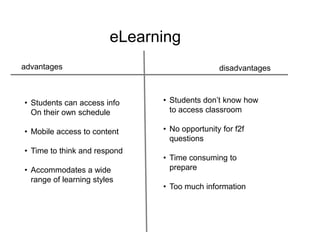
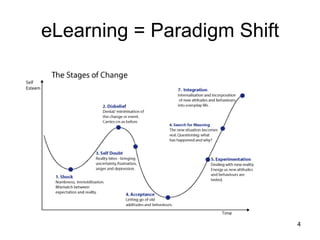
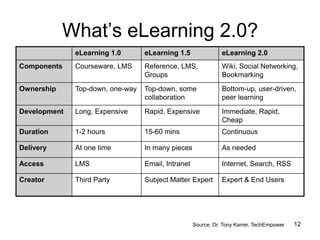
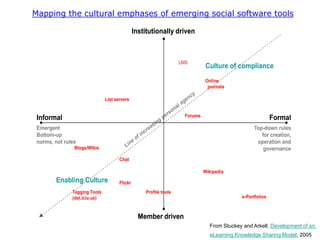
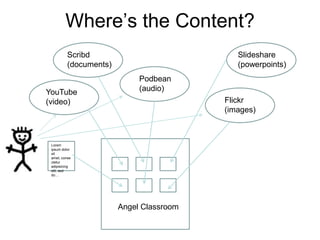
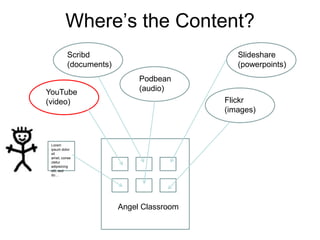
The document discusses the advantages and disadvantages of eLearning. Some key advantages include students being able to access information on their own schedule, having mobile access to content, and eLearning accommodating different learning styles. Some disadvantages are students not knowing how to access classroom resources, a lack of opportunities for in-person questions, and eLearning being time consuming to prepare. The document also suggests eLearning can be a valuable complement to face-to-face teaching when used appropriately.