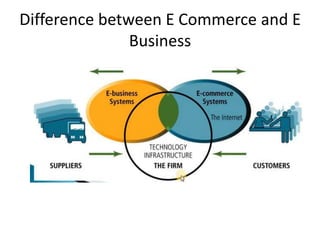
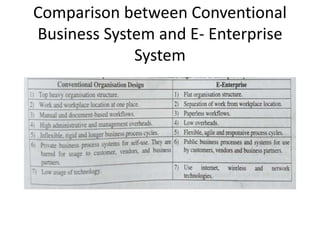
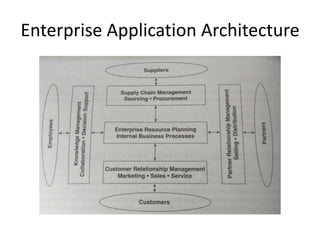
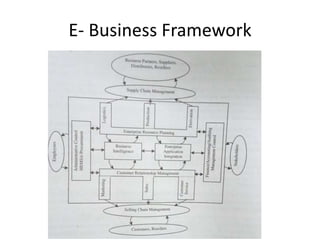
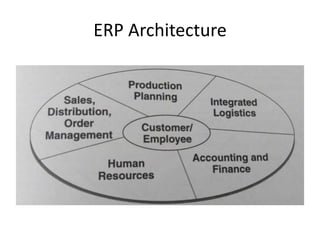
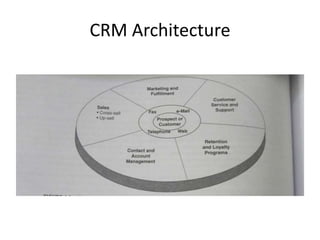
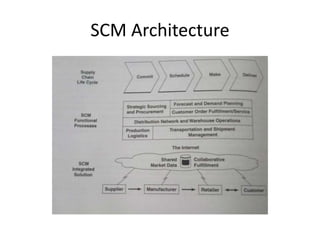
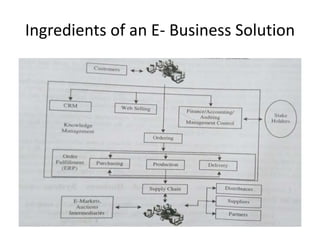
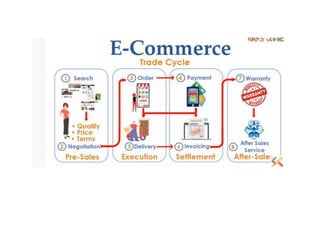
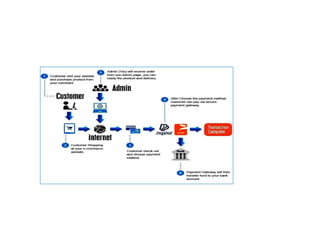
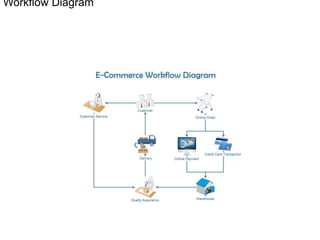
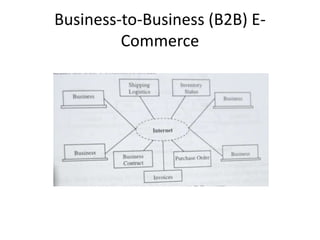
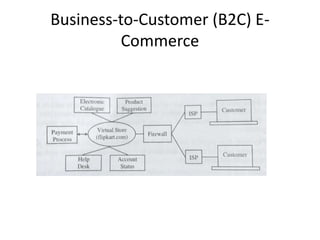
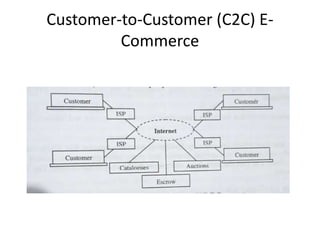
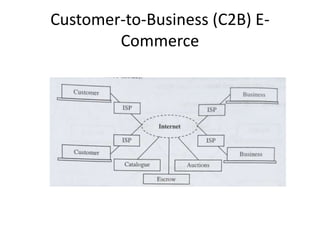
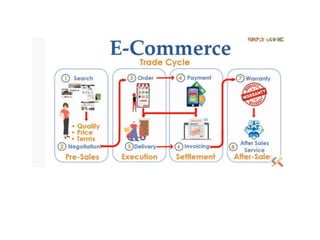
The document discusses different types of e-commerce and enterprise business systems. It defines electronic business (e-business) as using the web and internet for business processes beyond just online buying and selling. Enterprise systems include supply chain management, customer relationship management, and other processes. The key difference between e-commerce and e-business is that e-commerce refers specifically to online transactions, while e-business is a broader term that includes non-monetary activities. Popular enterprise software includes ERP systems like SAP and Oracle that manage internal operations, and CRM systems like Salesforce that manage customer relationships.