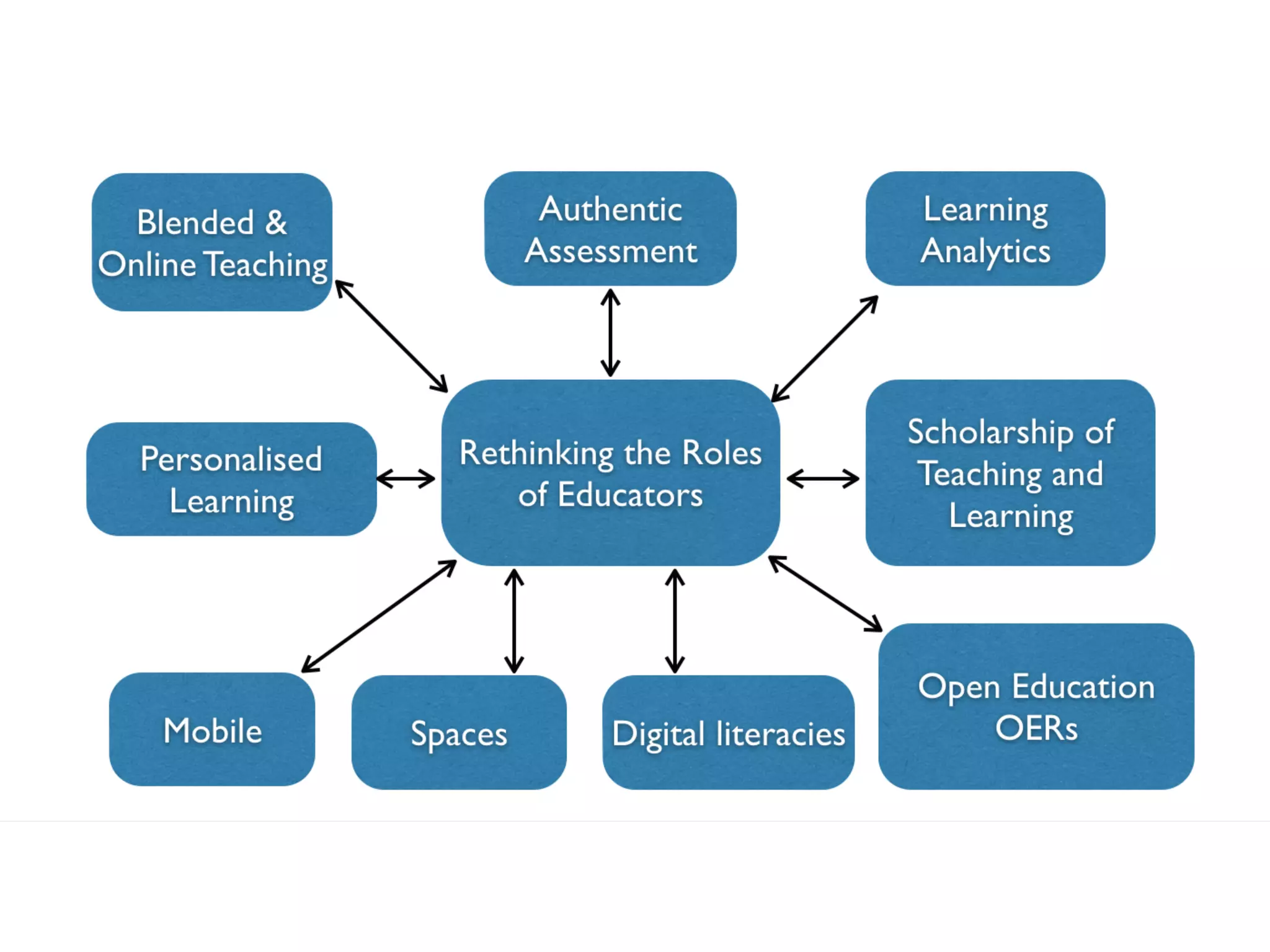
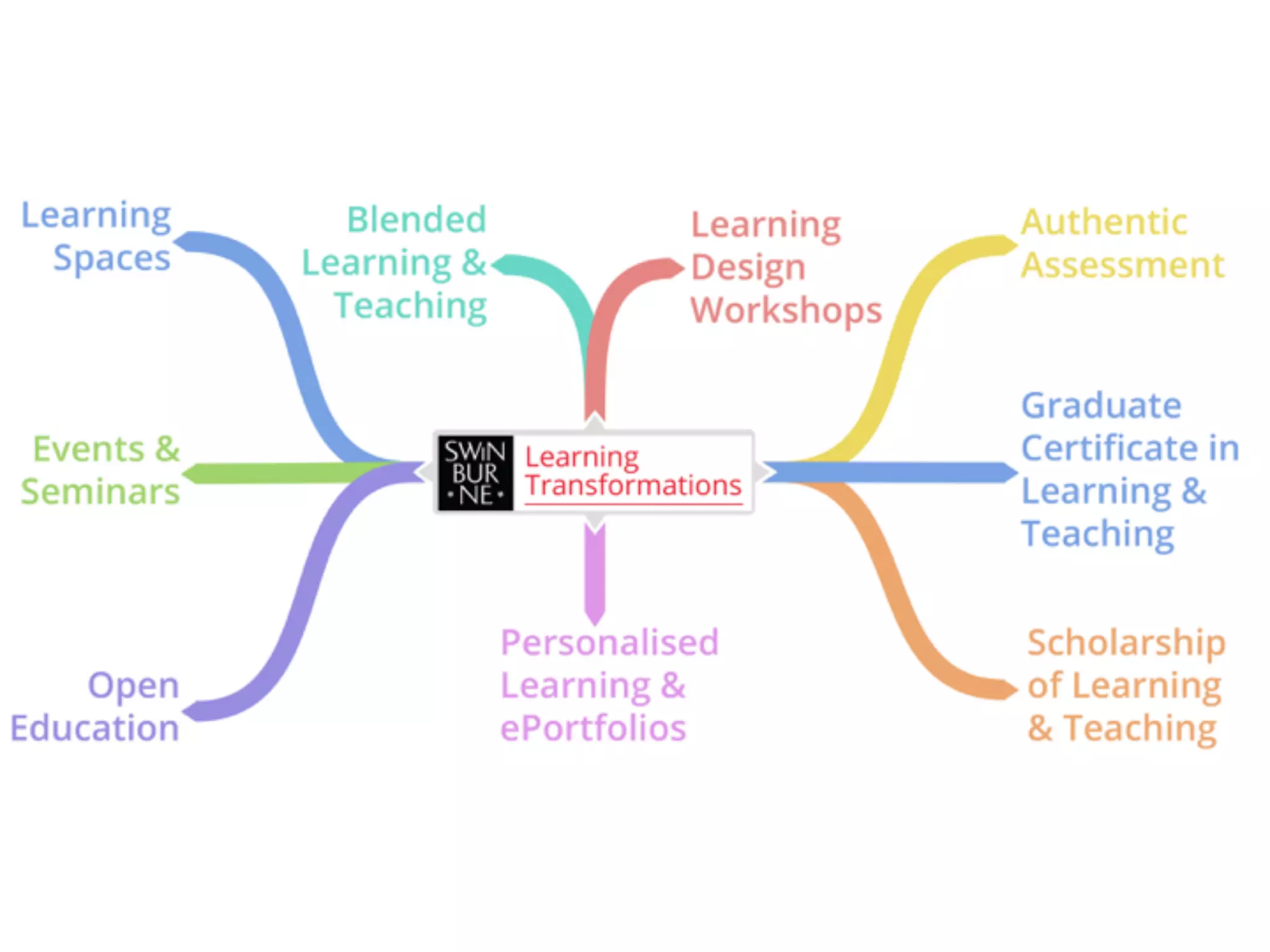
This document discusses developing integrated learning curriculum to engage learners. It outlines guiding pedagogies such as authentic learning, authentic assessment, personalized learning, and peer learning. Authentic learning involves completing complex real-world tasks over time in collaboration, simulating real work. Authentic assessment engages learners in important real-life problems. Personalized learning focuses on learning pathways, ePortfolios, and empowering continual learning. Peer learning emphasizes interdependent learning through sharing ideas. The document also discusses blended learning, professional development expectations, and learning design workshops on topics like authentic and personalized learning.