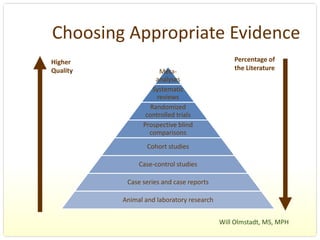
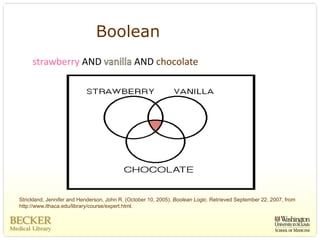
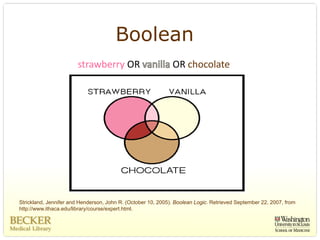
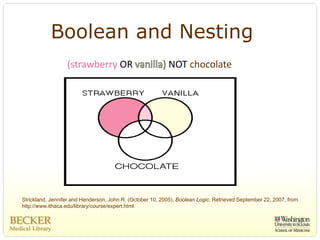
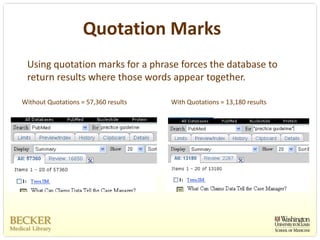
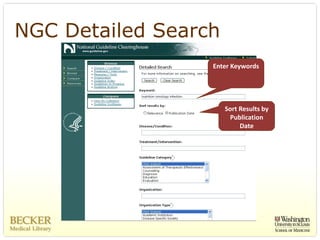
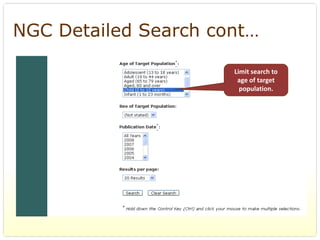
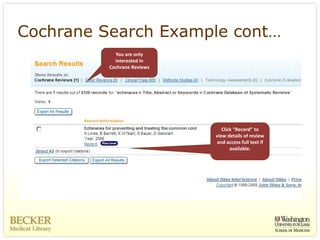
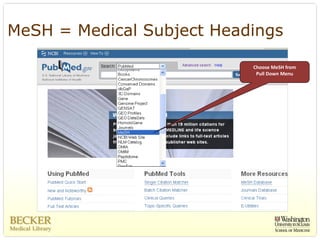
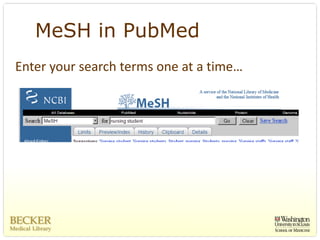
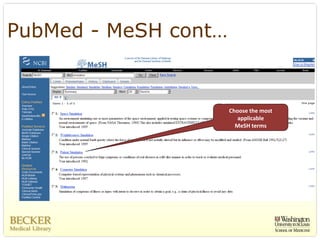
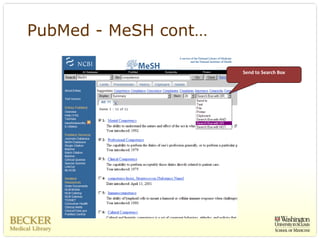
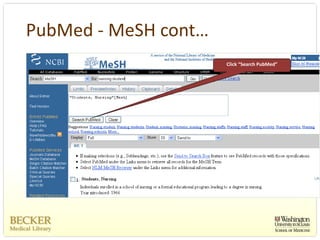
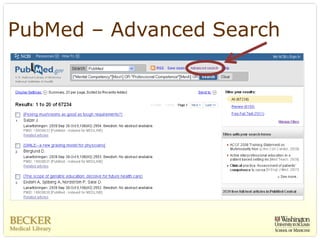
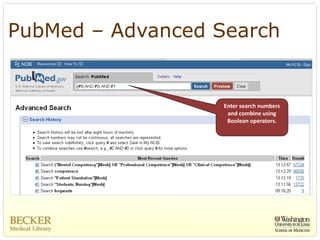
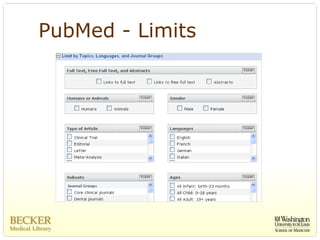
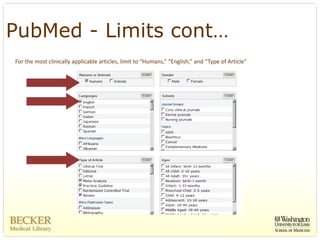
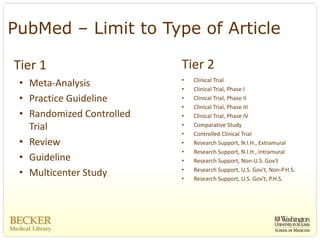
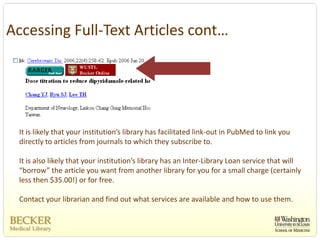
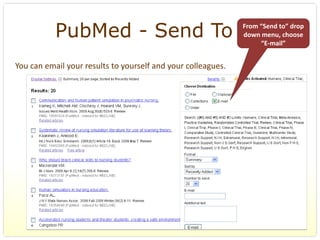
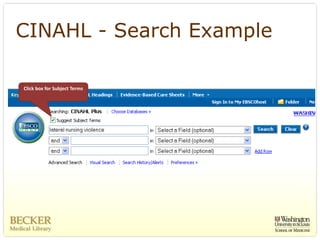
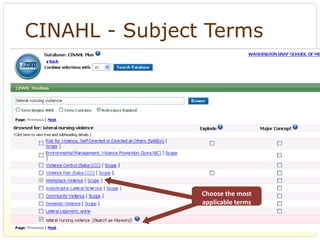
