The document discusses how the basic economic problems of what to produce, how to produce, and for whom to produce are solved differently in capitalist, socialist, and mixed economies.
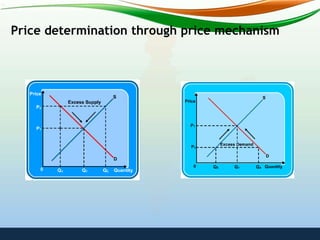
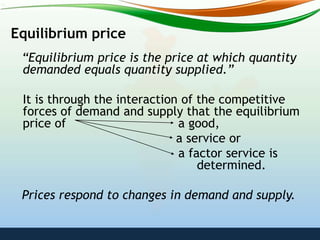
In a capitalist economy, the price mechanism determines solutions through market forces of supply and demand. In a socialist economy, a central planning authority makes production and distribution decisions. In a mixed economy, the price mechanism and private sector interact with government intervention through fiscal and monetary policies to influence economic outcomes.