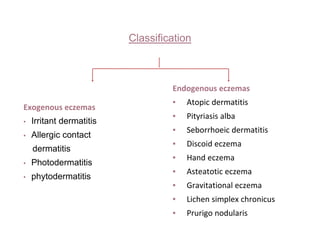
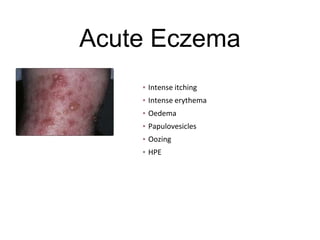
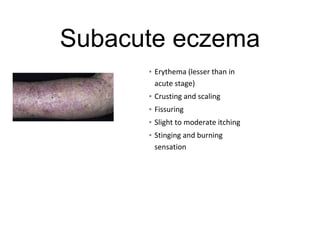
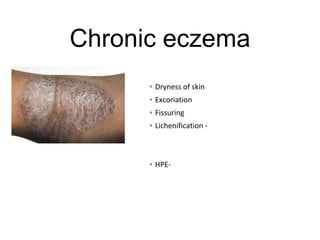
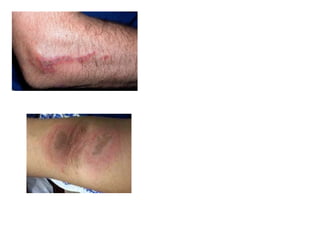
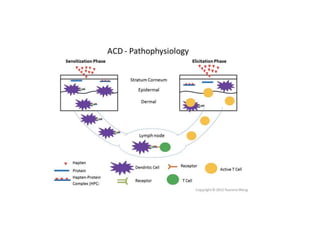
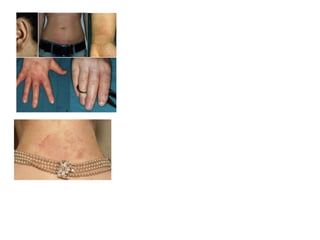
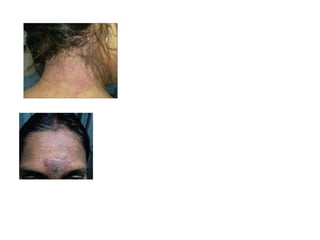
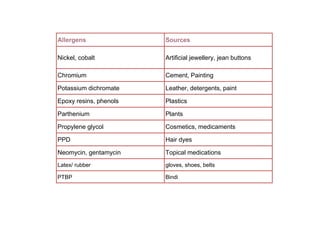
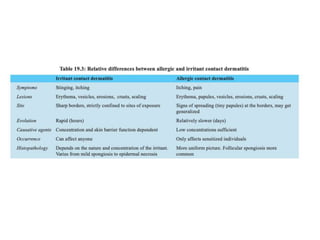
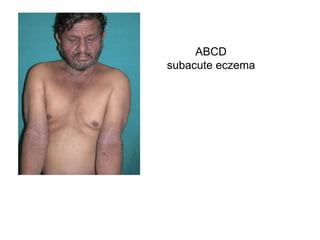
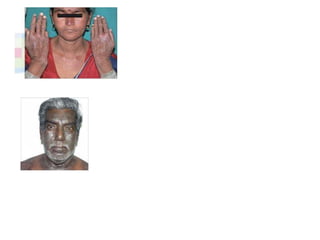
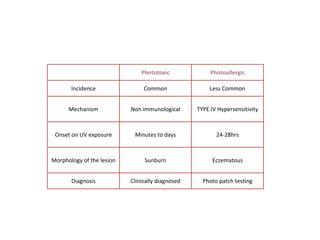
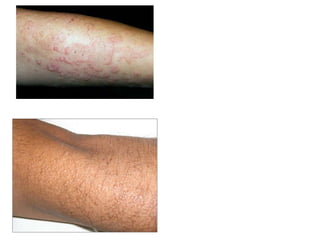
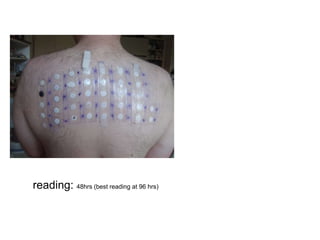
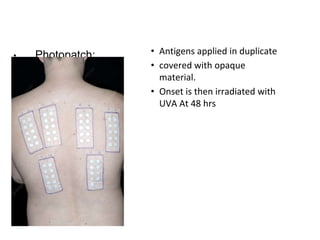
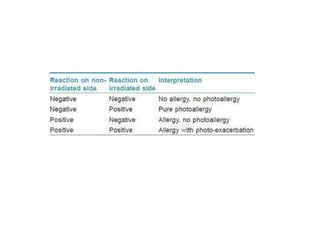
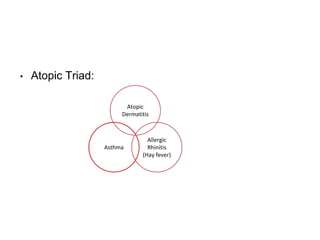
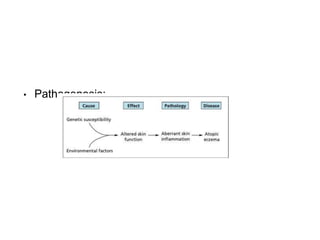
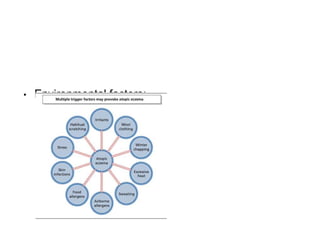
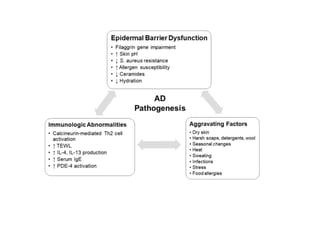
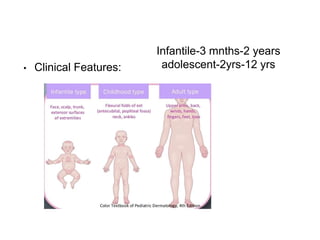
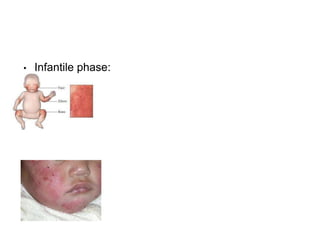
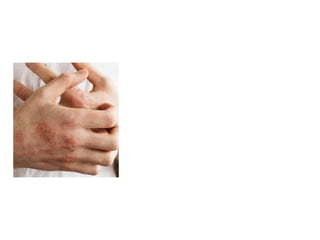
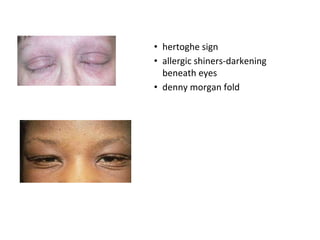
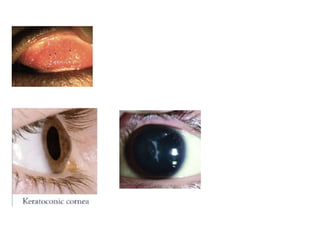
