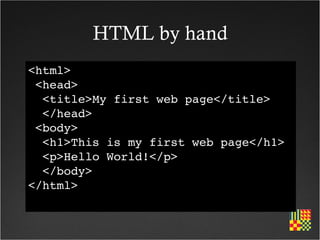
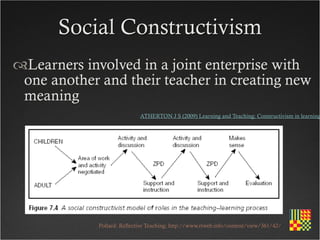
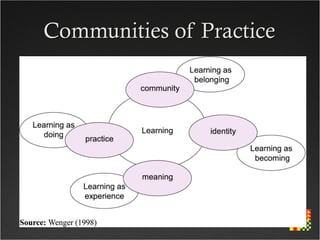
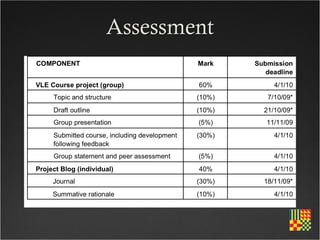
This course aims to help participants demonstrate understanding of how to effectively use the web for teaching and learning. It covers topics like government education initiatives, pedagogical approaches for e-learning, supporting safe internet use, and developing online course materials. The course structure includes exploring the web as a resource, designing for the web, e-learning tools, interactive technologies like blogs and wikis, digital safety, and assessing online learning.