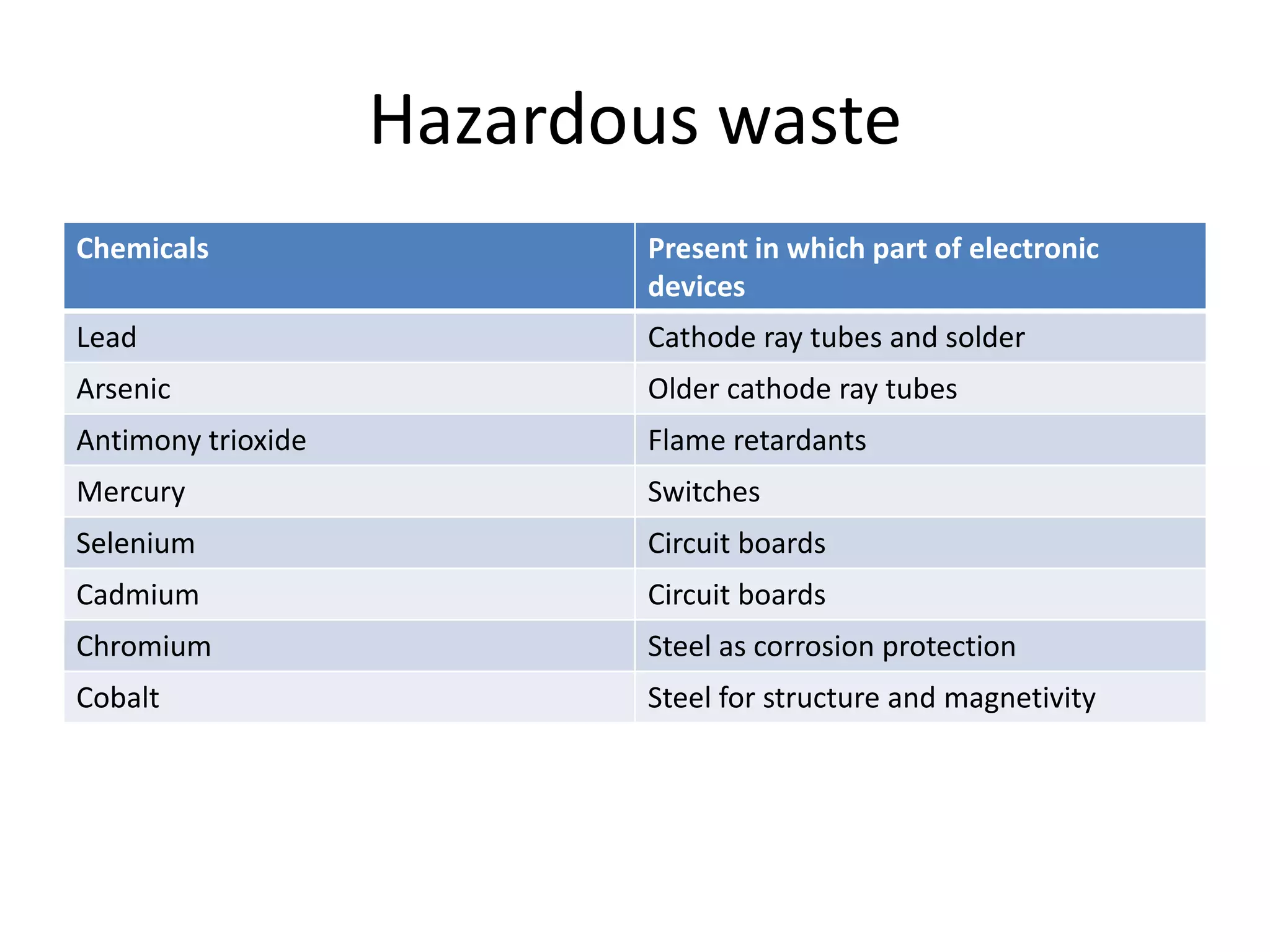
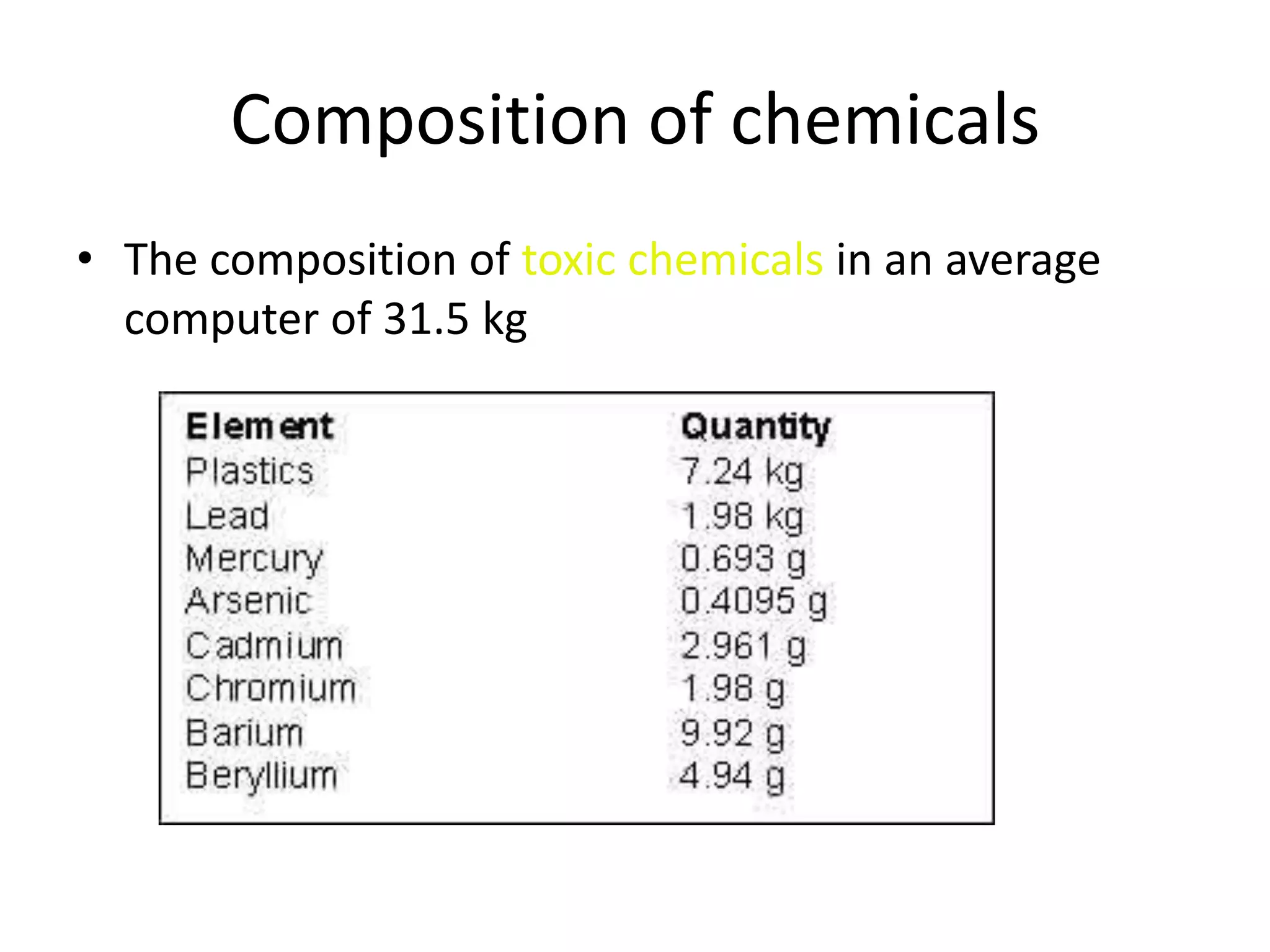
E-waste is electronic equipment that is nearing or at the end of its useful life. It contains toxic chemicals like lead, cadmium, and mercury. India generates large amounts of e-waste but only a small portion is recycled properly. Most e-waste is handled by informal recyclers who do not protect themselves from toxins, polluting the environment and harming health. Exposure to e-waste toxins can damage organs and increase risks of cancer, neurological impairments, and other diseases. India needs better regulations and incentives for formal recycling to safely manage its growing e-waste problem.