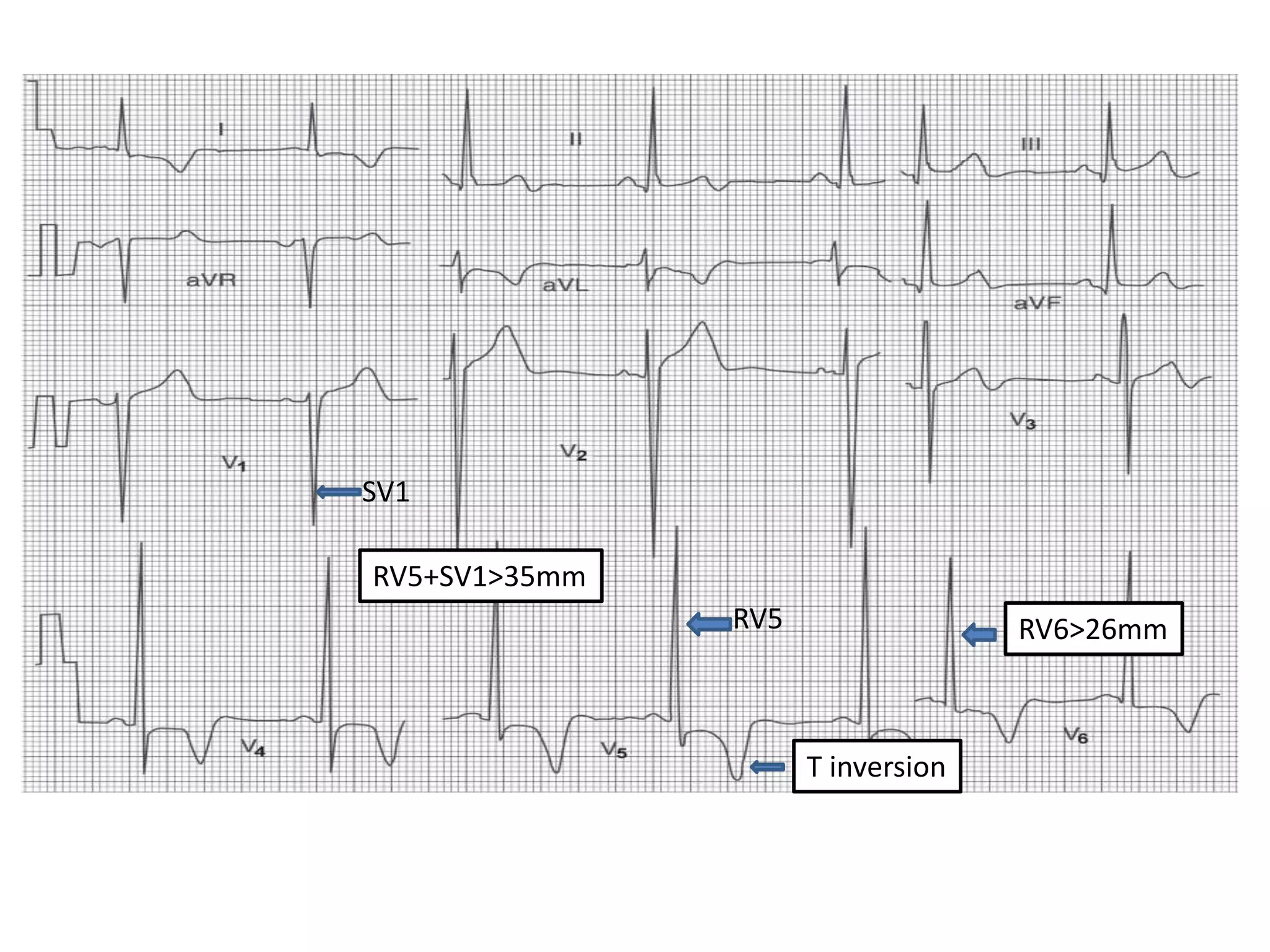
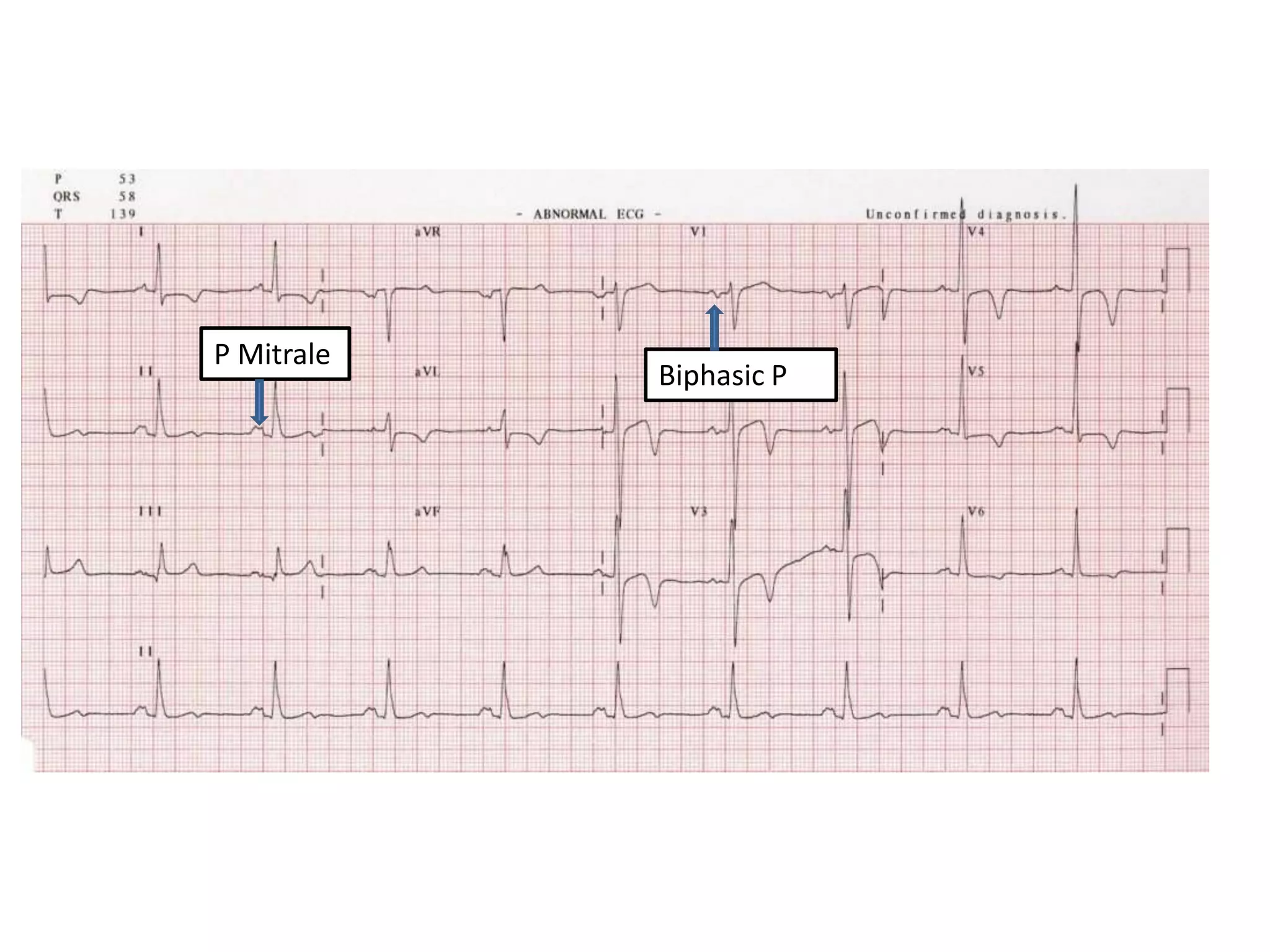
