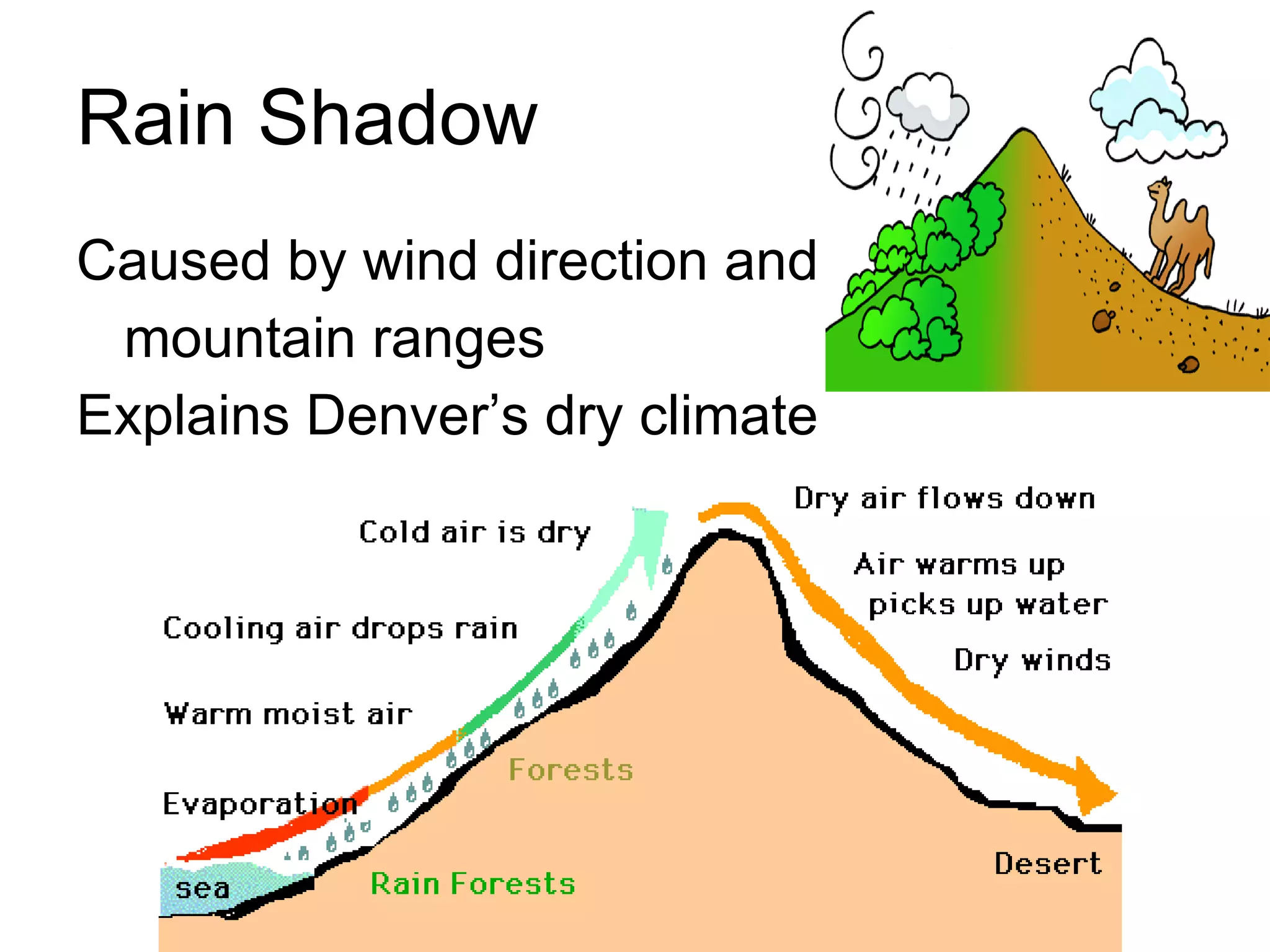
The document discusses several of Earth's biogeochemical cycles including the water, carbon, nitrogen, and ozone cycles. It describes the basic processes in each cycle, such as evaporation and precipitation in the water cycle, and photosynthesis and respiration in the carbon cycle. It also notes that most of the water is found in the oceans, most carbon is found in plants, soil, and oceans, most nitrogen is found in the atmosphere, and the ozone layer blocks UV light from the sun.