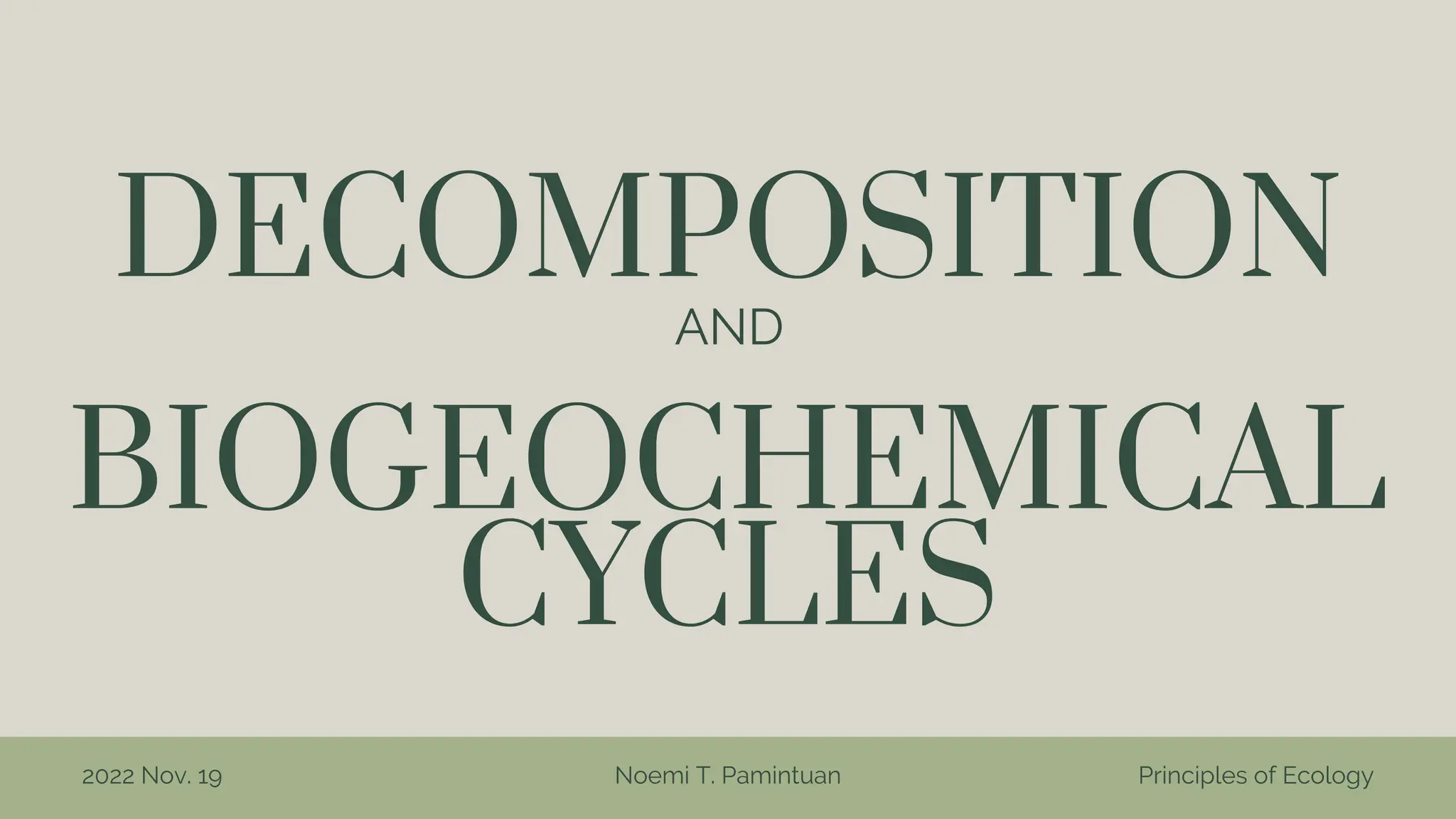
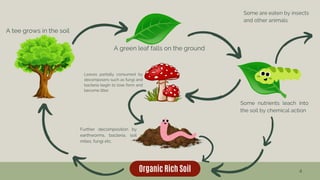
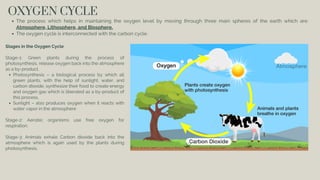
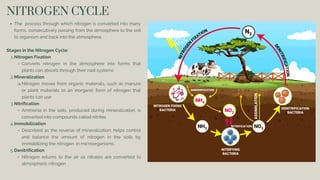
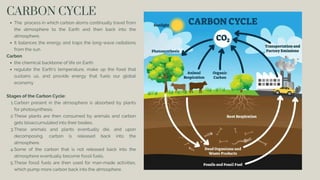
The document discusses the processes of decomposition and biogeochemical cycles, highlighting how decomposers like bacteria and fungi break down organic matter, and detailing the roles of the nitrogen, carbon, and oxygen cycles. It explains the stages of each cycle, their significance to ecosystems, and the factors affecting them, such as deforestation and land development. These cycles are essential for nutrient recycling and maintaining environmental balance.