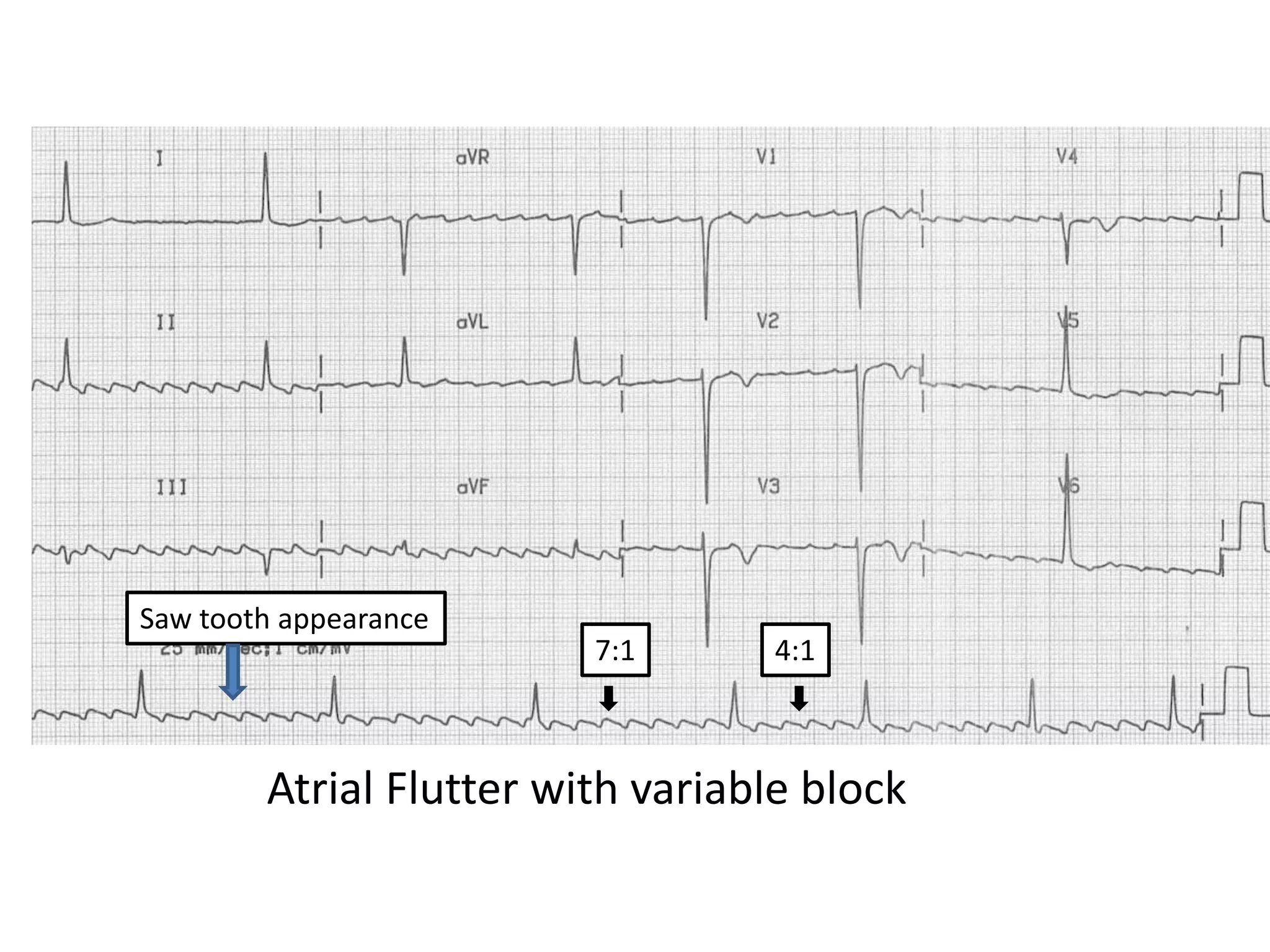
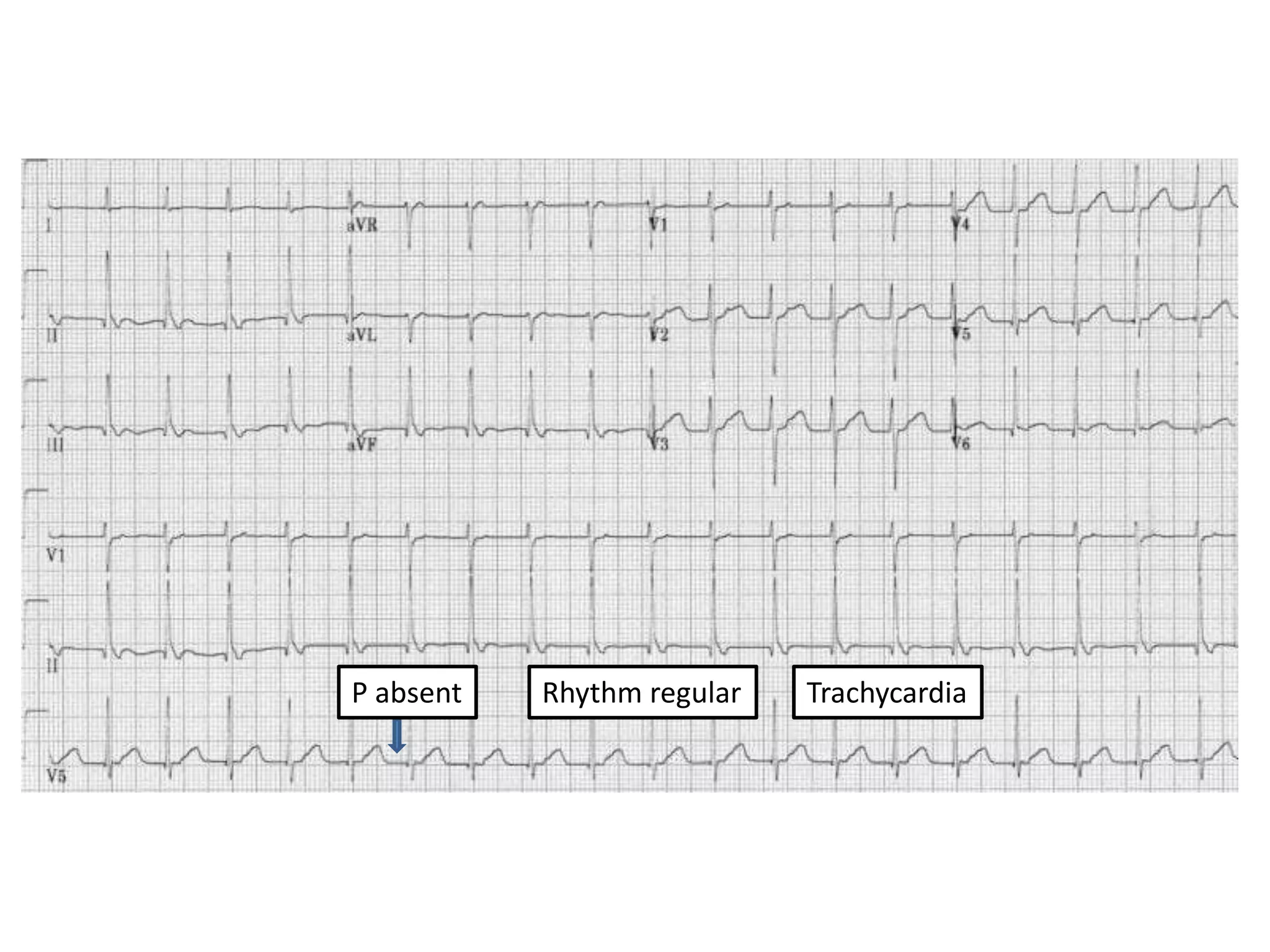
