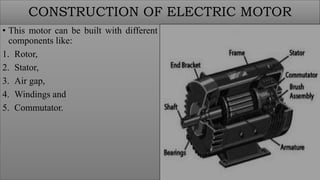
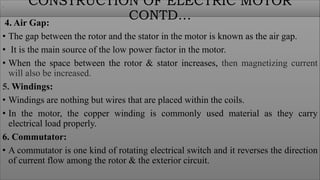
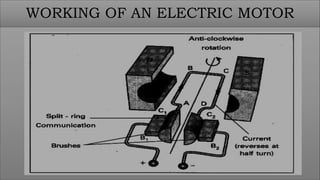
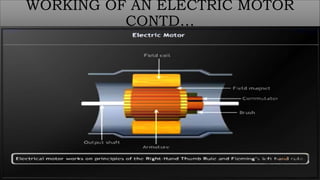
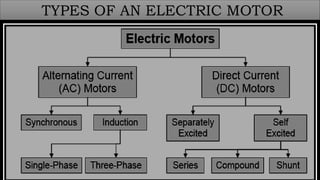
The document discusses electric motors, including their construction, working principles, and types. It describes how electric motors convert electrical energy to mechanical energy using electromagnetic phenomena. The key components of an electric motor are identified as the rotor, stator, air gap, windings, and commutator. The working principle involves the interaction of current-carrying conductors and a magnetic field to generate torque that rotates the shaft. The two main types are AC motors, which are driven by alternating current, and DC motors, which use direct current to power the movement of a rotor within a magnetic field and convert it to rotational motion.