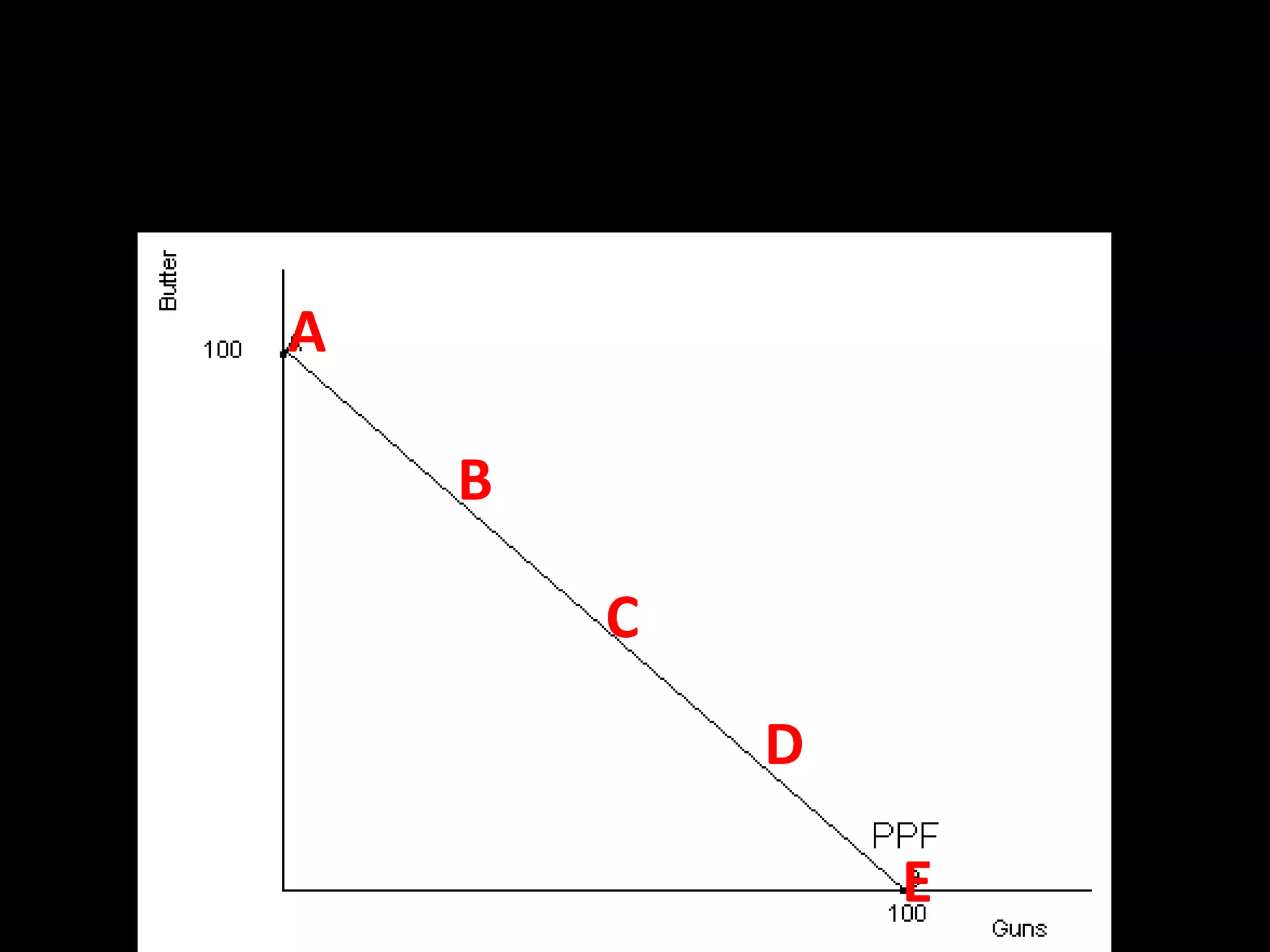
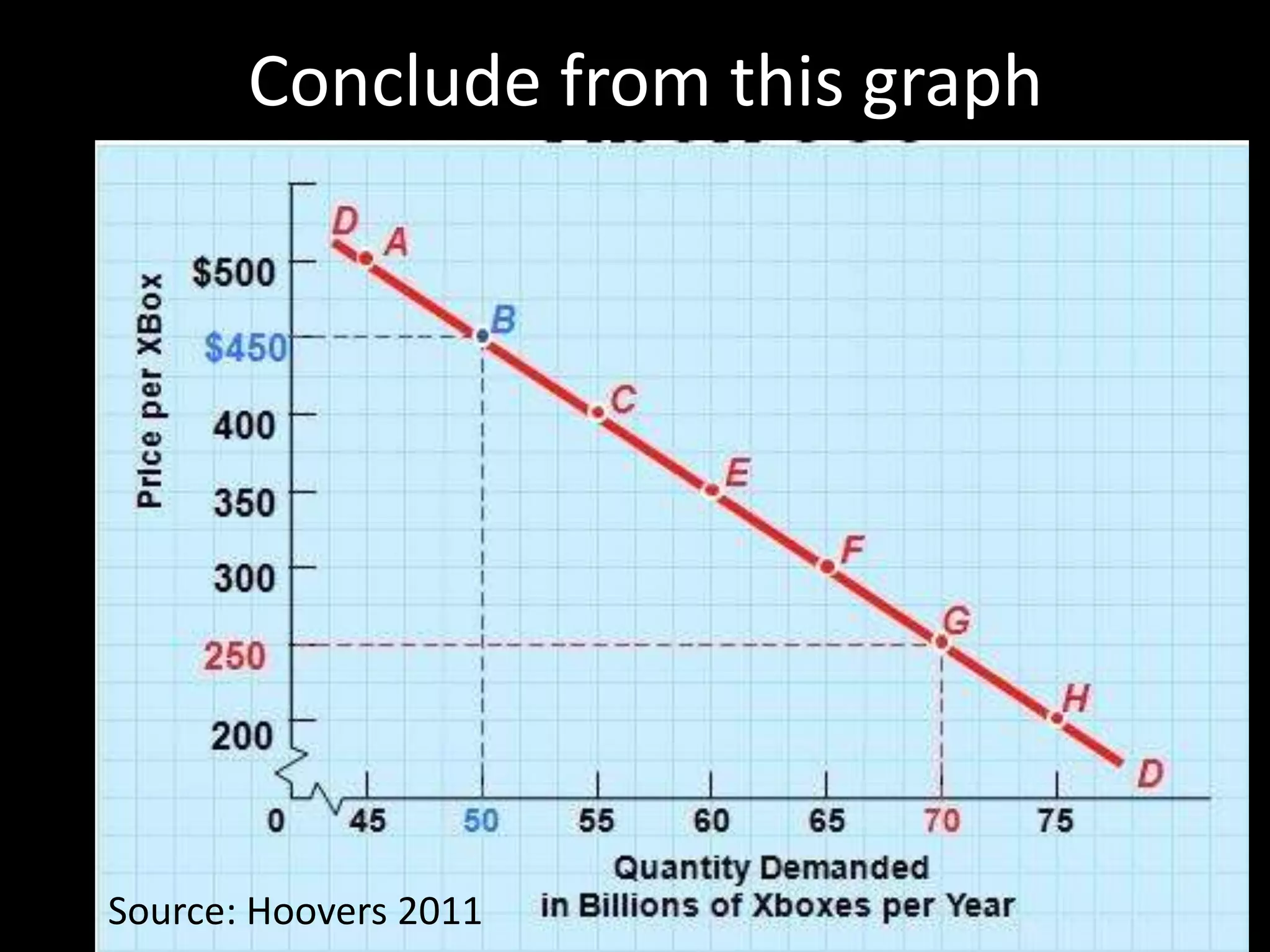
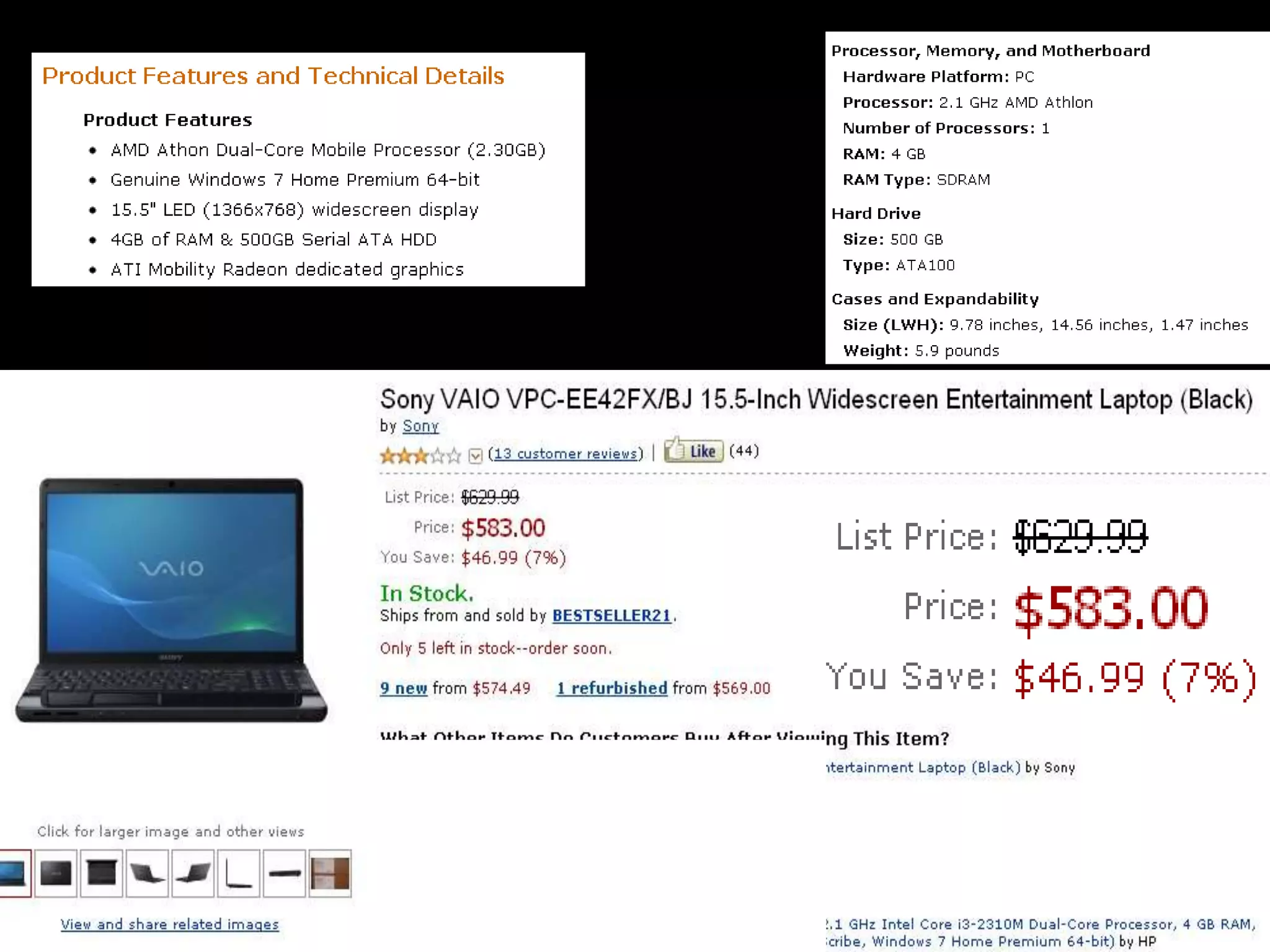
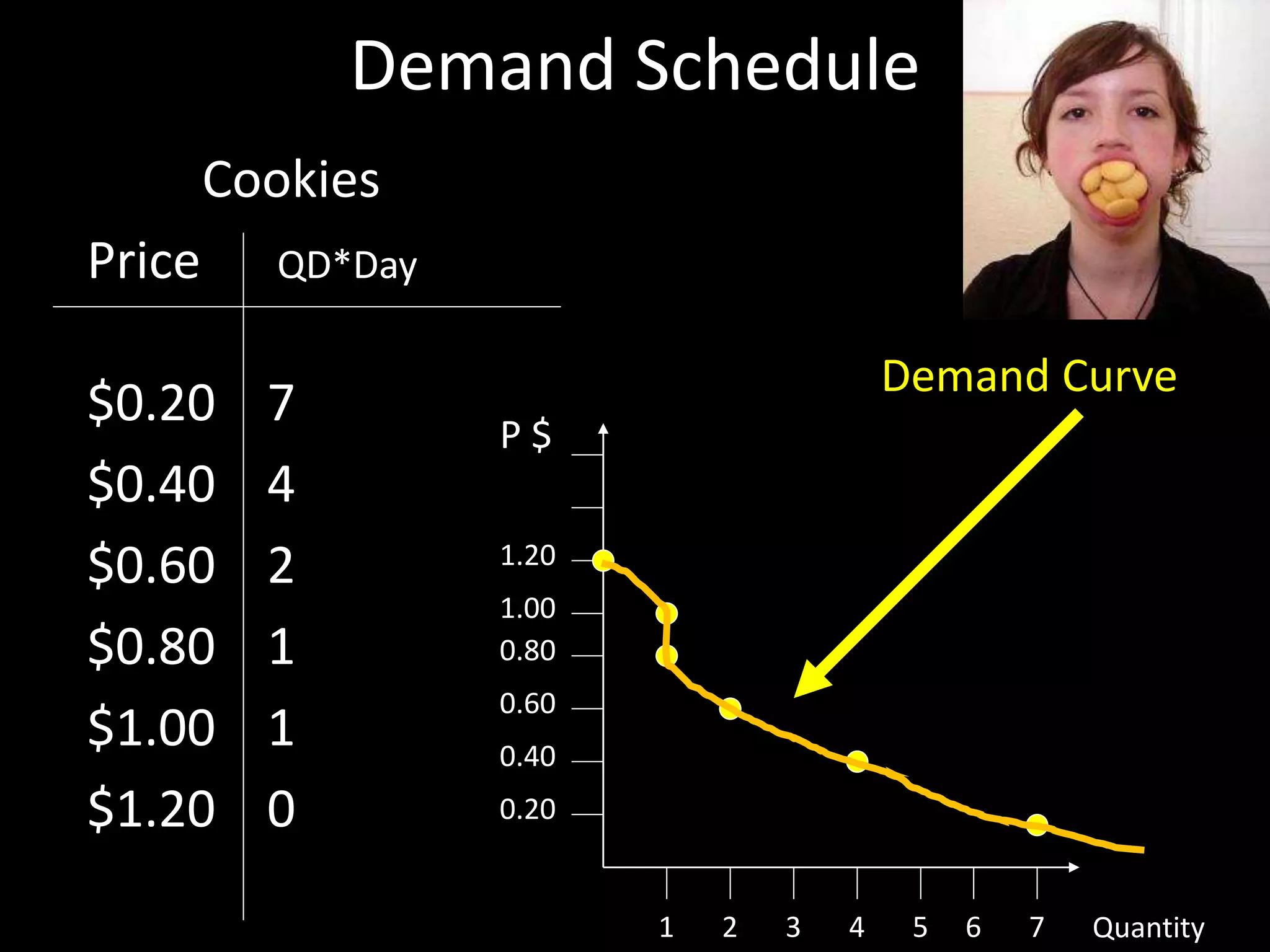
