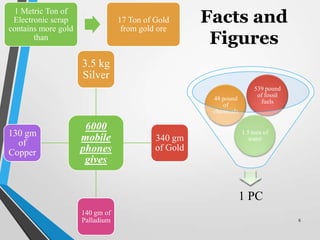
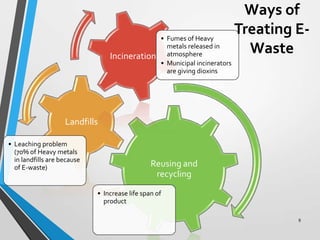
E-waste or electronic waste refers to old, end-of-life electronics that are discarded. India generates around 0.8 million tons of e-waste annually, which is growing by 10% each year. E-waste contains hazardous materials like lead, cadmium, and mercury and needs to be properly managed to avoid environmental pollution and health impacts. Common approaches to managing e-waste include reuse, refurbishment, material recovery through formal recycling, and environmentally-sound disposal. However, in India much of the e-waste is handled by the informal sector, which recovers valuable materials but can also lead to environmental and health issues due to unsafe practices. Improved regulations, take-back programs, and awareness