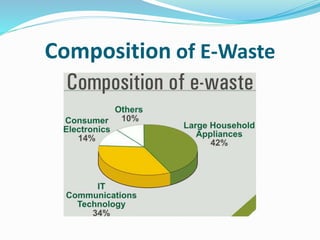
This document discusses electronic waste (e-waste), including its definition, production, composition, disposal issues, health problems, and management. It notes that e-waste includes obsolete or discarded electrical/electronic equipment like computers, TVs, and cell phones. About 50 million metric tons of e-waste are produced globally each year, with improper disposal releasing toxic materials that can harm the environment and human health. The document outlines some steps to properly manage e-waste, including detoxification to remove hazardous components, shredding the materials into pieces, and refining to extract reusable components.