Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX








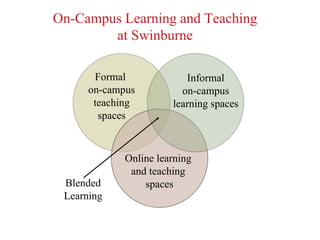
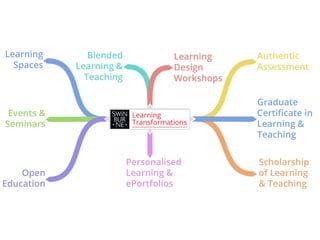


1. The document discusses learning with technology and key considerations for effective implementation, such as authentic learning outcomes, affordances of the chosen technology, and evidence of enhanced learning. 2. It advocates for a learning ecosystem that incorporates simple to complex scenarios, complements other training methods, includes authentic assessment, and allows for refresher training. 3. Guiding pedagogies discussed are authentic learning, authentic assessment, personalized learning, and peer learning. Authentic learning involves complex real-world tasks completed over time in collaboration, mirroring a real workplace.










