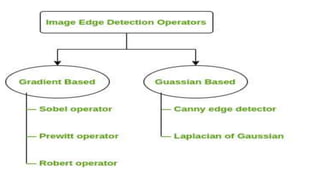
Edge detection is a technique used in digital image processing to identify boundaries between objects in an image. There are three types of edges: horizontal, vertical, and diagonal. Edge detection segments an image into regions of discontinuity and is used for tasks like pattern recognition, image morphology, and feature extraction. It reduces data while preserving structural image properties. Edge detection operators can be gradient-based, using techniques like Sobel, Prewitt, and Robert, or Gaussian-based, using techniques like Canny and Laplacian of Gaussian. The Sobel, Prewitt, and Robert operators use kernels or masks to calculate vertical and horizontal derivative approximations to identify edges.