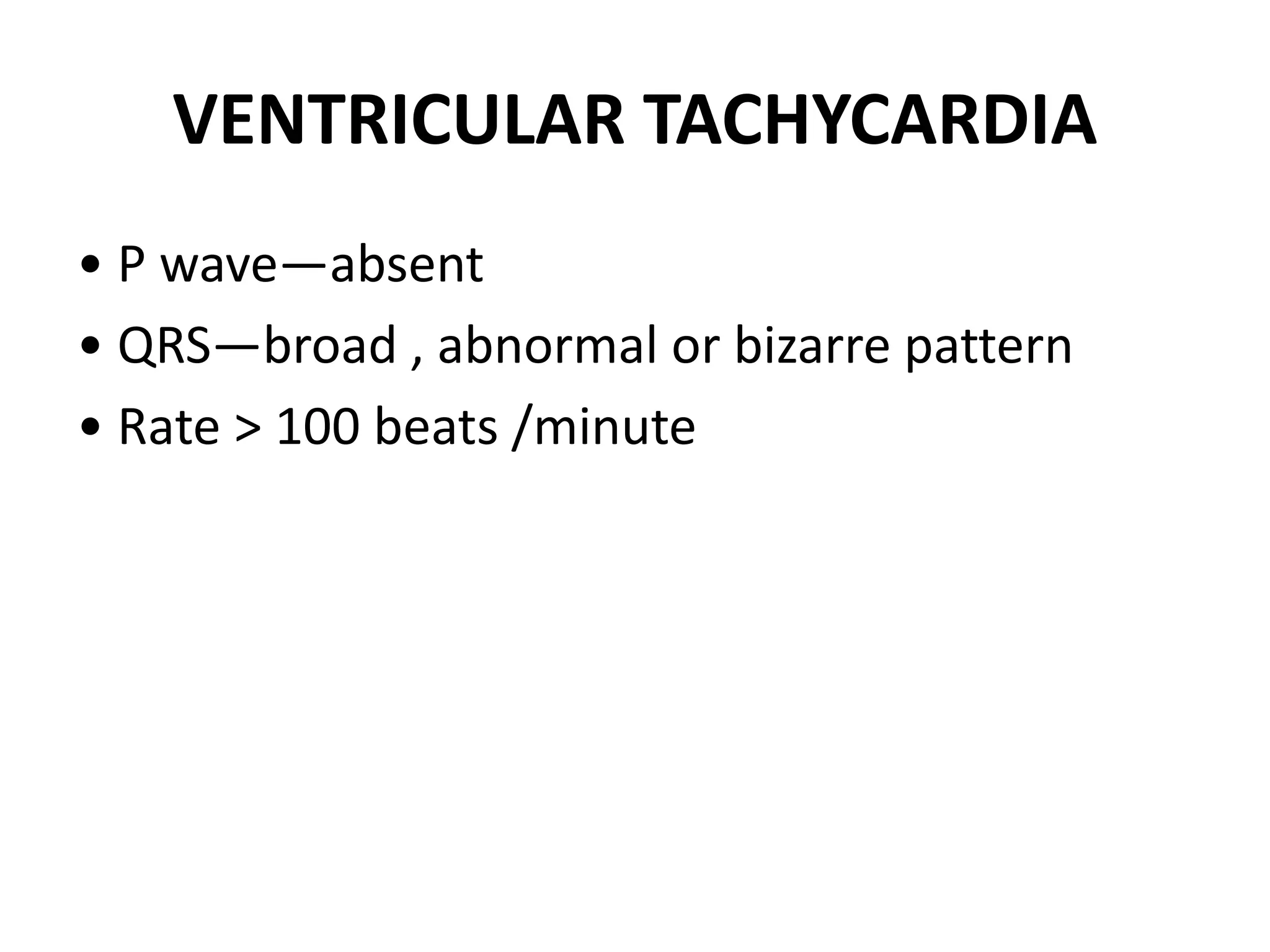
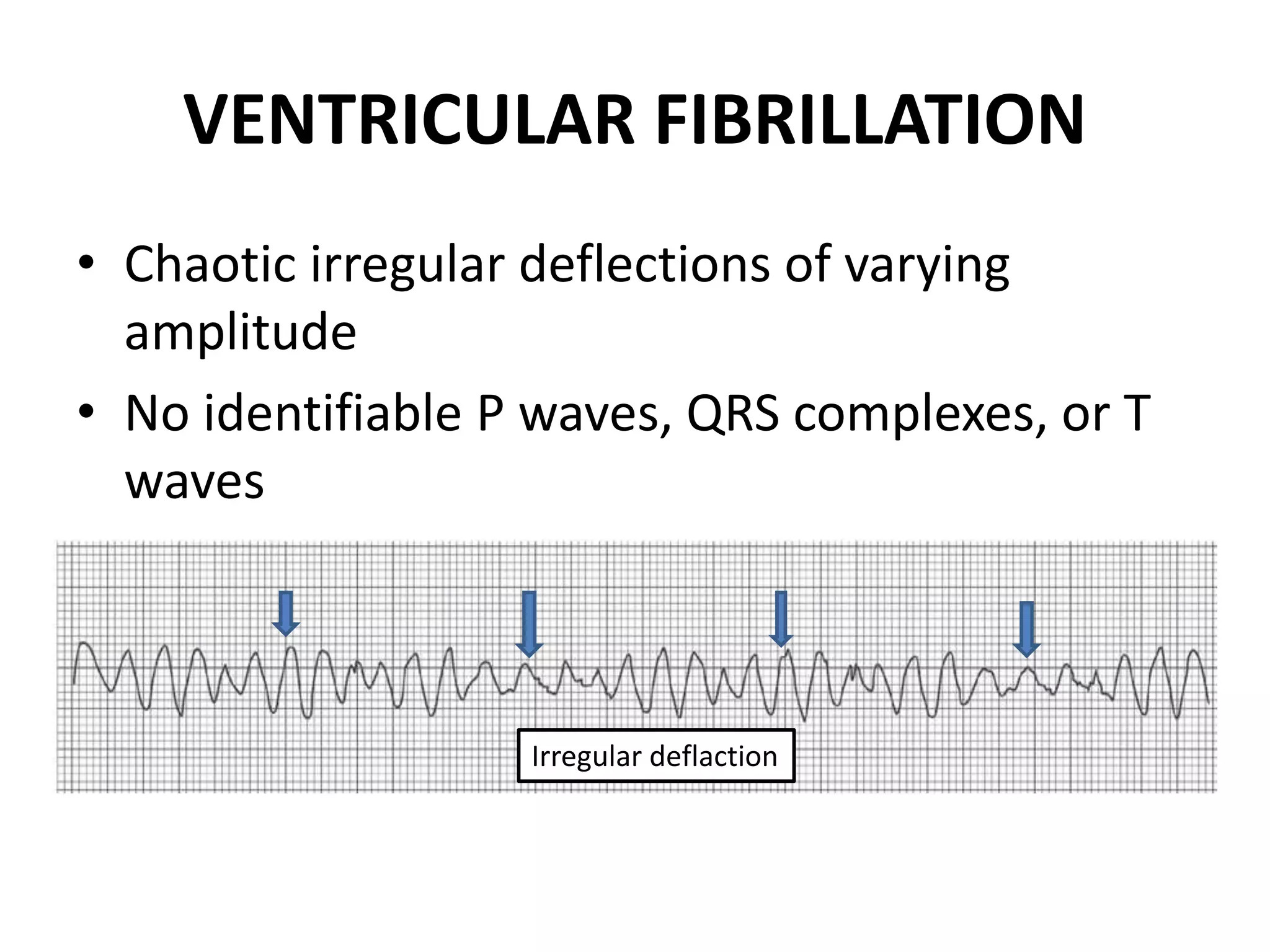
