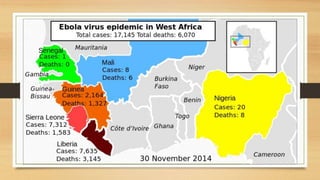
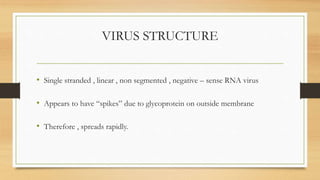
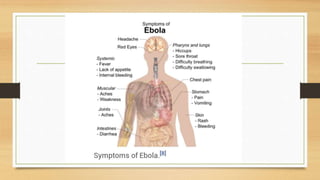
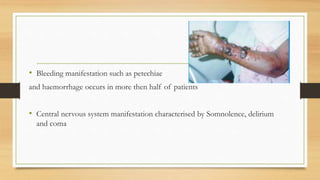
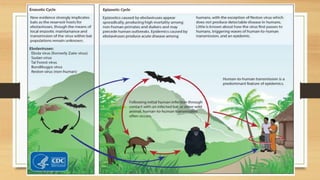
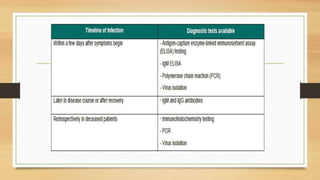
Ebola virus disease is a severe and often fatal illness in humans and nonhuman primates. The virus is transmitted through contact with bodily fluids of infected animals or humans. Symptoms include fever, headache, muscle pain and bleeding. There is no approved vaccine or treatment, so care is supportive to maintain hydration and treat complications. The largest outbreak occurred in West Africa from 2014-2016 infecting over 28,000 people. India has had no outbreaks but has protocols to screen passengers from affected areas and isolate any suspected cases.