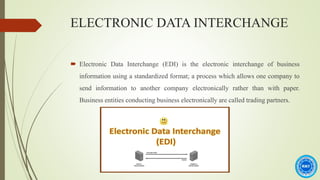
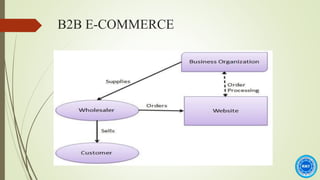
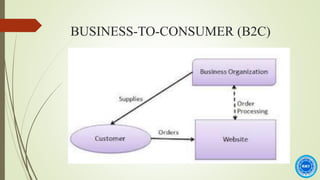
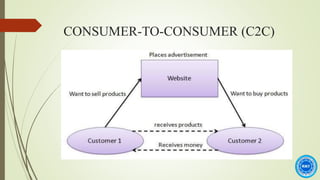
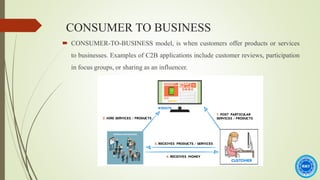
The document discusses the history and process of e-commerce and the role of customer relationship management (CRM). It outlines the different types of e-commerce relationships including business-to-business, business-to-consumer, consumer-to-consumer, and consumer-to-business. It also discusses e-commerce CRM applications and advantages/disadvantages of e-commerce, emphasizing the importance of building trust in e-commerce relationships.