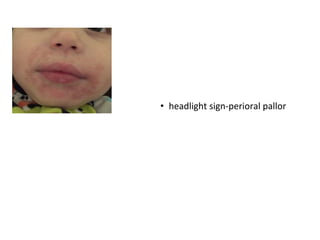
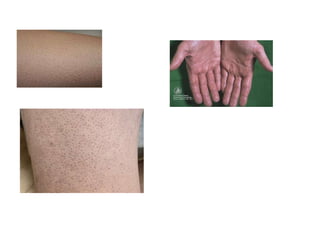
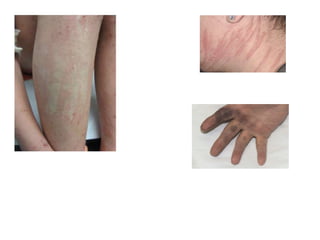
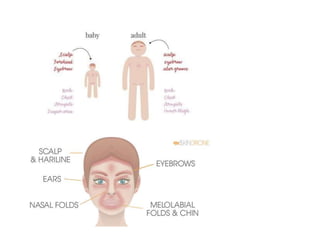
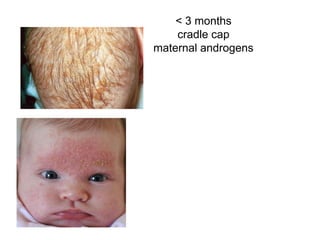
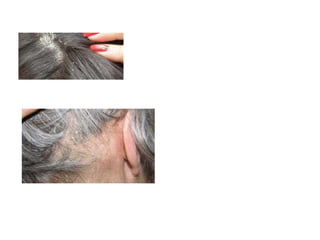
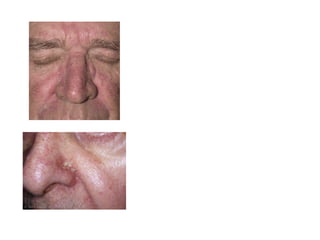
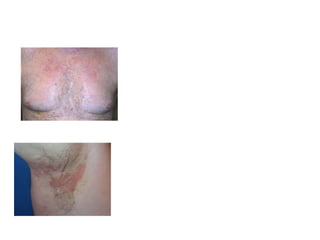
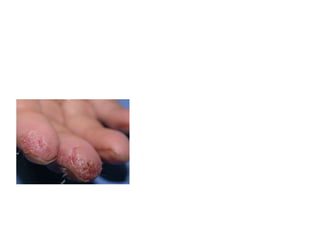
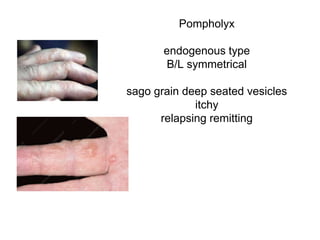
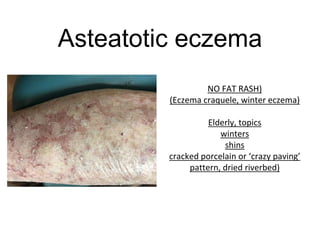
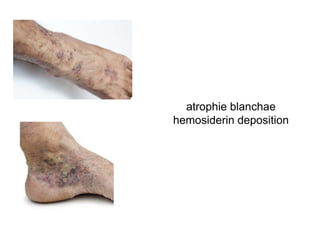
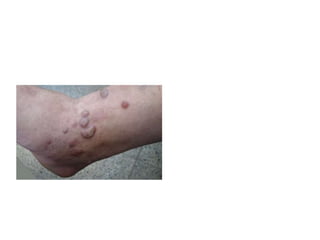
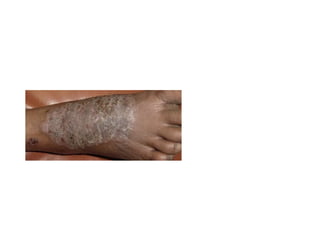
This document discusses different types of eczemas. It classifies eczemas into exogenous types caused by external irritants or allergens, and endogenous types caused by internal factors. Some common endogenous eczemas mentioned are atopic dermatitis, seborrheic dermatitis, and hand eczema. The stages of eczema progression and clinical features at each stage are also outlined. Various allergens that can cause allergic contact dermatitis as well as treatments for different eczemas are described.