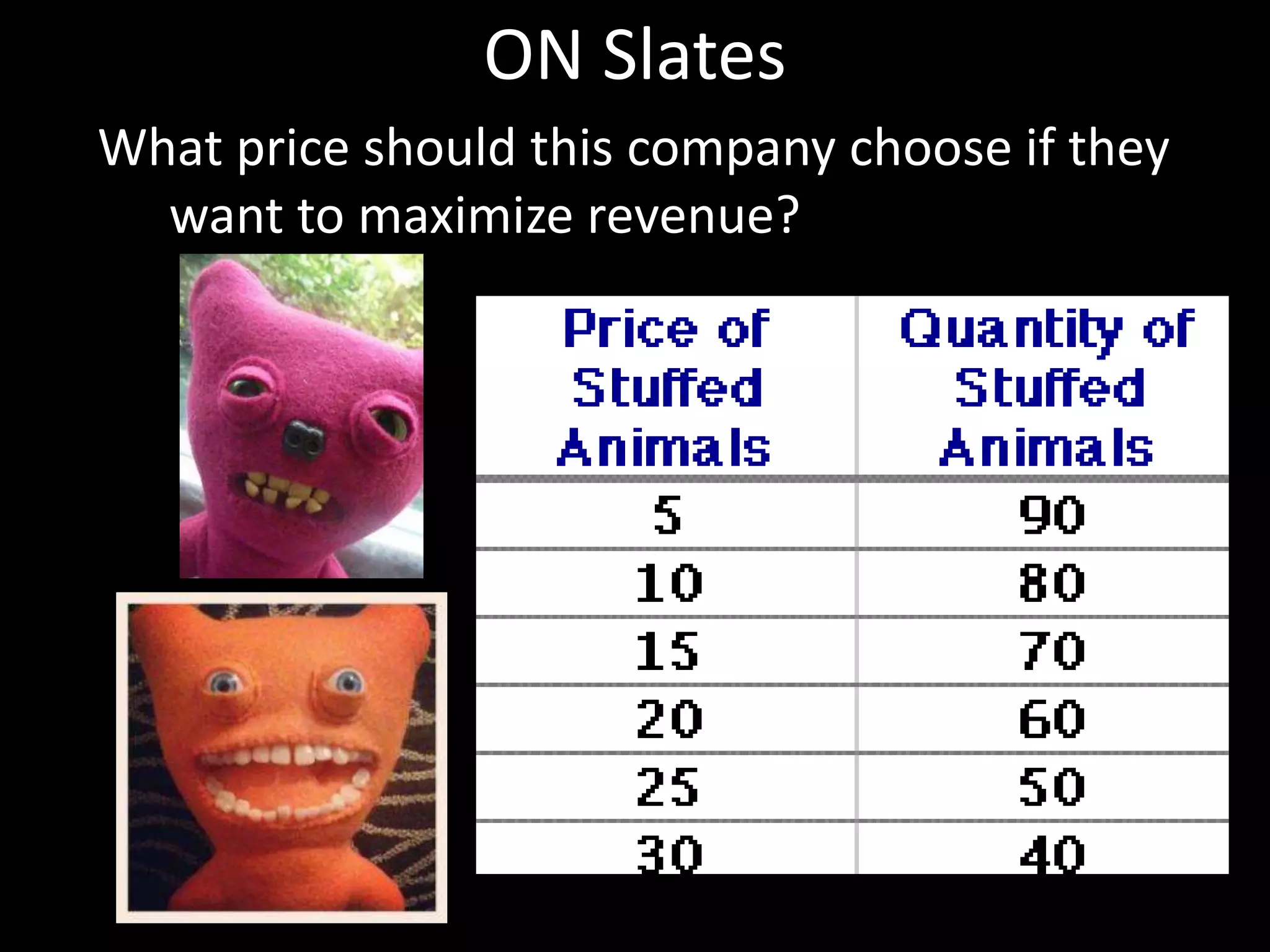
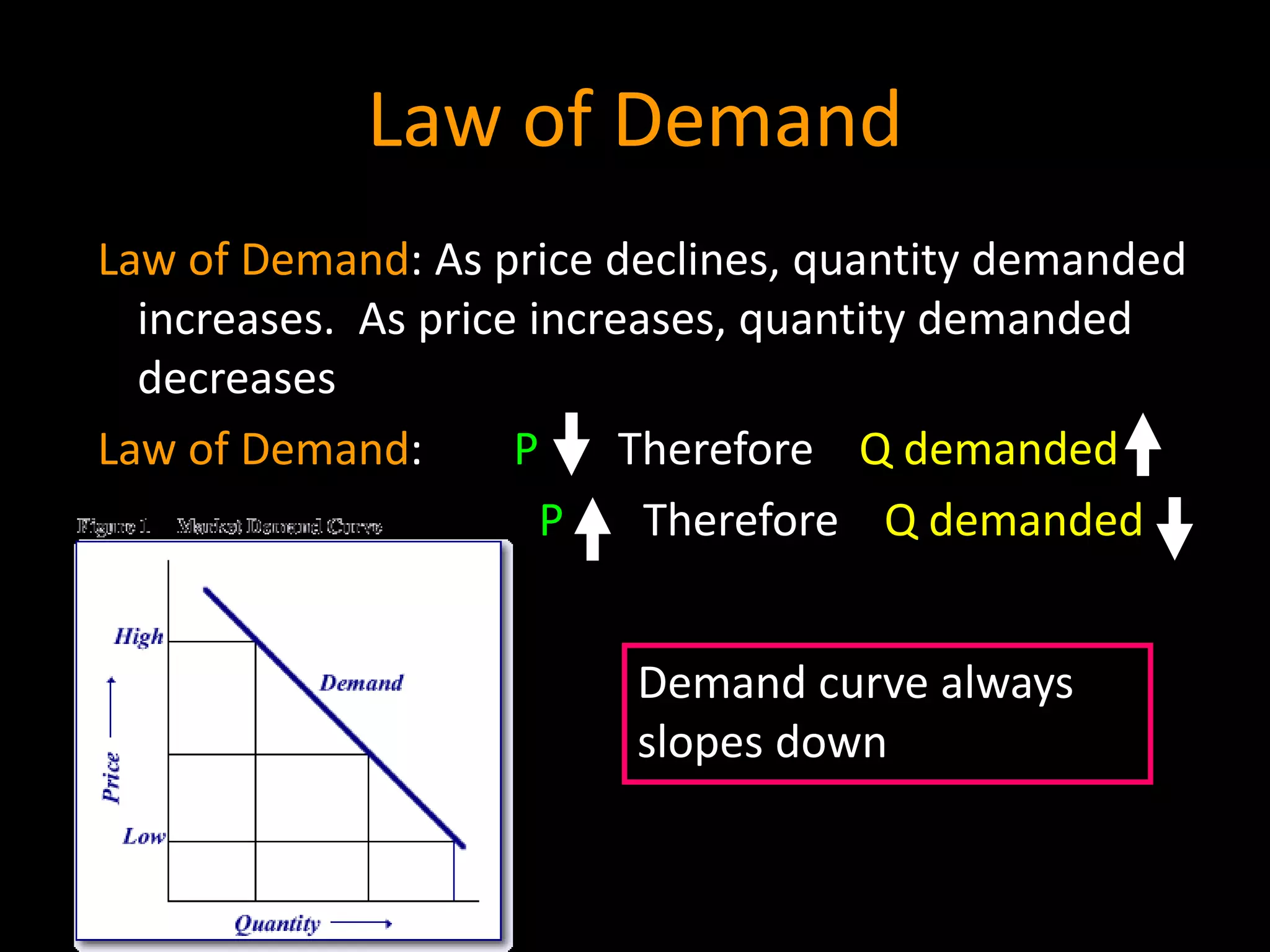
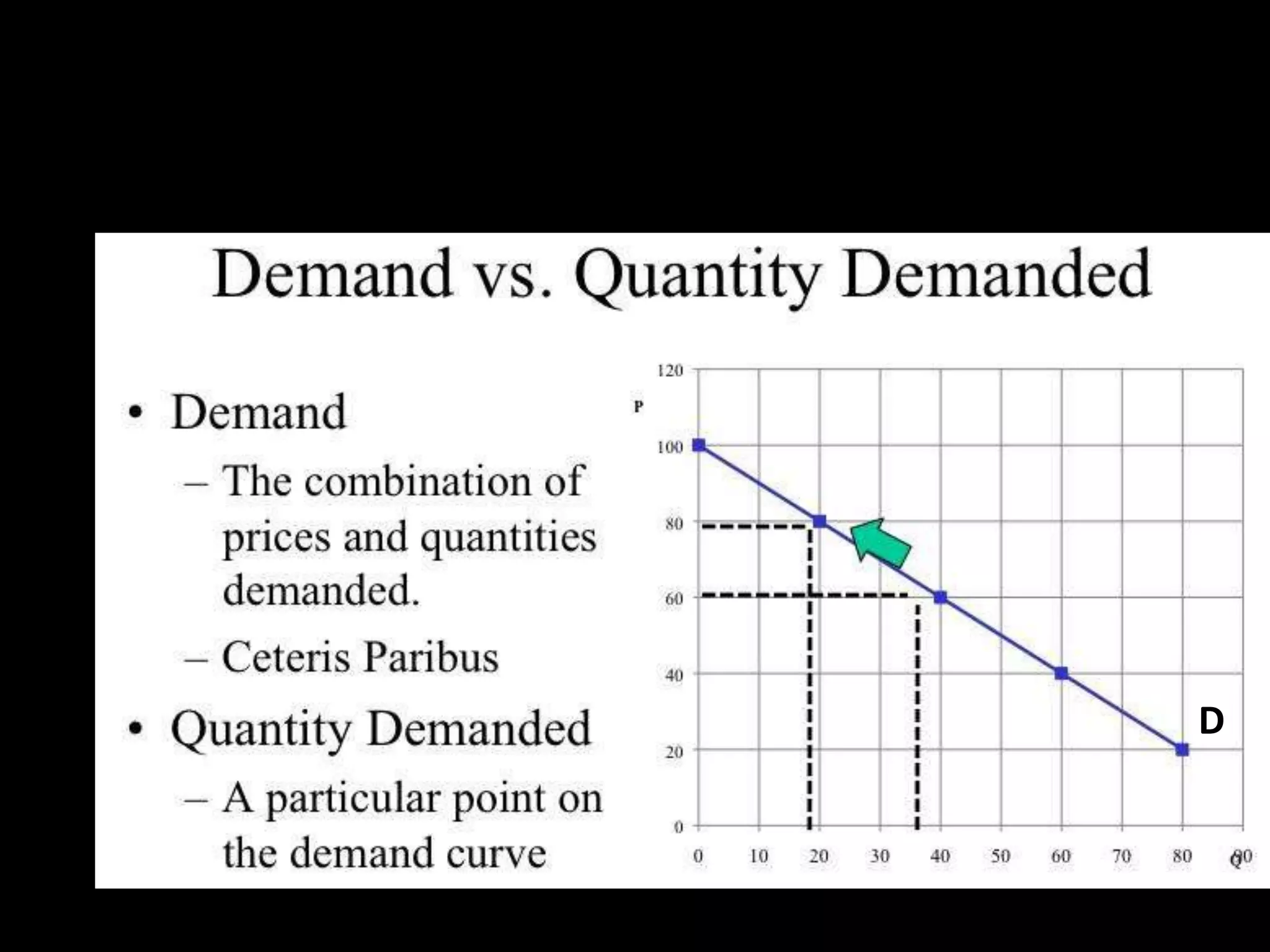
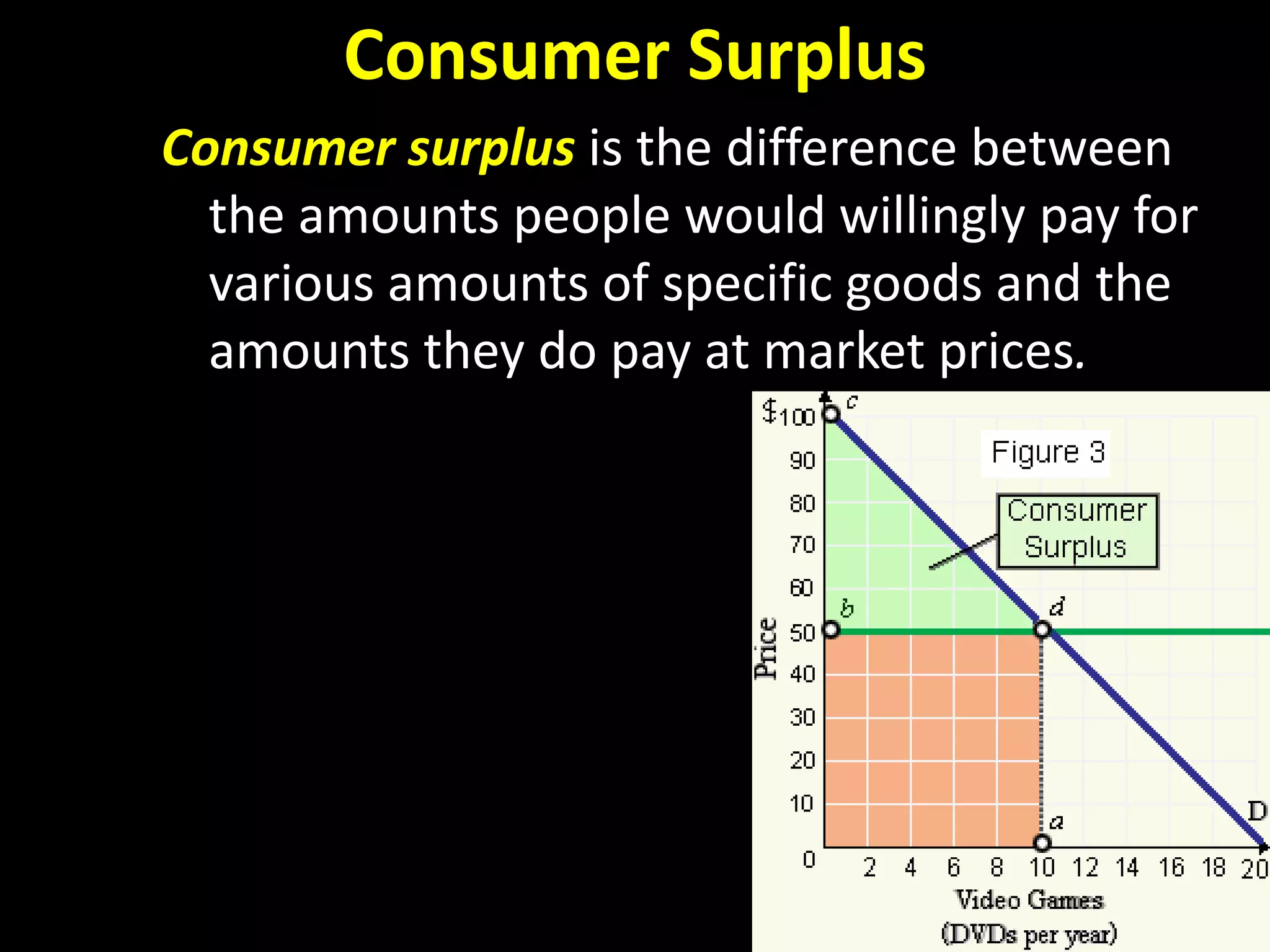
