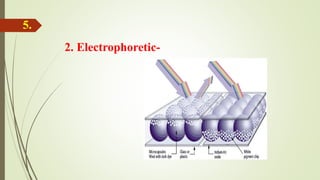
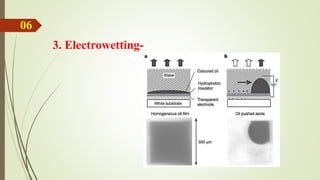
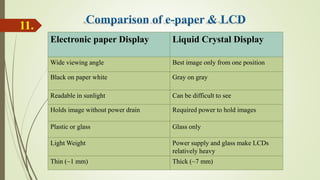
Rohit Egade presented on e-paper technology. E-paper is also called electronic paper or electronic ink display. It is flexible, portable, and can hold text and images like ordinary paper but uses electronic components. E-paper was first developed in the 1970s and two main technologies are electrophoretic and gyricon. It has a front plane made of e-ink and a back plane of electronic circuits. E-paper has properties like being thin, flexible, requiring no power to hold images, and being readable in sunlight. It can be used in applications like e-readers, watches, mobile phones, and status displays. Advantages include low power use and reading like paper while disadvantages are slow switching speeds