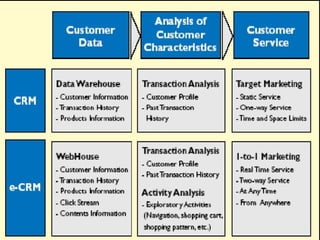
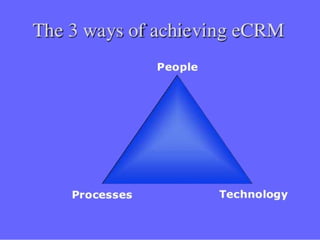
Chapter 7 discusses the evolution from relationship marketing (RM) to customer relationship management (CRM) and electronic customer relationship management (e-CRM), emphasizing the role of technology in enhancing customer engagement and satisfaction. e-CRM integrates various electronic channels and focuses on providing a seamless customer experience while driving profitability and loyalty. Key applications include information integration, customer analysis, real-time decision making, and personalized messaging, all aimed at improving business efficiency and relationships.