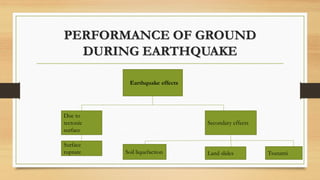
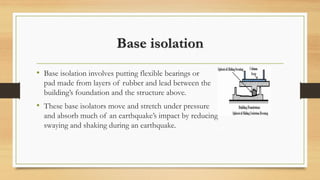
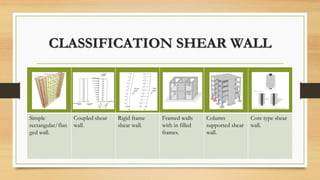
The document discusses various earthquake-resistant techniques and elements in high-rise buildings, emphasizing the importance of seismic design to safeguard structural integrity and occupant safety during earthquakes. It covers topics such as shear walls, base isolation, seismic dampers, and their roles in improving a building's ability to withstand seismic forces. Additionally, it highlights the classification of shear walls, design considerations, and modern technologies in earthquake-resistant architecture.