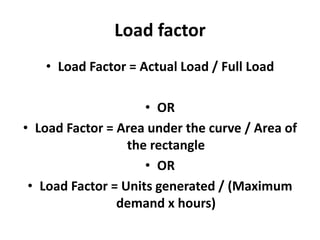
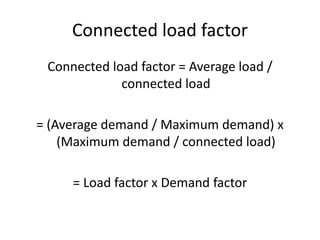
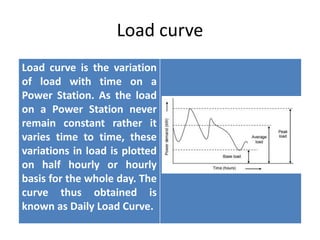
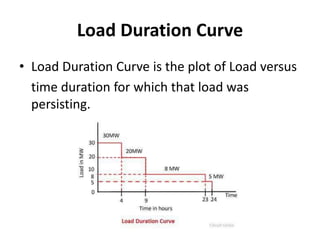
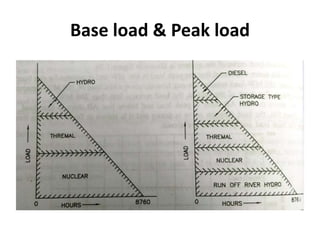
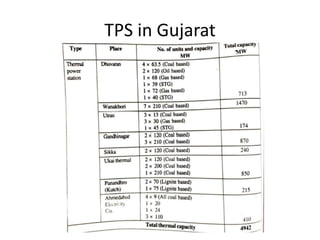
The document discusses key terms related to electrical power generation and load curves. It defines terms like connected load, demand factor, load factor, diversity factor, coincidence factor, loss factor, plant capacity factor, utilization factor, plant use factor, base load, and peak load. Load curves plot the variation in load over time and are important for understanding energy generation and demand. Base load refers to the minimum required electricity demand while peak load is the time of high demand.