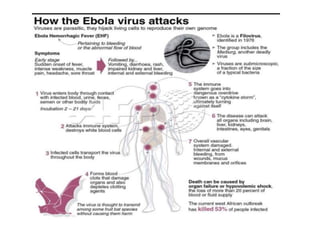
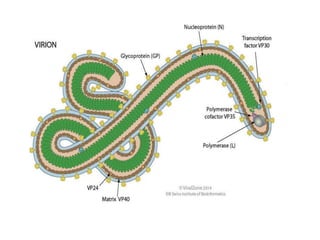
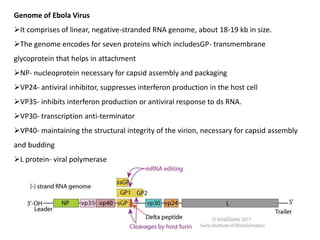
- Ebola virus causes a severe hemorrhagic fever in humans and non-human primates. It belongs to the filovirus family.
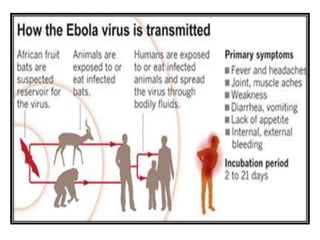
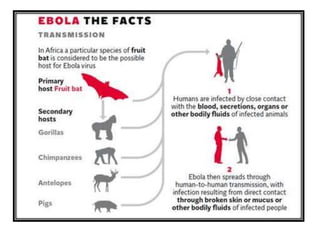
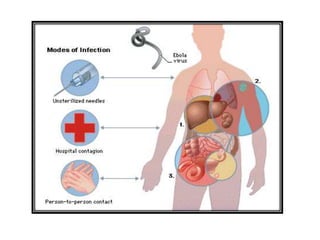
- The natural reservoir of the virus is unknown, though fruit bats are suspected. It is transmitted via contact with bodily fluids.
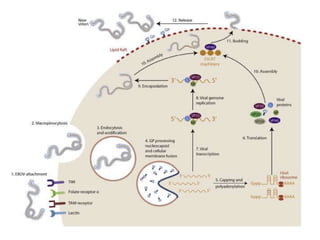
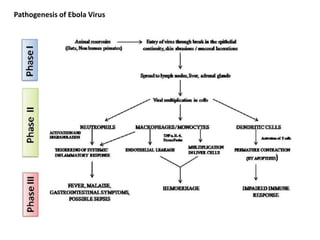
- The virus enters host cells and hijacks their machinery to replicate. It disrupts the host immune response, causing systemic damage and bleeding. No approved treatments exist, though supportive care is given. Isolation and protective equipment are emphasized for control.