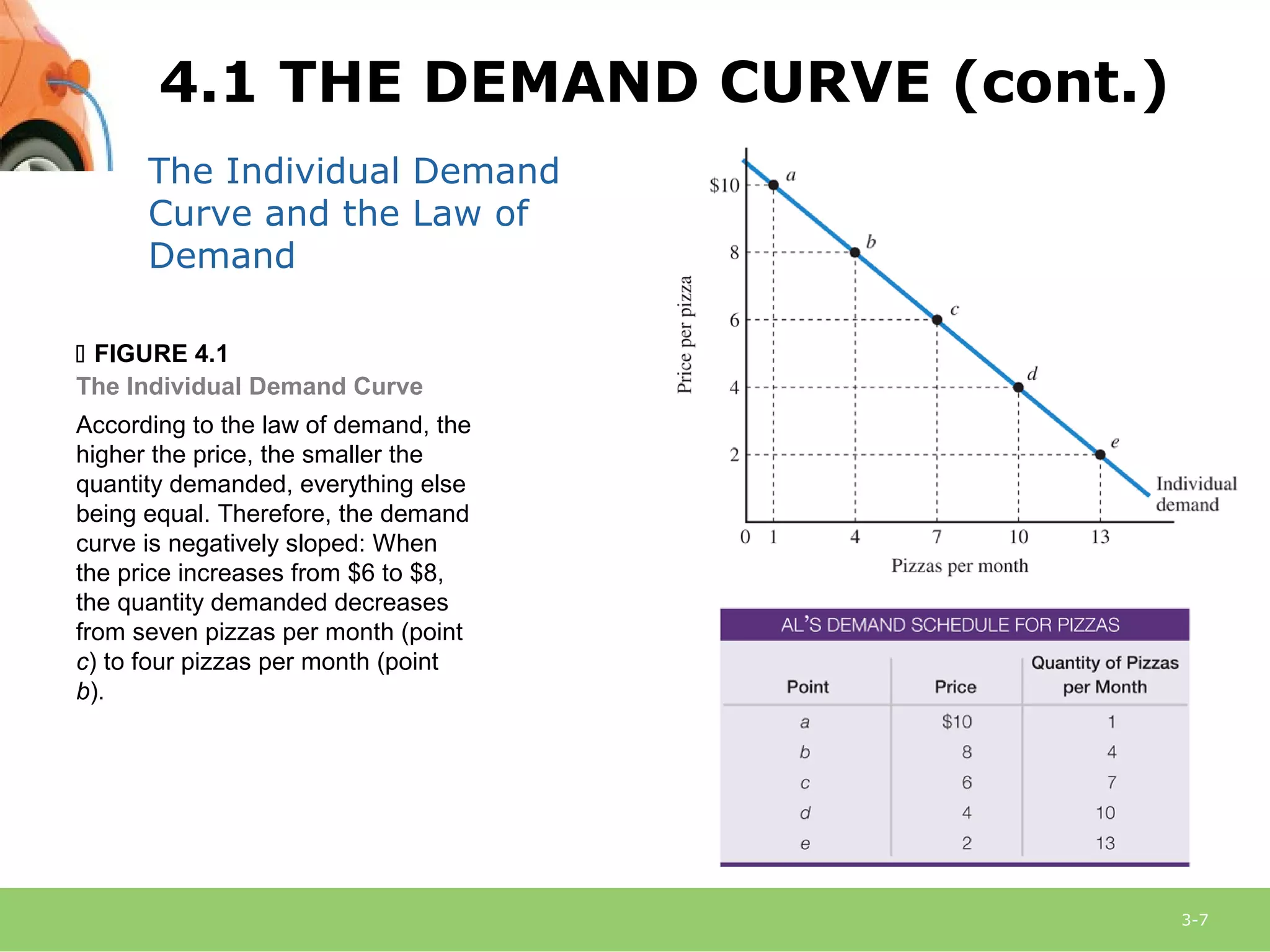
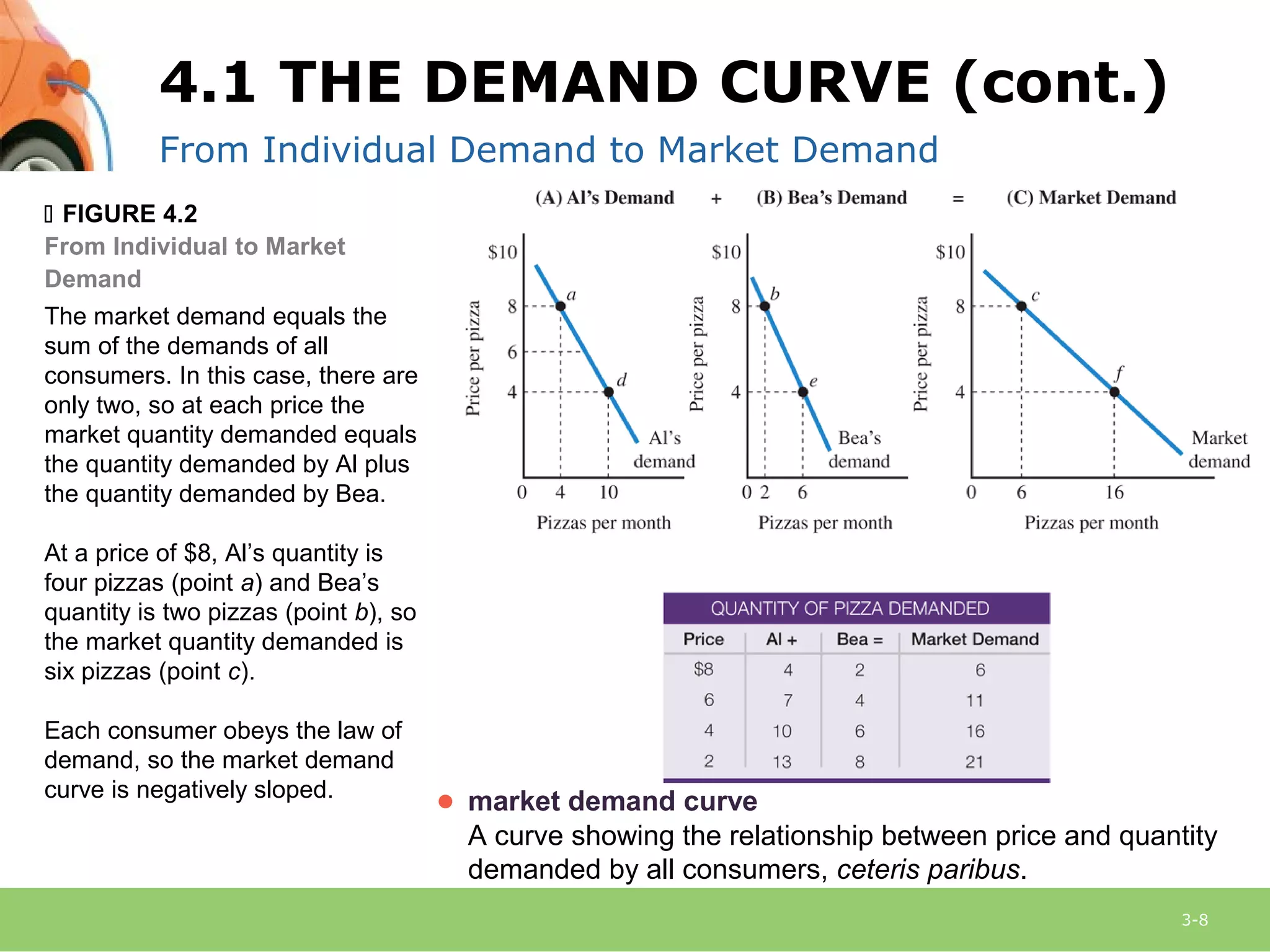
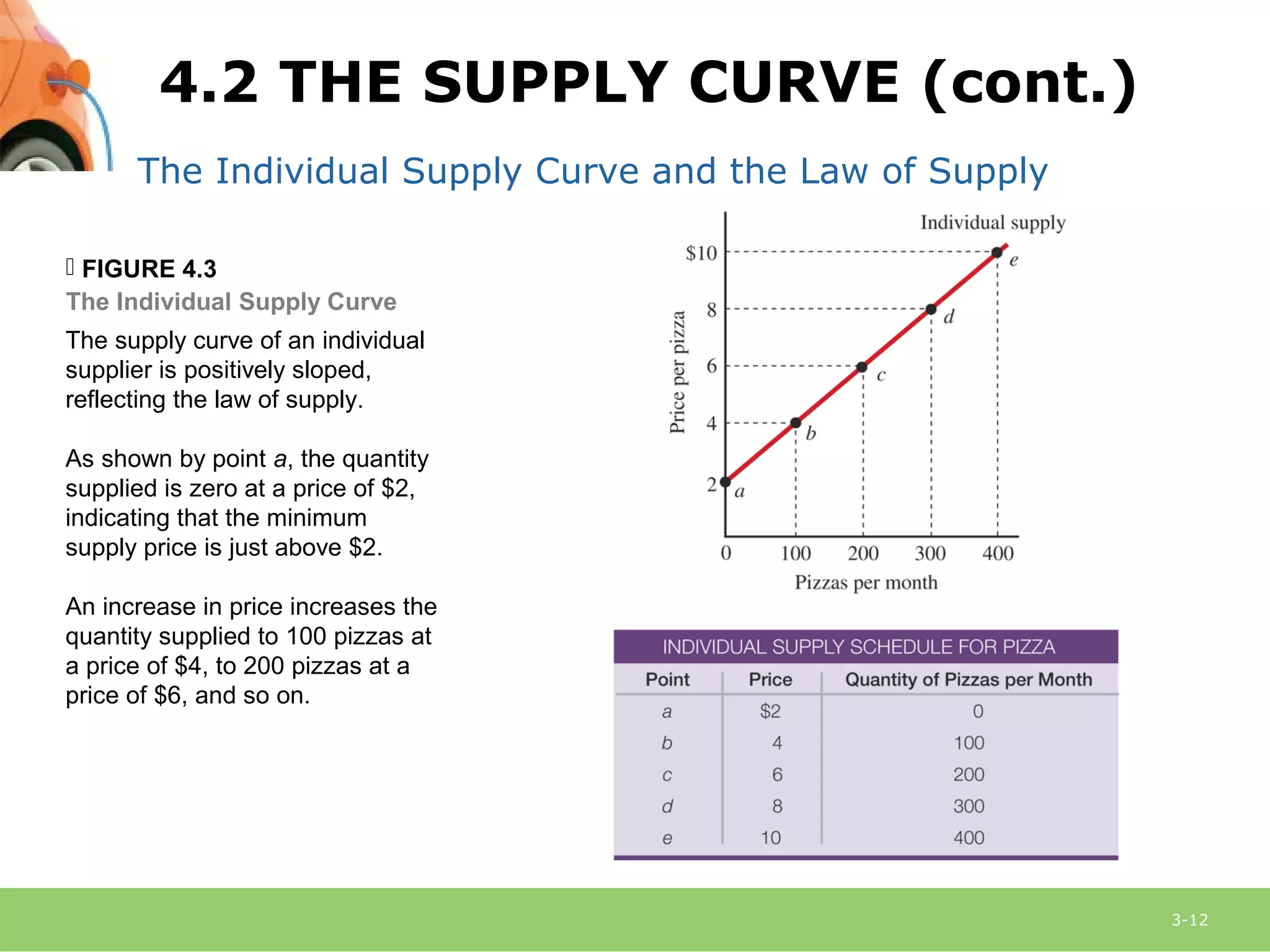
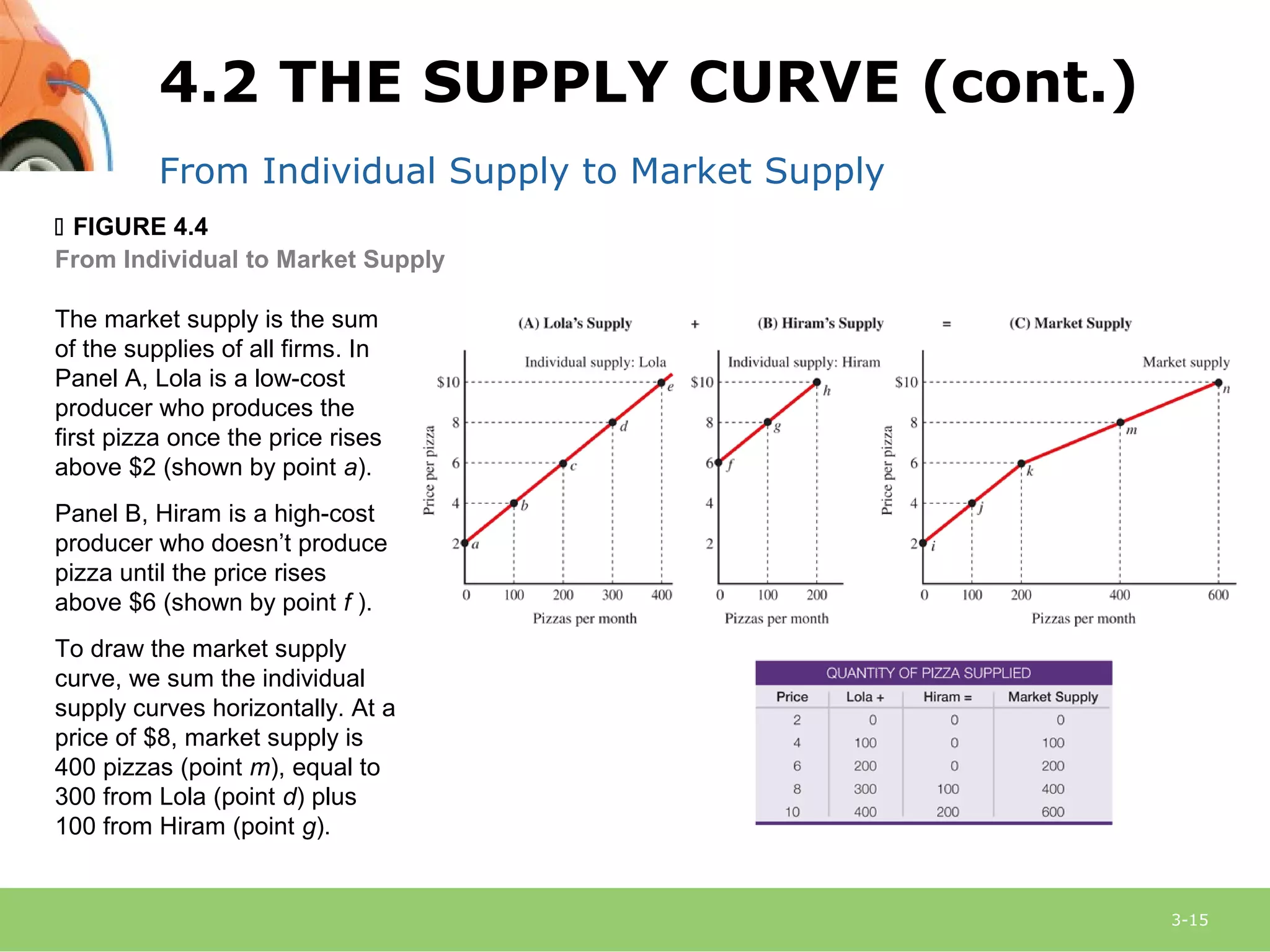
