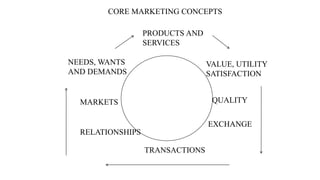
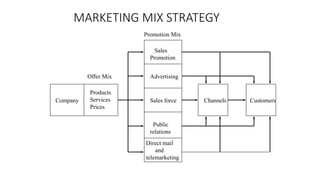
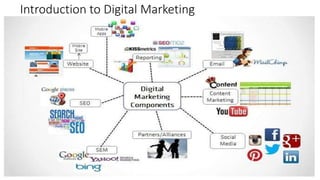
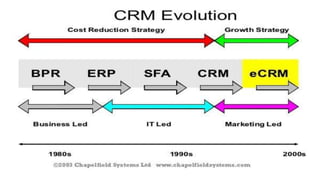
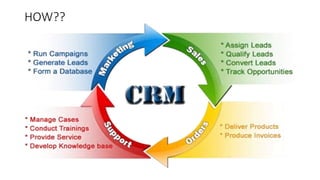
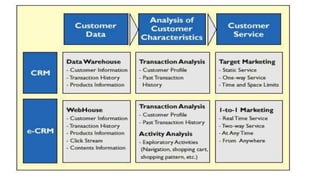
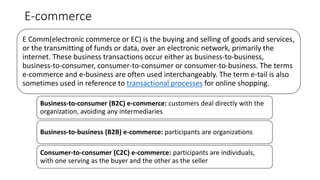
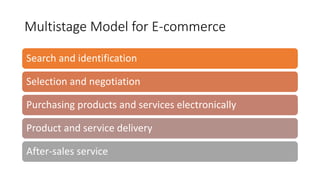
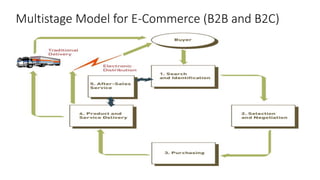
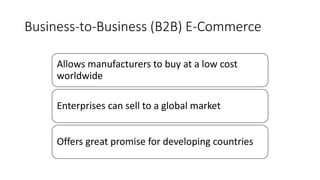
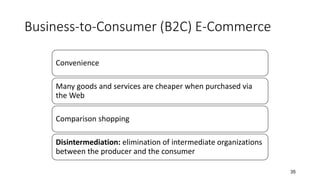
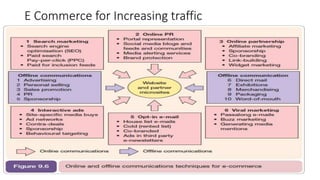
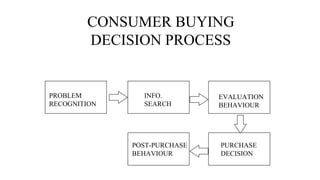
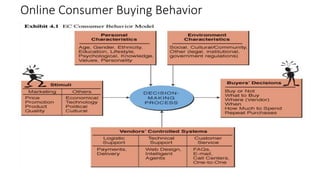
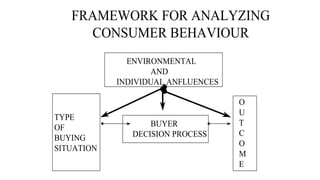
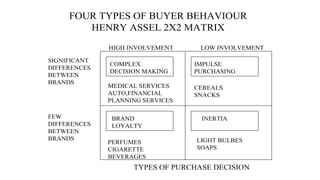
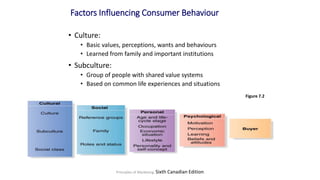
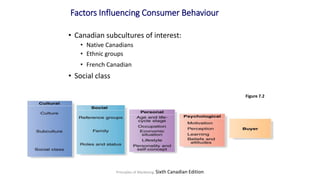
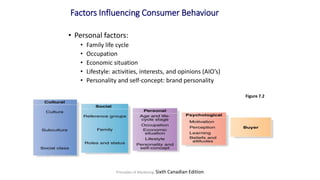
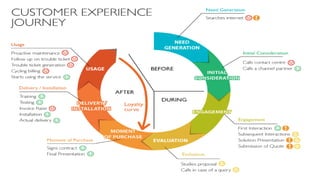
The document discusses key concepts related to e-commerce and internet marketing. It covers topics like the online marketing mix, online branding and traffic building, managing digital content, and factors that influence consumer behavior online. It also examines concepts like e-CRM in virtual worlds and how organizations can leverage customer relationship management systems to better understand customers and improve relationships. The document provides an overview of various components of e-commerce like business-to-business, business-to-consumer, and consumer-to-consumer models.