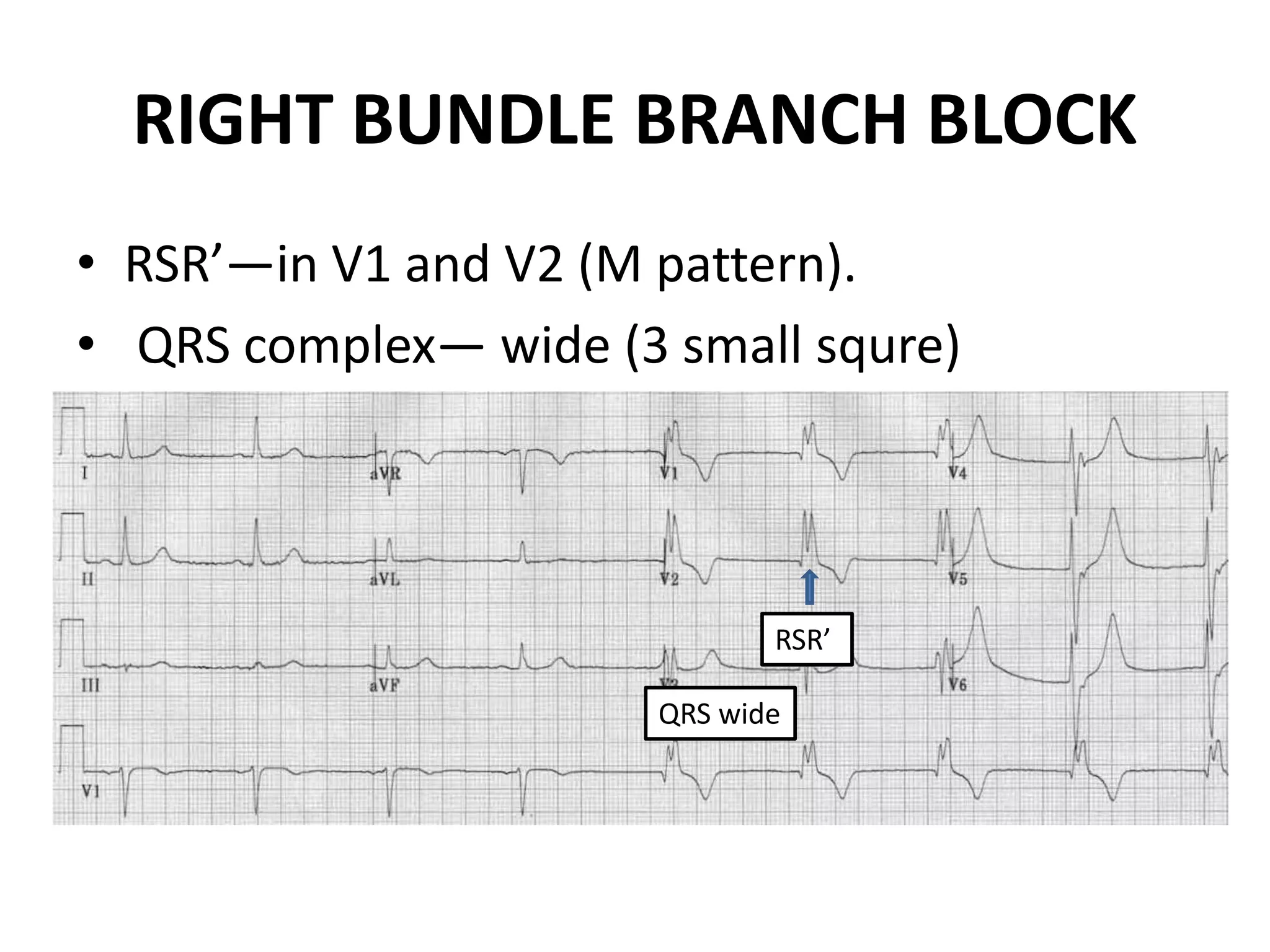
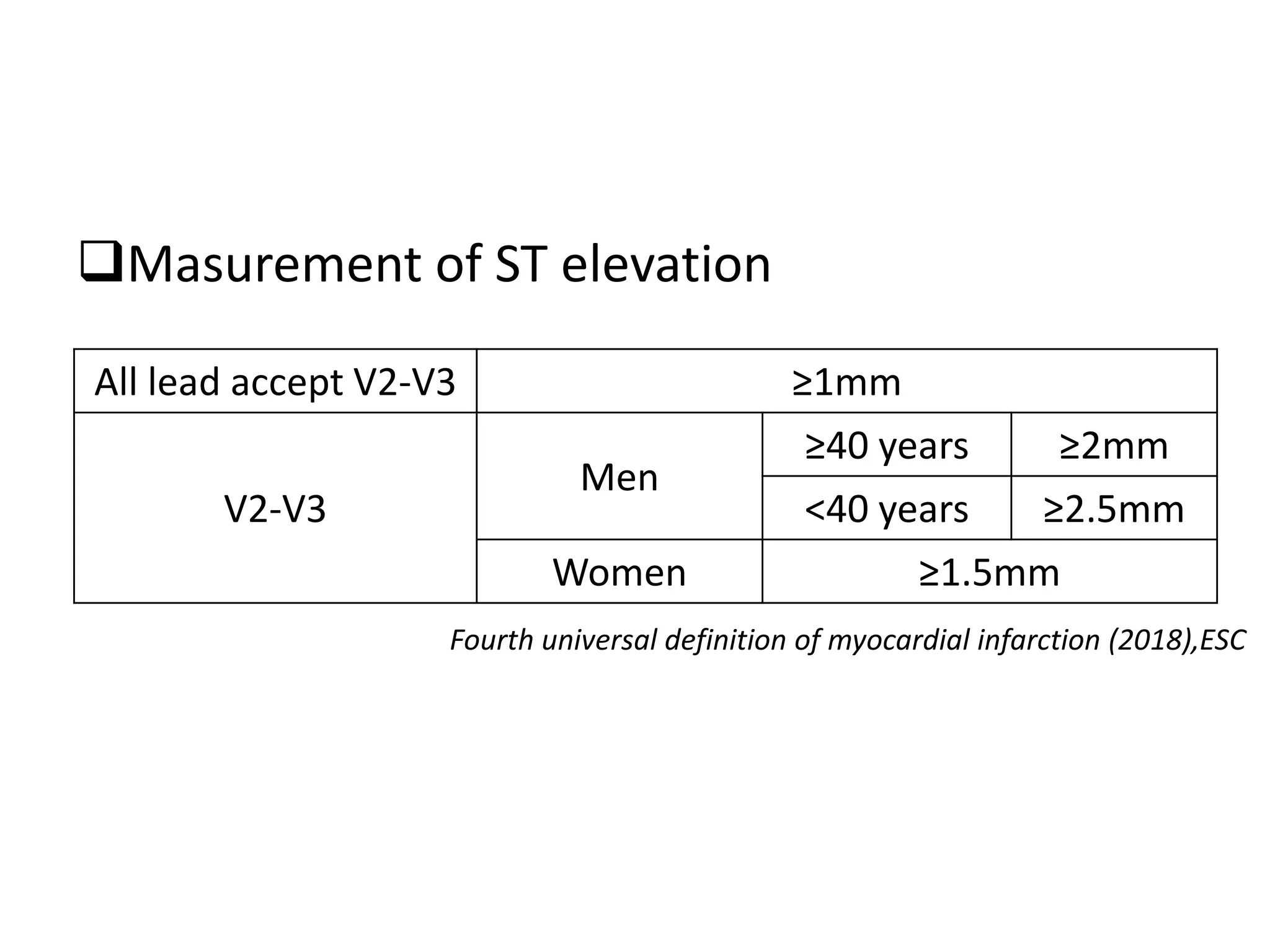
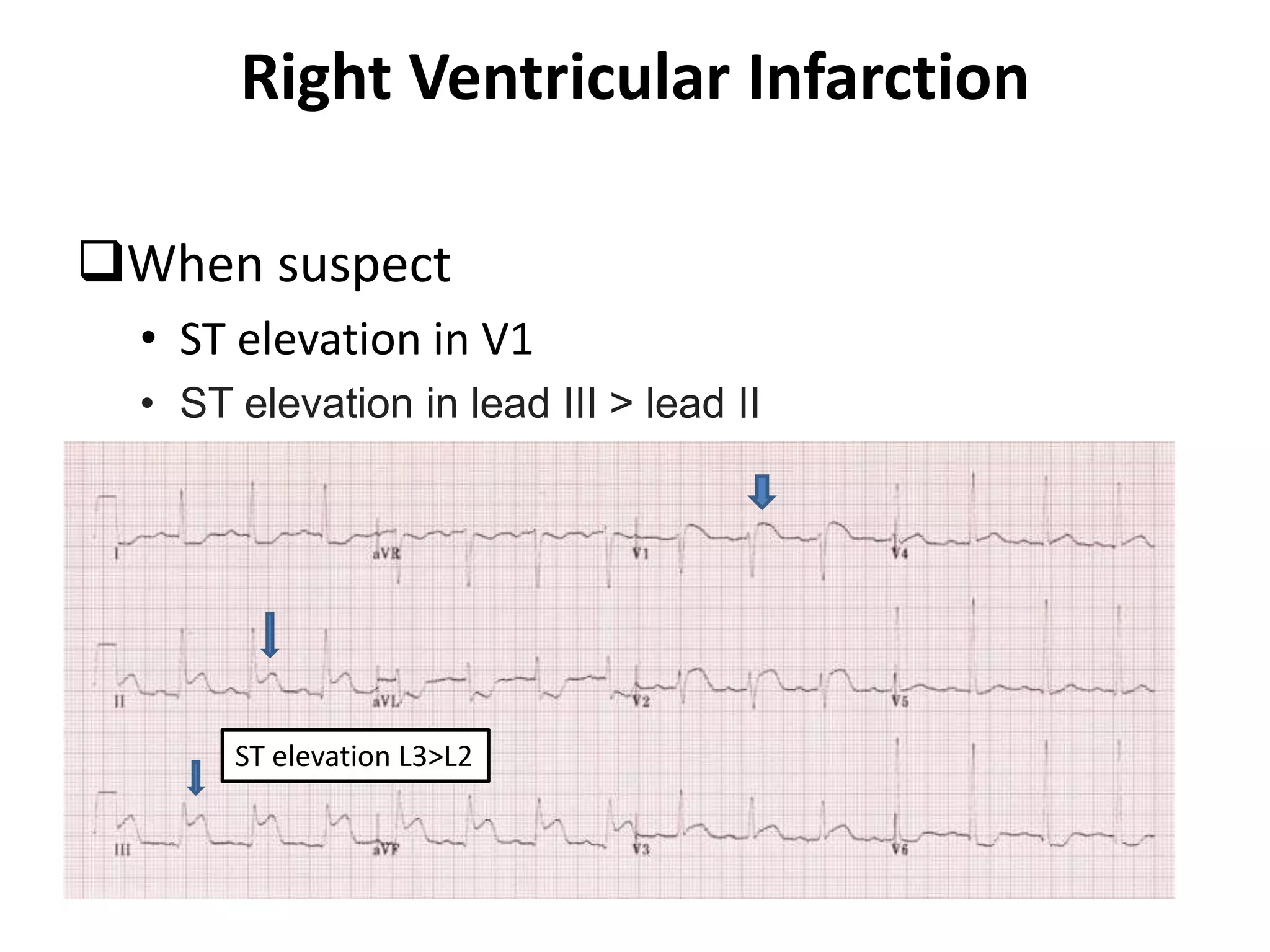
