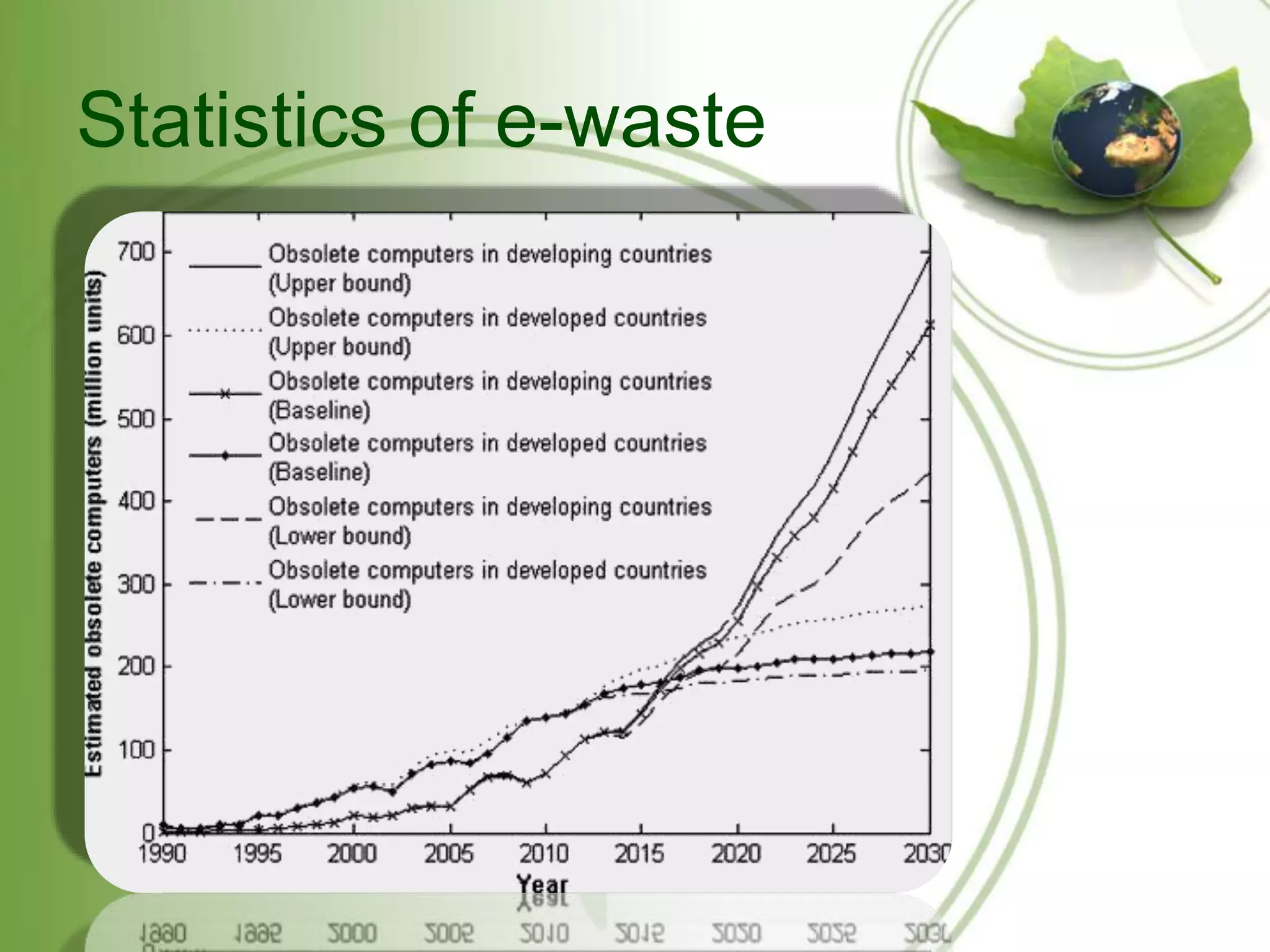
E-waste refers to outdated or broken electronics, contributing significantly to global toxic waste due to hazardous materials like lead and mercury. The increase in e-waste is driven by rapid technological advancements and consumer behavior, with both developed and developing countries facing disposal challenges. Effective management includes recycling, raising awareness, and improving accessibility to recycling facilities, but it requires specialized methods and considerable investment.