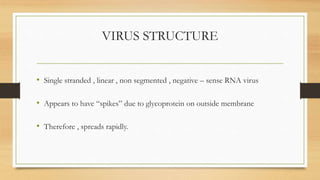
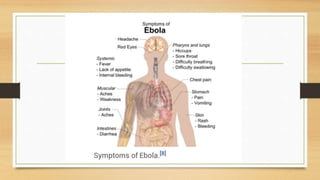
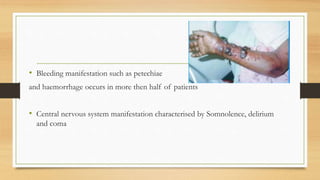
- Ebola virus disease is a severe and often fatal illness in humans and nonhuman primates, with a high fatality rate of up to 90%.
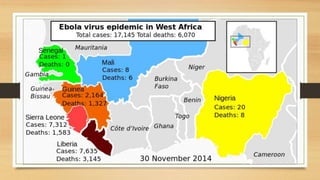
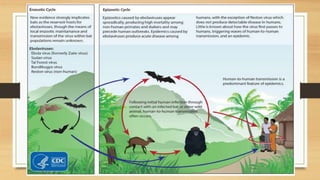
- The virus is transmitted through contact with bodily fluids of infected animals or humans. During the 2014 outbreak in West Africa, over 17,000 cases were reported in Guinea, Liberia and Sierra Leone.
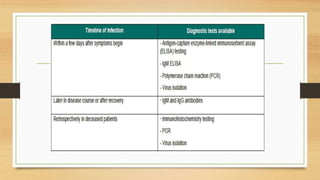
- There is no approved vaccine or treatment, so care is supportive to maintain hydration and treat symptoms. Isolating patients suspected of infection and proper disposal of contaminated materials is crucial to control spread of the disease.