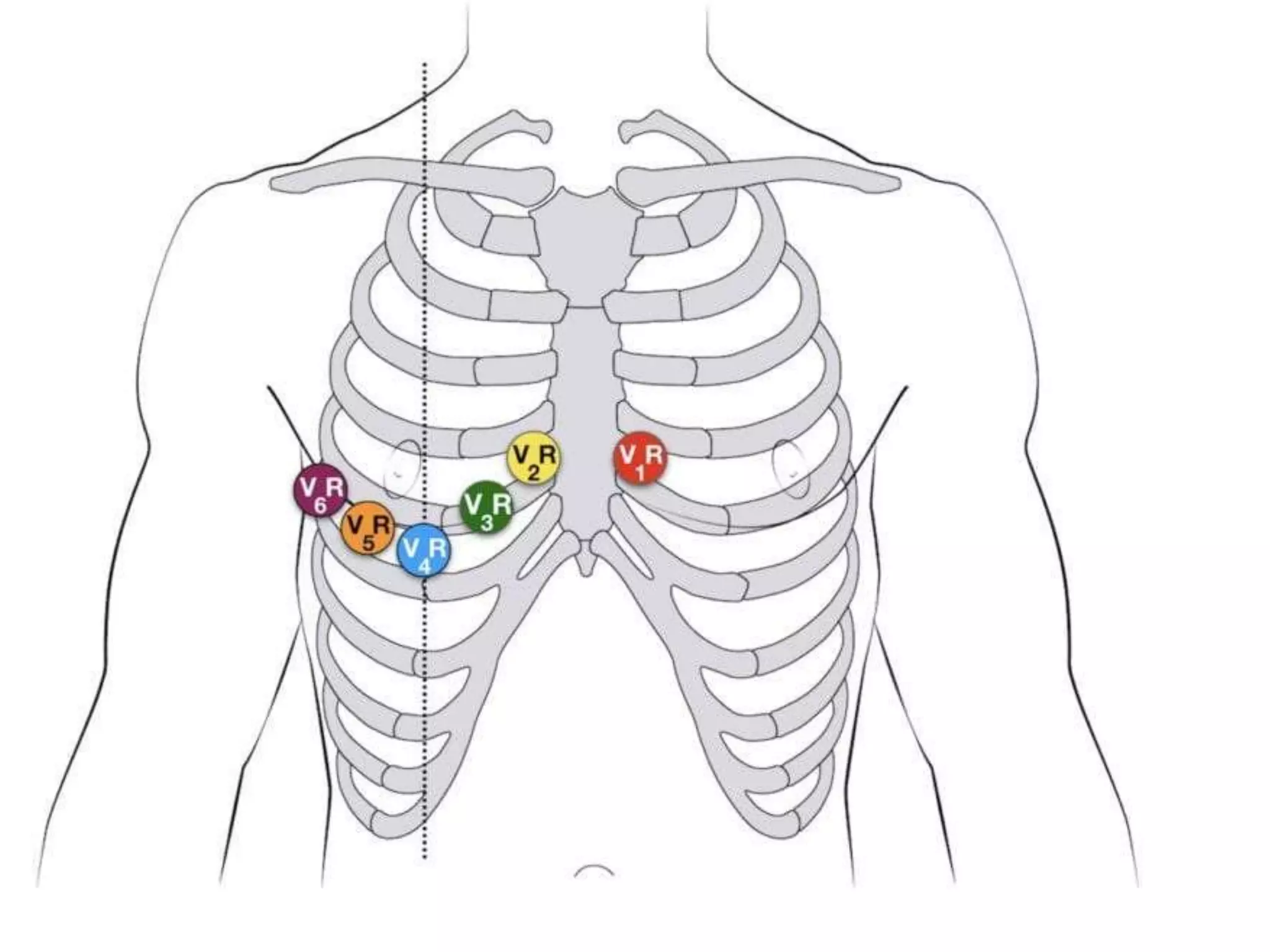
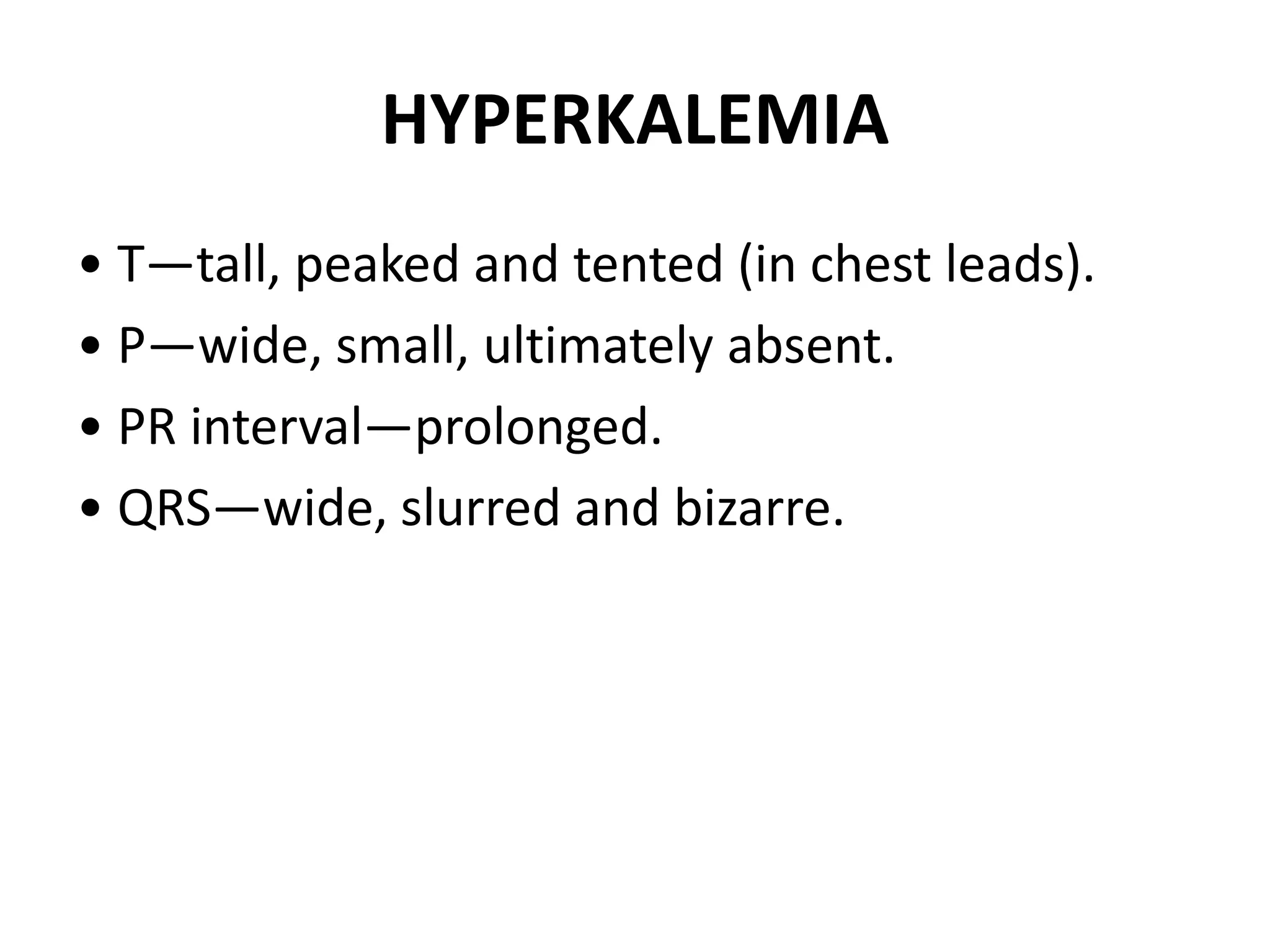
