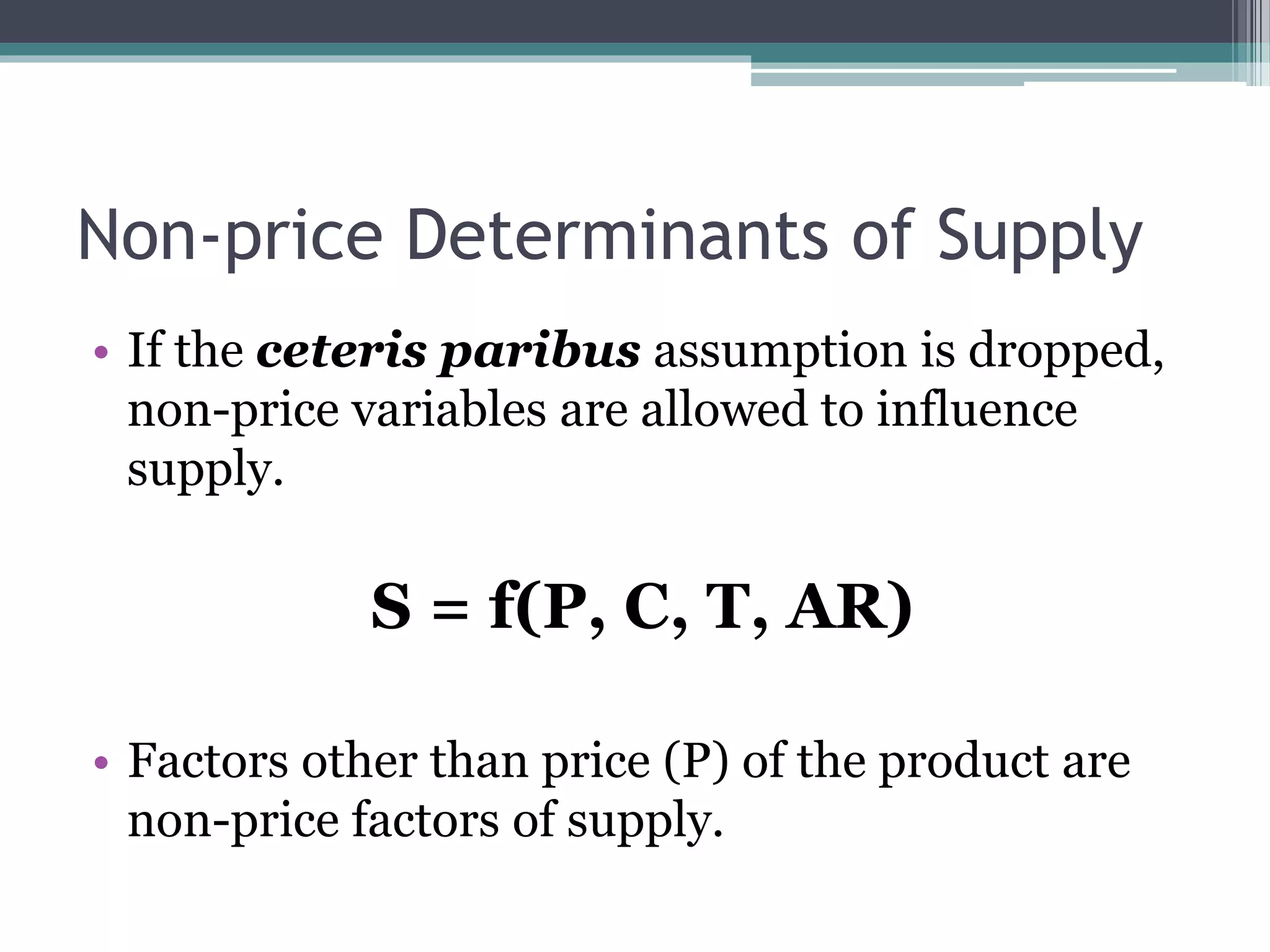
The document discusses the basic principles of demand and supply. It defines a market as the interaction between buyers and sellers, where goods, labor, and financial assets are exchanged. The market ensures that goods move from those with excess to those with need. Demand refers to how much a consumer is willing to buy at different prices, while supply refers to how much a producer is willing to sell. Both demand and supply decrease with rising prices and increase with falling prices, as shown by the downward sloping demand curve and upward sloping supply curve. Non-price factors like income, tastes, expectations, and number of consumers also impact demand, while costs, technology, and resource availability impact supply.