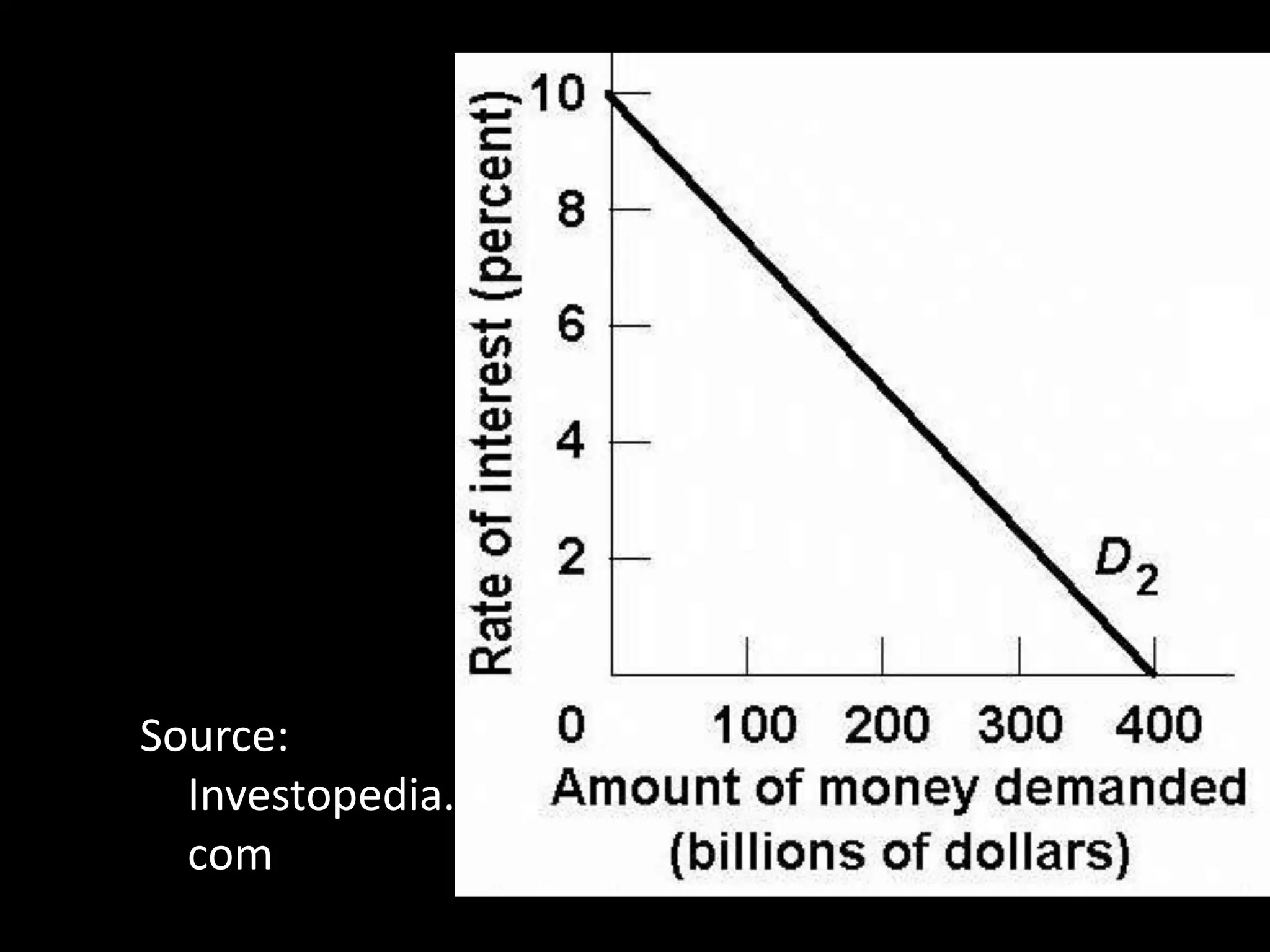
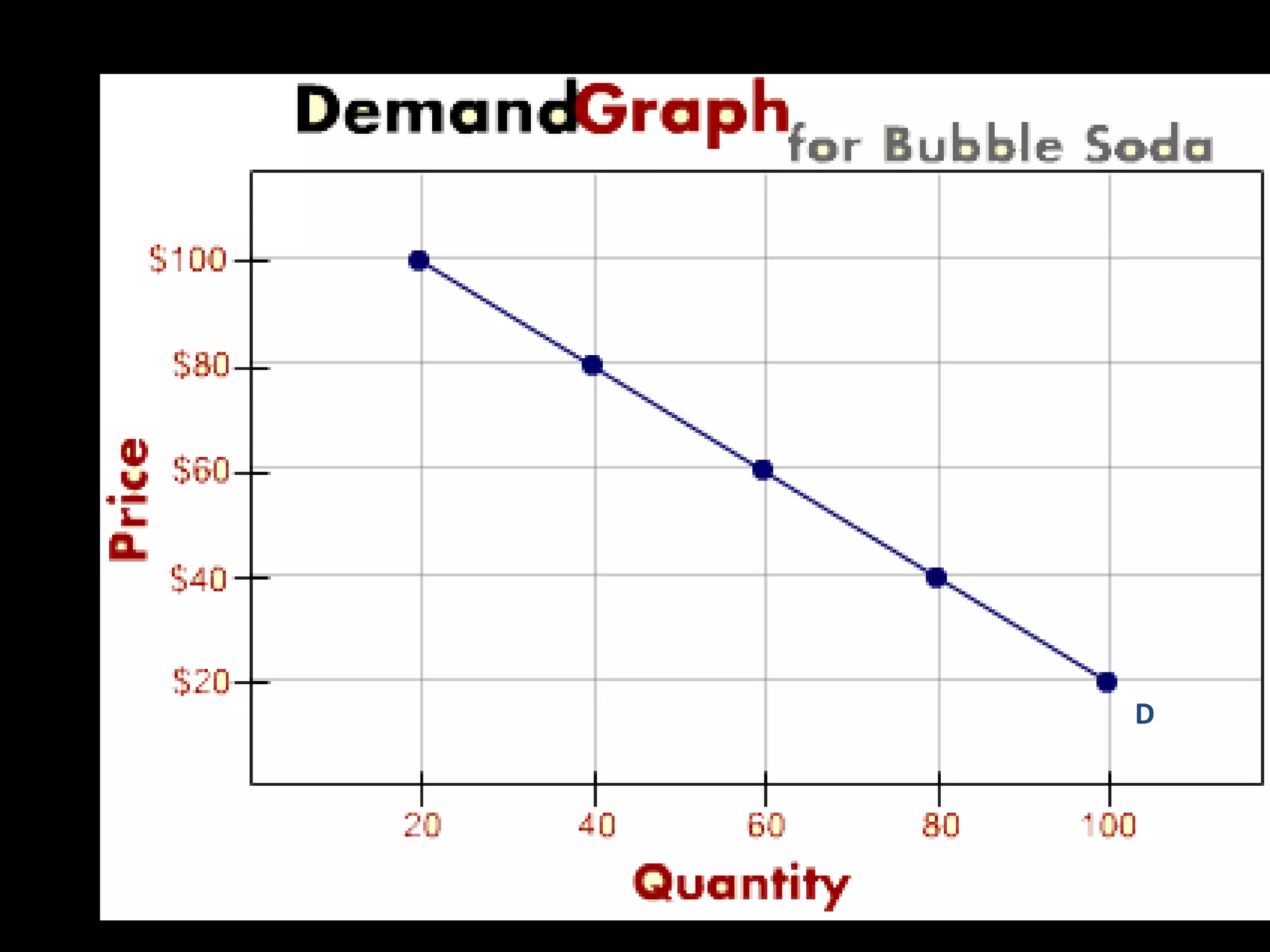
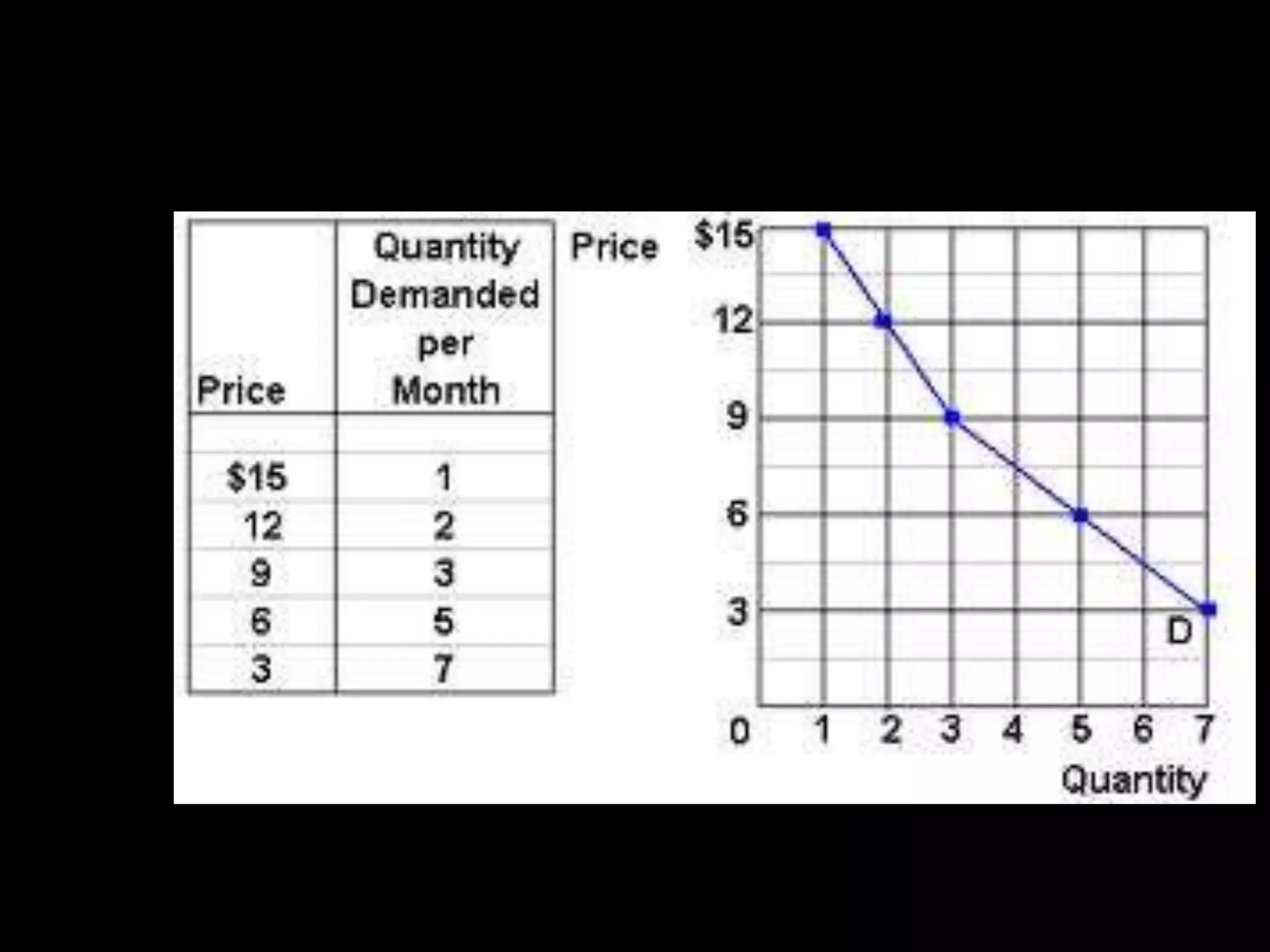