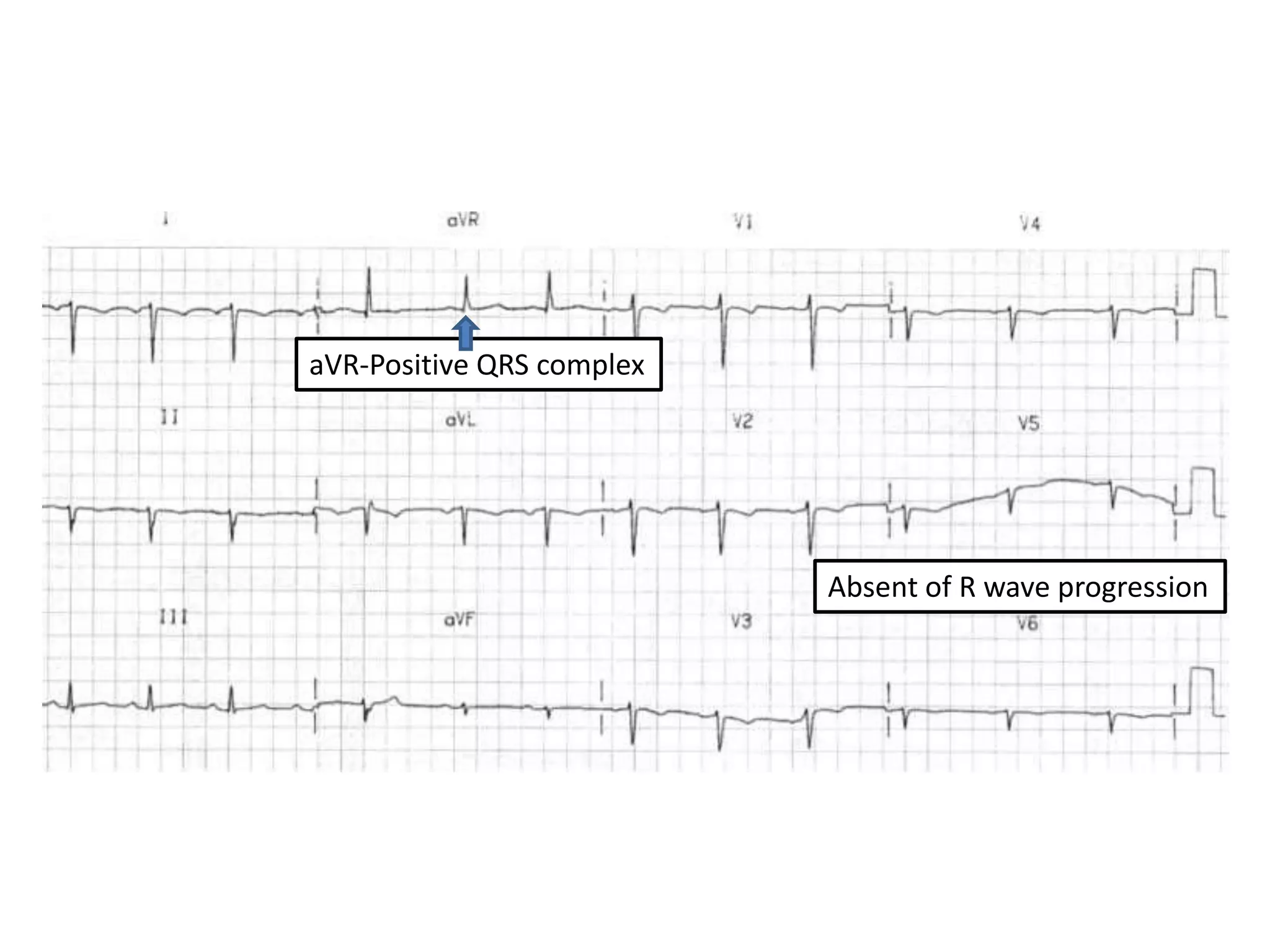
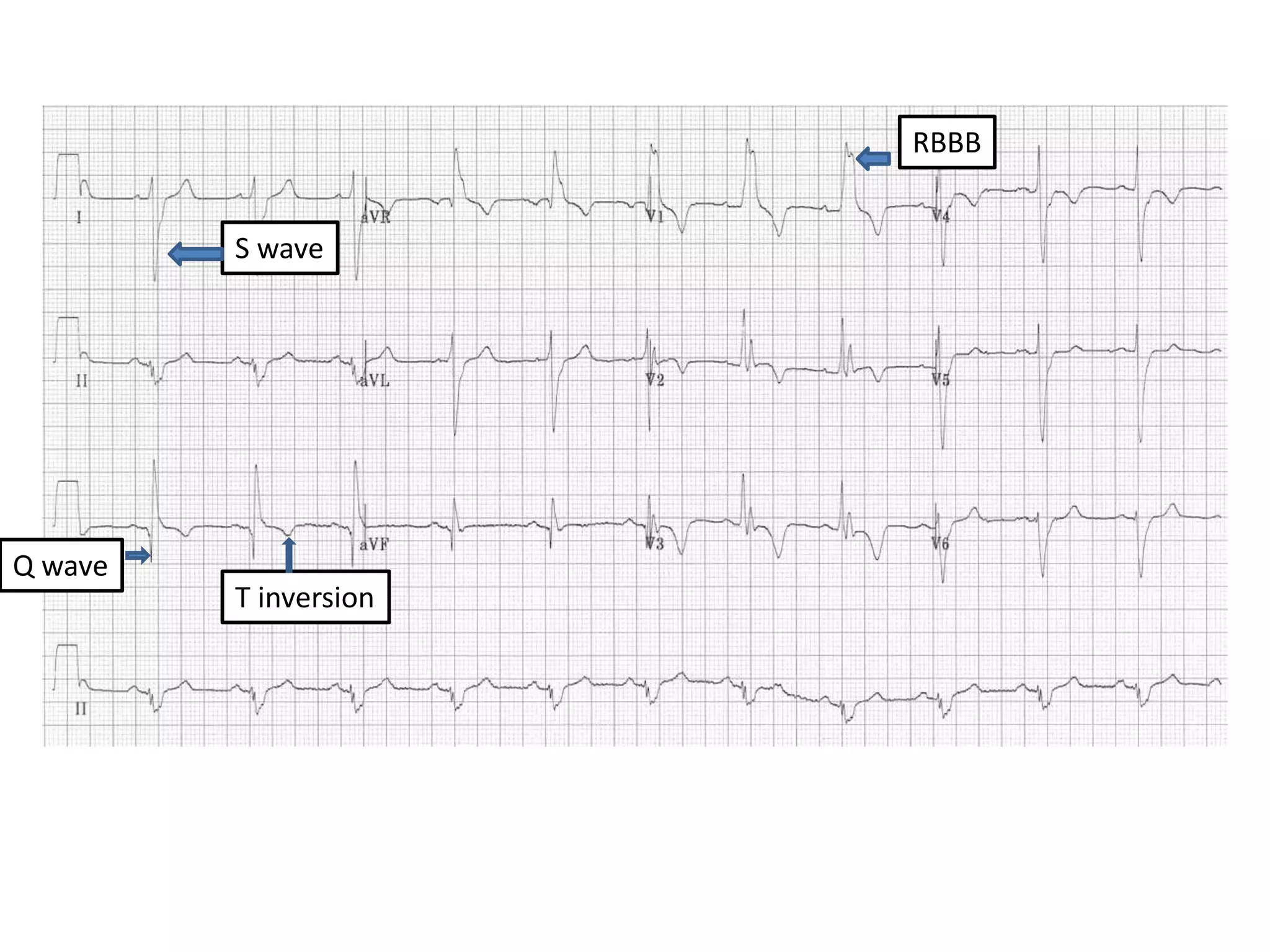
