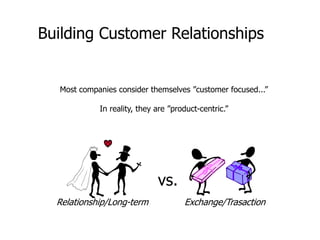
CRM aims to integrate customer-focused activities like sales, marketing and customer service to establish long-term customer relationships. It involves selecting and acquiring customers, retaining them through quality service and personalized communication, and extending relationships through additional sales. CRM systems automate sales, service and marketing processes to gain a comprehensive view of customers. This allows companies to better understand customer needs and provide a consistent, high-quality experience across all interactions. While requiring investment, CRM can increase customer satisfaction, sales and operational efficiencies if implemented appropriately for a company's specific needs and culture.