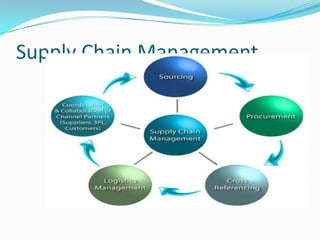
This document outlines the topics covered in a presentation on e-commerce and e-business. It discusses e-commerce fundamentals, e-business infrastructure, the e-commerce environment, supply chain management, e-marketing, customer relationship management, change management, analysis and design of m-commerce, and the management of m-commerce services. The goal is to provide an introduction to key concepts in e-business and e-commerce.