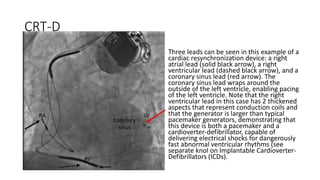
Cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) uses an implanted device to resynchronize heart ventricle contractions, improving heart pumping efficiency. CRT-Ds additionally treat abnormal heart rhythms. CRT benefits include improved hemodynamics, reduced heart remodeling, and reduced hospitalizations and mortality. CRT is indicated for patients with left ventricular dysfunction, heart failure symptoms, and prolonged QRS duration, especially over 150ms with left bundle branch block. Randomized trials show CRT effectiveness includes these benefits compared to conventional therapy.





![CRT and ICD
• (CRT) is also known as biventricular pacing or multisite ventricular
pacing, involves simultaneous pacing of the right ventricle (RV) and
the left ventricle (LV). To this end, a coronary sinus lead is placed for
LV pacing in addition to a conventional RV endocardial lead (with or
without a right atrial [RA] lead).
• ICDs “implantable cardioverterdefibrillators” have revolutionized the
treatment of patients at risk for sudden cardiac death due to
ventricular tachyarrhythmias.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/crt-171101052655/85/Cardiac-Resynchronization-Therapy-and-ICDs-7-320.jpg)

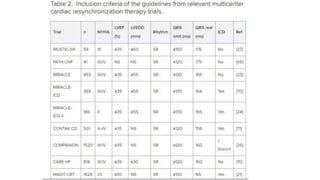
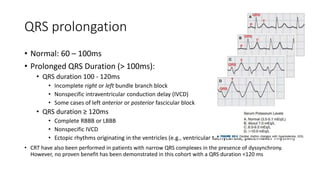
![CRT indications criteria
• From the current clinical practice guidelines, there is 369 indications
• There is no single criterion such as QRS width or mechanical
desynchrony assessed by any echocardiographic measure should be
chosen for the prediction of CRT outcome on its own.
• Most of the benefits appear to be associated with the presence of left
bundle branch block (LBBB) on electrocardiography (ECG); the longer
the QRS duration (particularly >150ms), the more beneficial CRT is
likely to be.
• In patients with other forms of conduction disturbance (e.g. right
bundle branch block [RBBB] or RV pacing), CRT is of questionable
utility and therefore cannot be recommended at this time](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/crt-171101052655/85/Cardiac-Resynchronization-Therapy-and-ICDs-10-320.jpg)