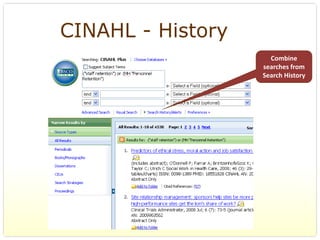
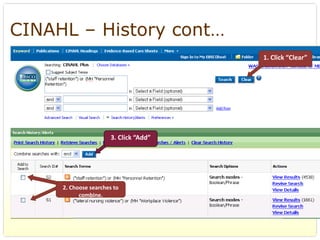
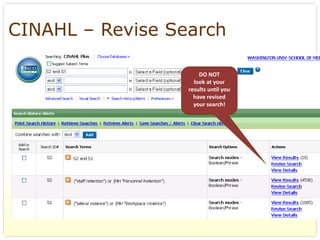
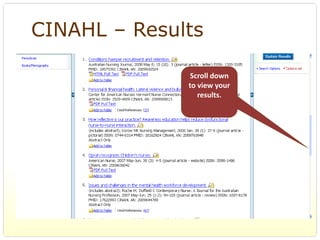
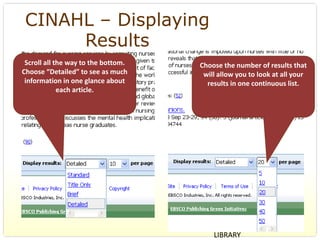
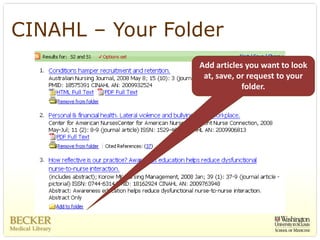
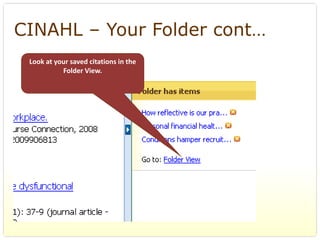
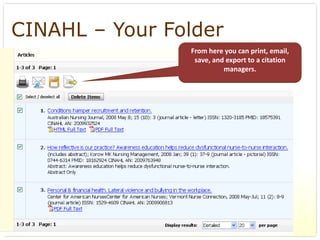
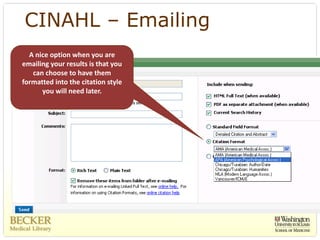
This document provides an overview of evidence-based practice resources for healthcare practitioners. It discusses search strategies including developing PICO questions and using keywords, Boolean operators, truncation and wildcards. It also summarizes key databases for finding evidence including the National Guidelines Clearinghouse, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, PubMed, and CINAHL. Tips are provided for evaluating search results and choosing appropriate study designs and evidence levels.