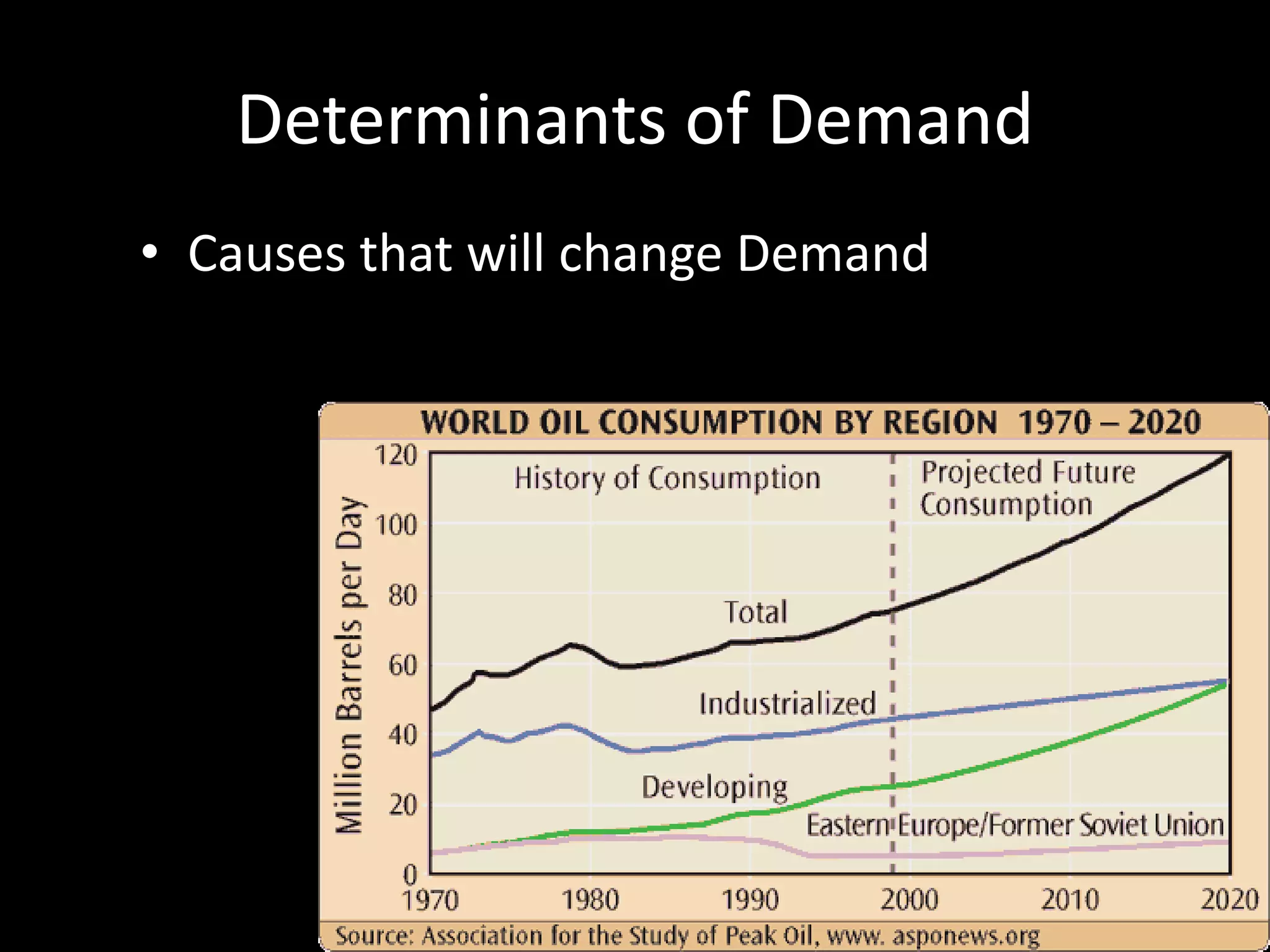
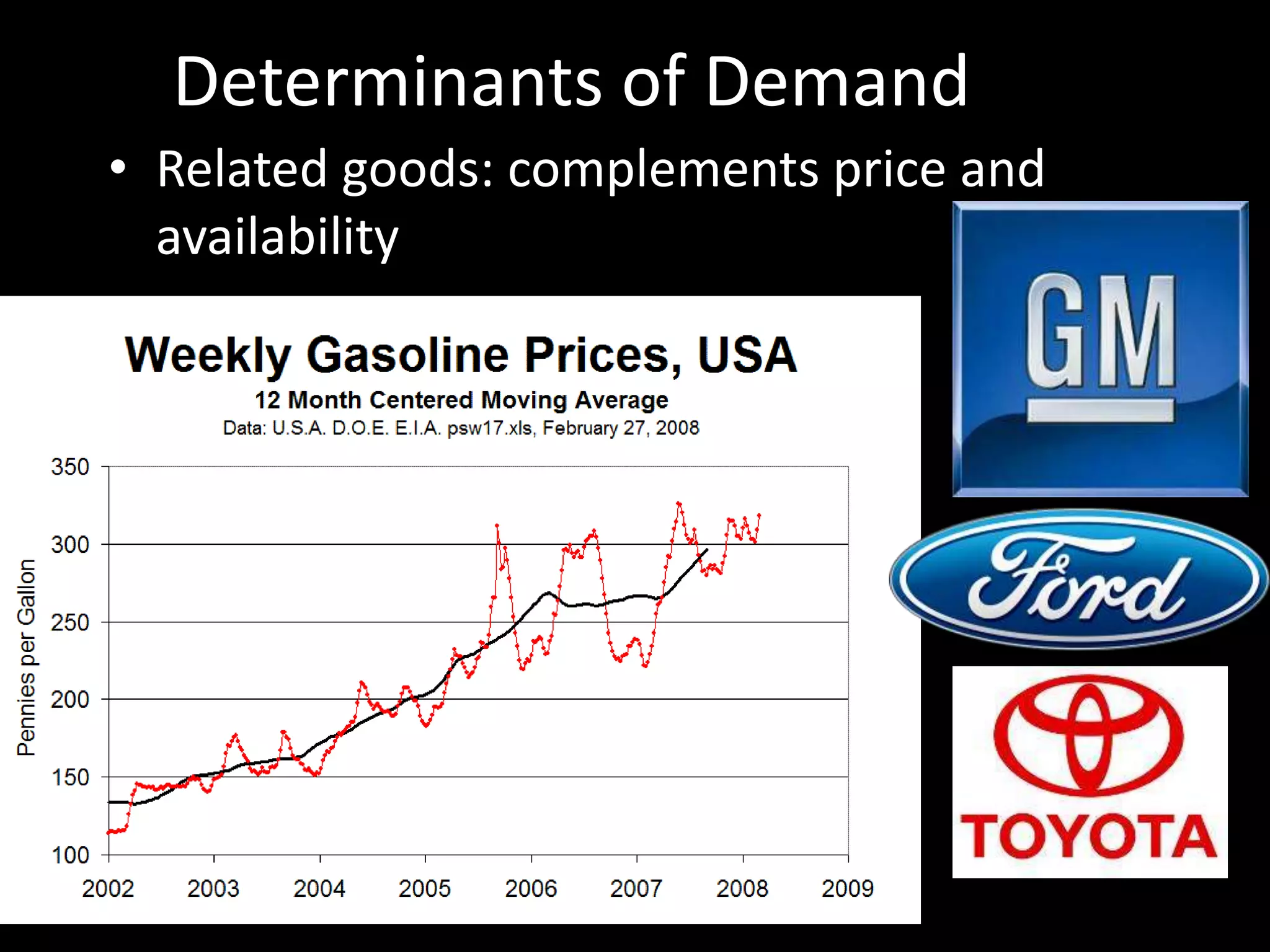
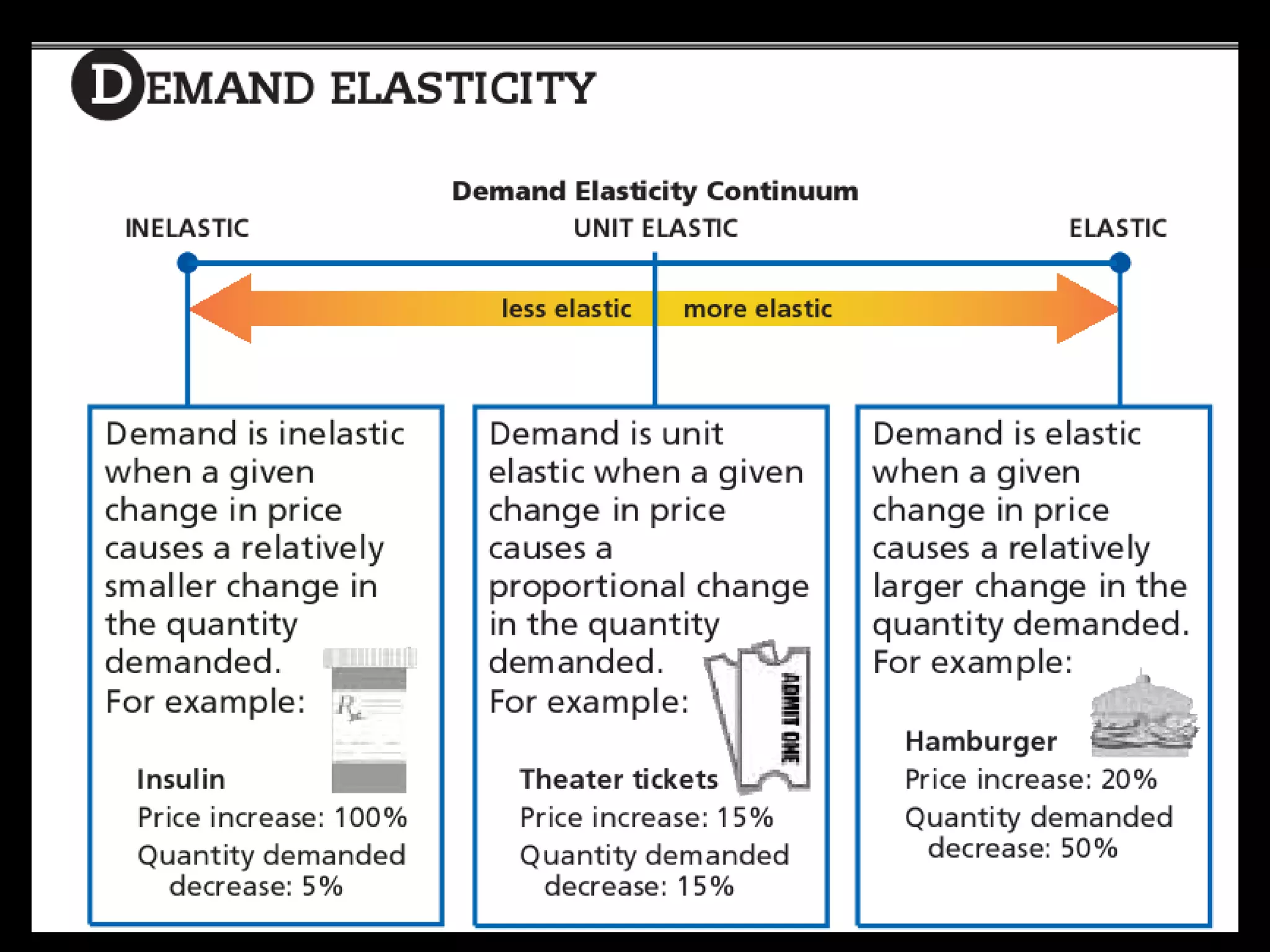
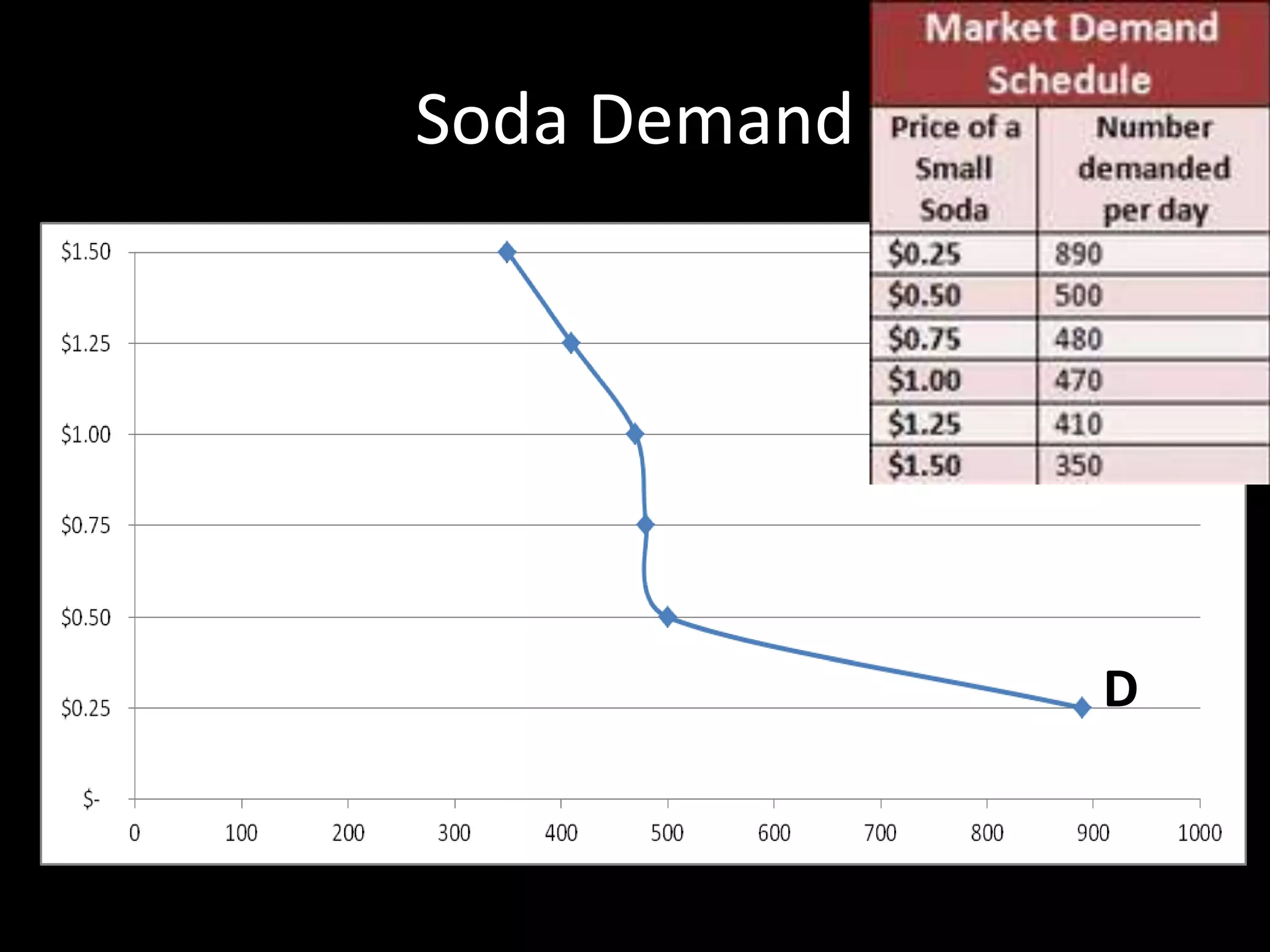