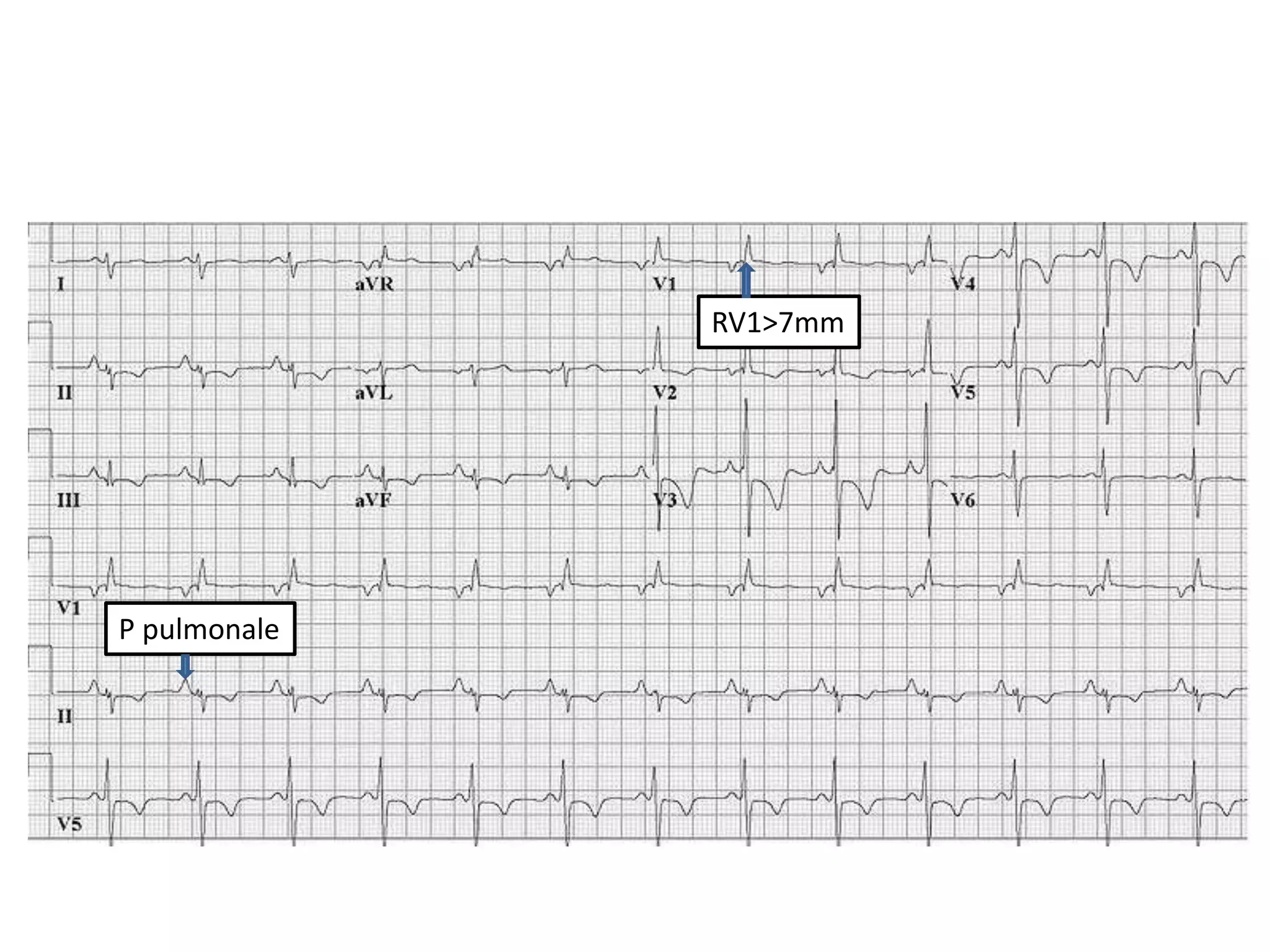
3. Common abnormalities seen in ECGs such as arrhythmias, conduction blocks, ventricular hypertrophy and myocardial infarction.