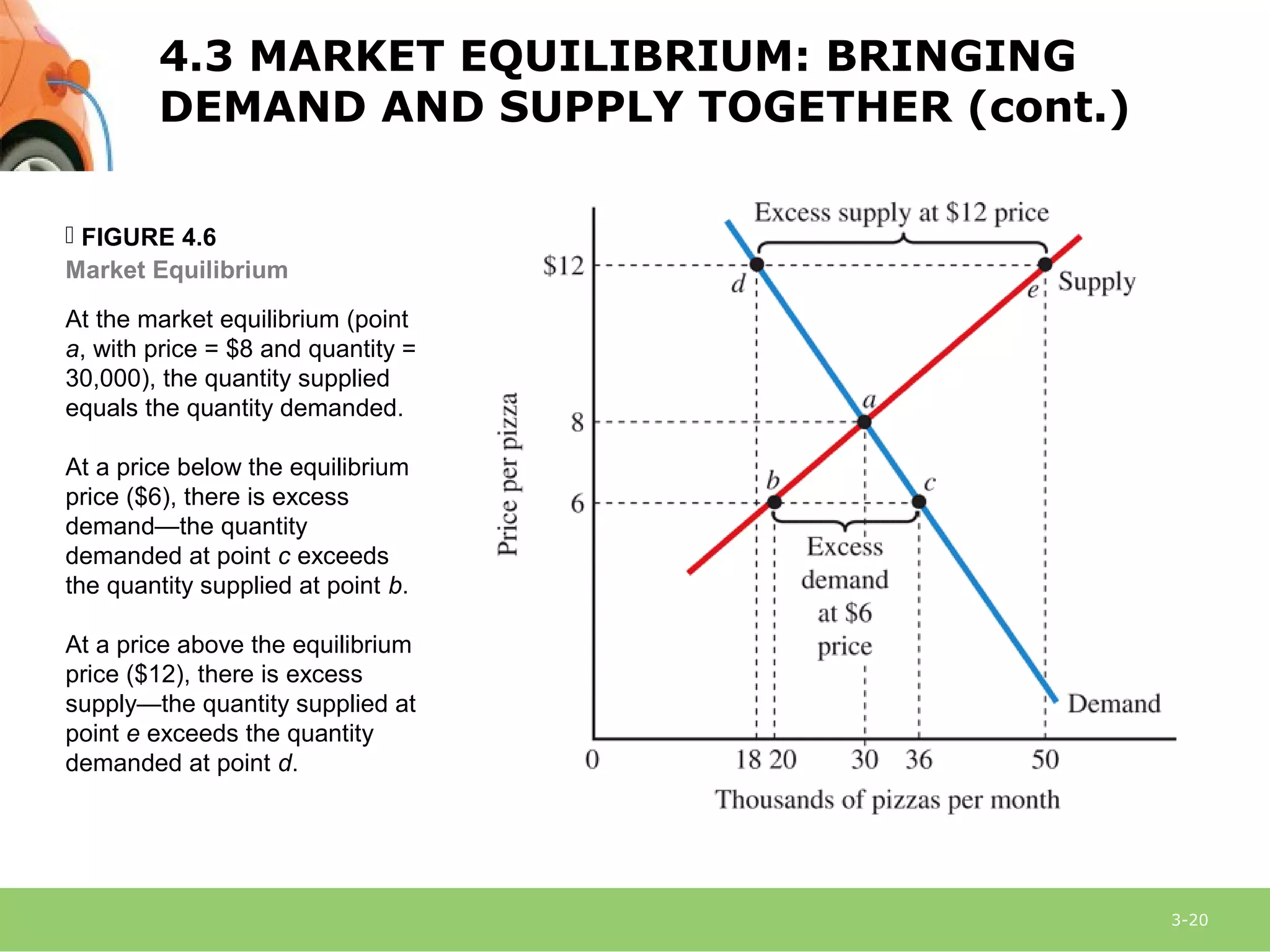
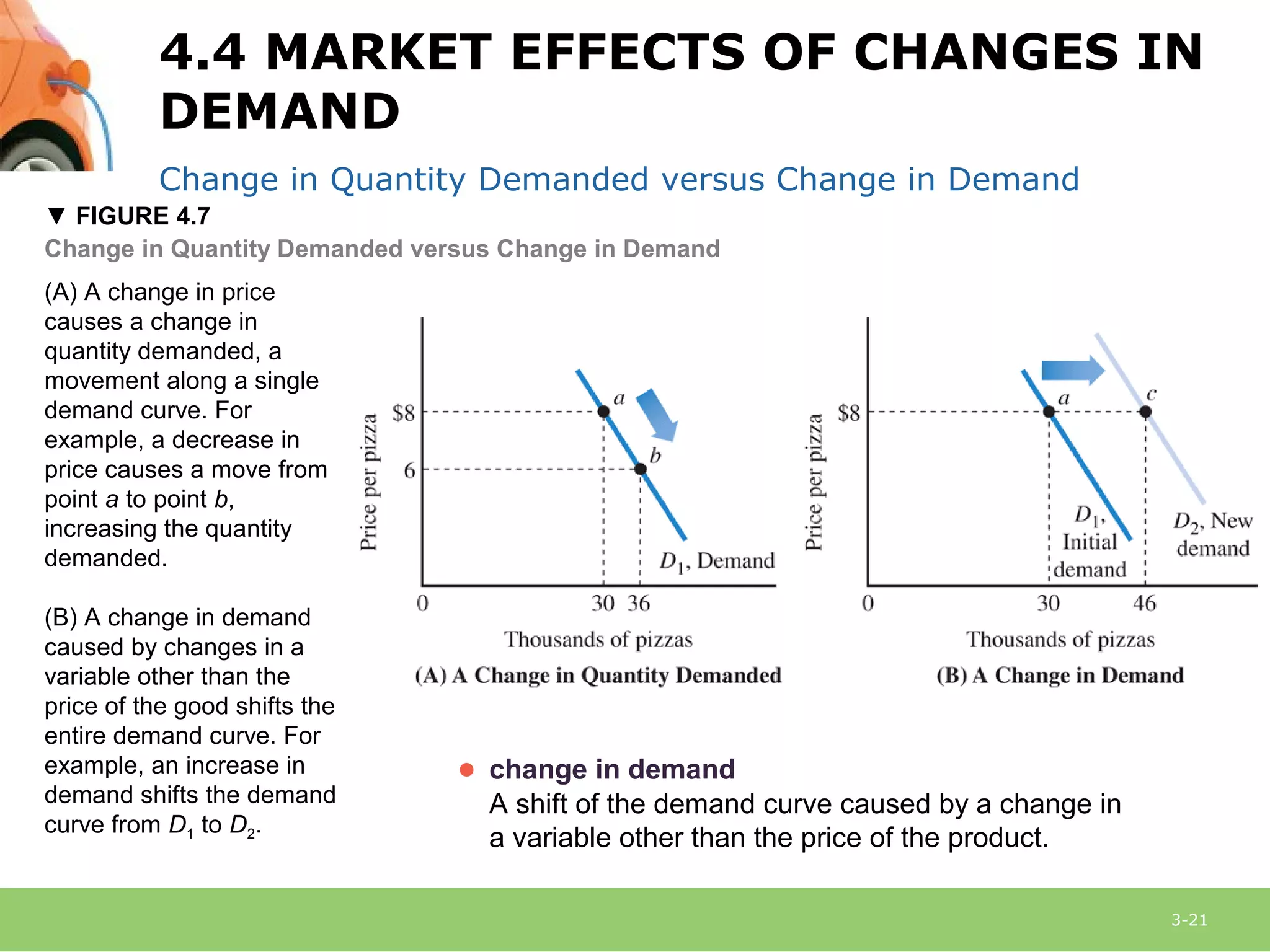
This document provides an overview of demand, supply, and market equilibrium. It defines key terms like demand, supply, quantity demanded, quantity supplied, and discusses the laws of demand and supply. Specifically, it explains that the law of demand states that as price increases, quantity demanded decreases, while the law of supply states that as price increases, quantity supplied also increases. It then discusses how individual demand and supply curves combine to form market demand and supply curves and how equilibrium is reached at the price where quantity demanded equals quantity supplied. Finally, it analyzes how changes in demand or supply can shift the curves and impact equilibrium price and quantity.