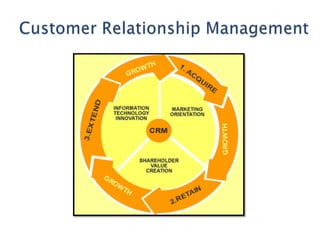
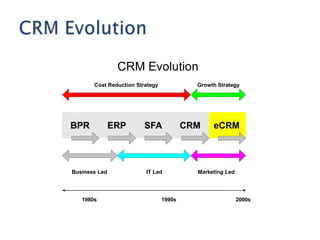
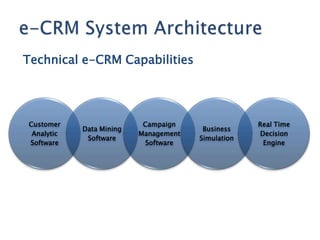
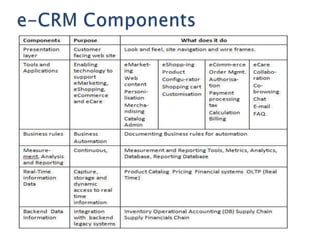
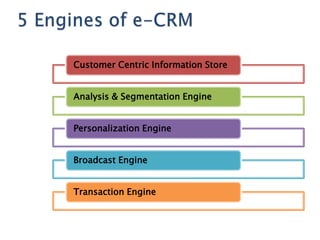
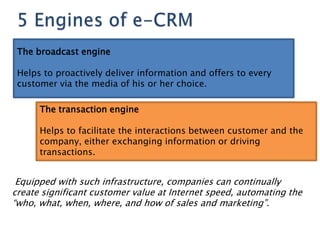
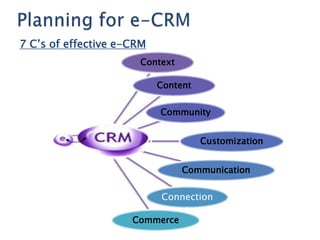
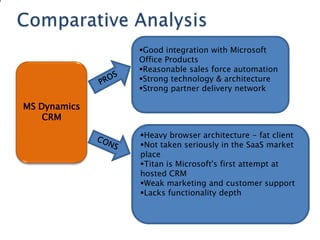
The document discusses customer relationship management (CRM) and its evolution with technology. It explains that CRM aims to optimize profitability through enhanced customer satisfaction, automating and enhancing customer-centric processes. eCRM expands traditional CRM by integrating electronic channels like web and wireless technologies. Effective eCRM requires understanding customers, capturing and analyzing data, and providing personalized, targeted experiences across channels to improve customer retention and reduce costs.