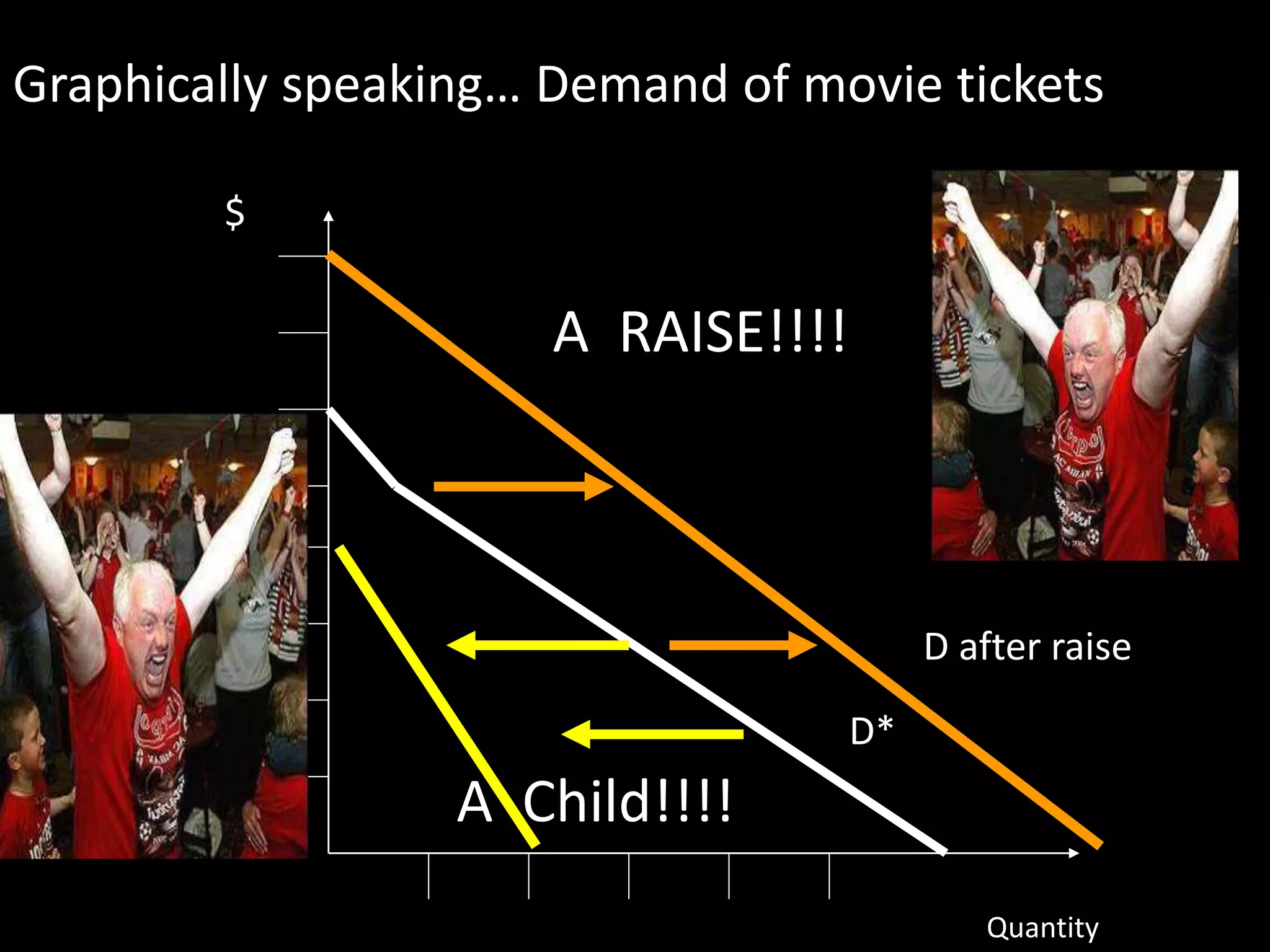
This document contains a series of questions and prompts related to economics concepts like demand, elasticity, and determinants of demand. It includes examples of demand schedules and graphs to illustrate key ideas. Students are asked to analyze demand curves, identify price points that maximize revenue, and explain how changes described in various scenarios would impact demand. The document aims to help students learn how to apply concepts of demand, elasticity, and their determinants through examples, practice questions, and interactive activities on whiteboards and slates.