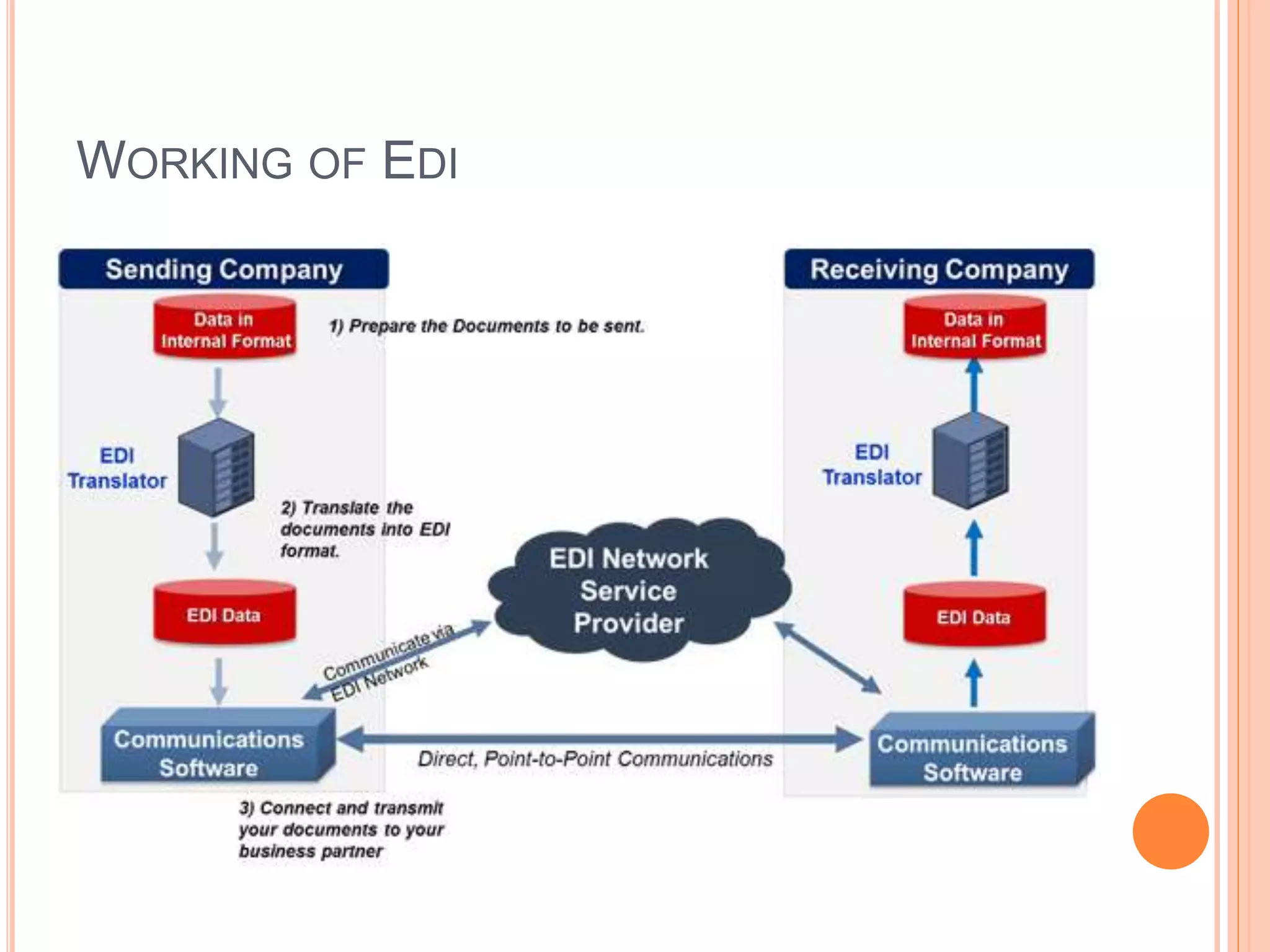
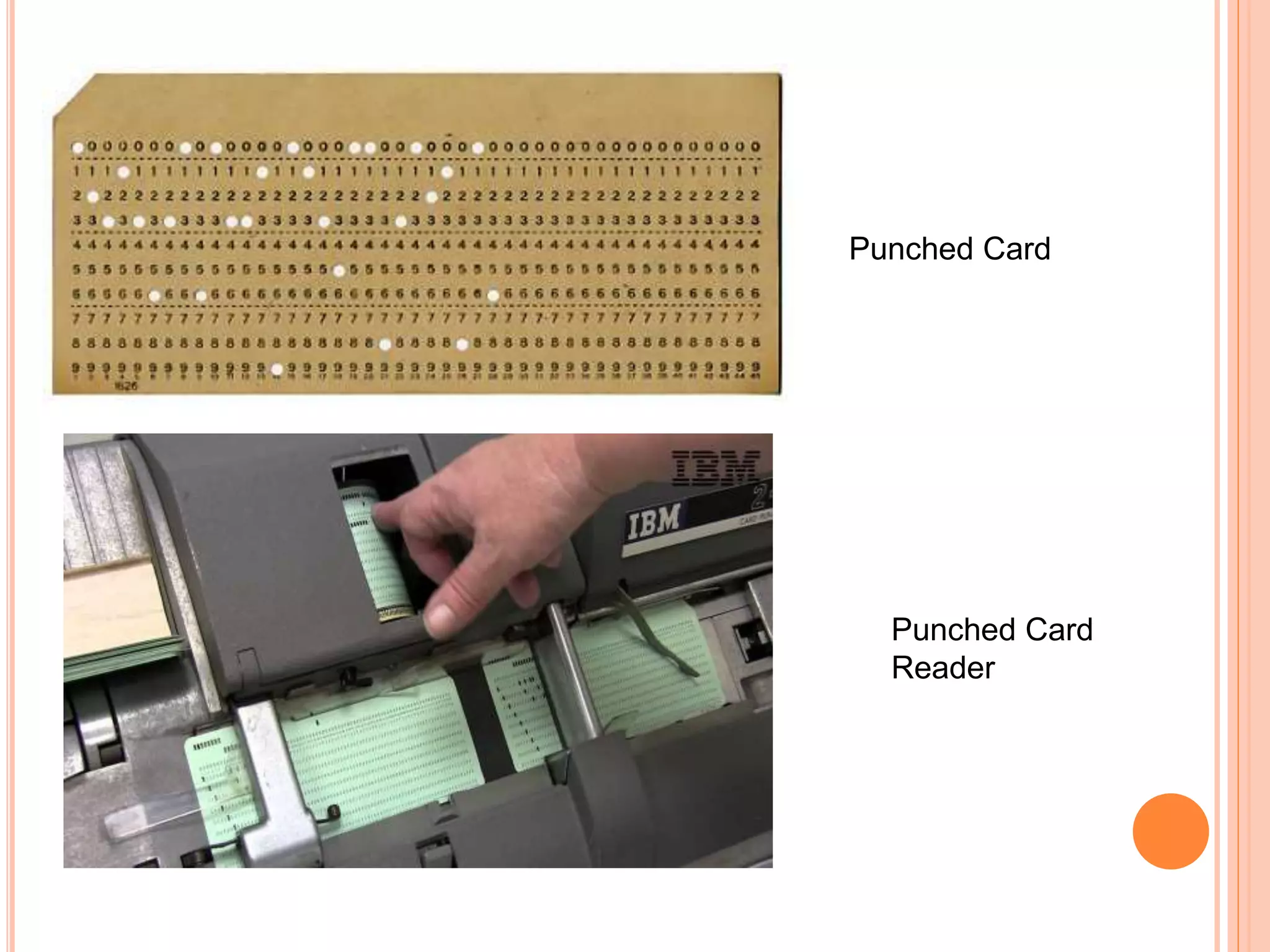
E-business involves conducting business operations over the internet through activities like online shopping, sales, and customer support. It originated in the 1950s with computers processing internal transactions, and expanded in the 1970s with electronic data interchange between banks. E-business offers advantages over traditional business like reduced errors, lower costs, and faster processing times. Key areas of e-business include banking, healthcare, retail, and tourism. It requires tools like websites, payment systems, and security to function.