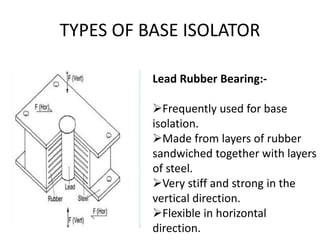
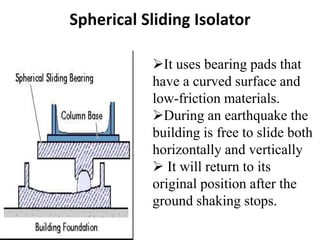
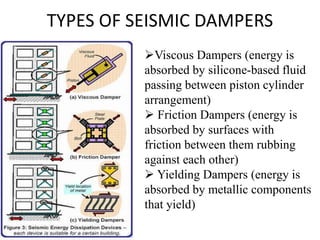
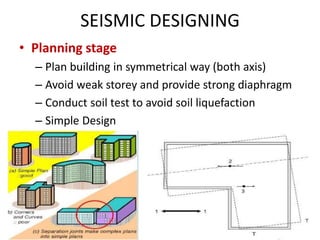
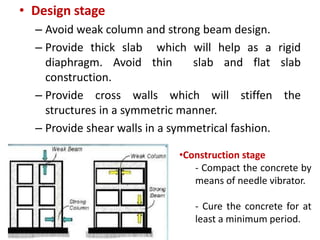
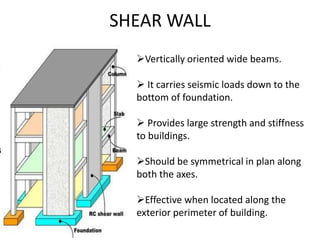
This document discusses techniques for making structures resistant to earthquakes, including base isolation and energy dissipation devices. Base isolation involves separating the building from the ground using flexible rubber devices to allow it to move independently during an earthquake. Energy dissipation devices, like seismic dampers, absorb seismic energy to dampen the motion of the building. Common types of base isolators are lead rubber bearings and spherical sliding isolators, while common seismic dampers include viscous, friction, and yielding dampers. Proper seismic design involves principles like avoiding brittle elements, providing strength throughout the building, and well-connecting the building to its foundation.