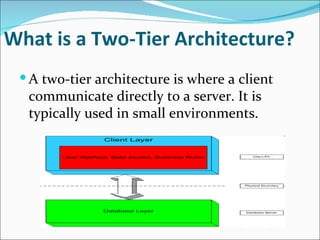
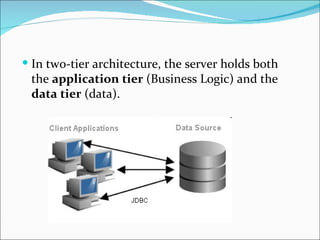
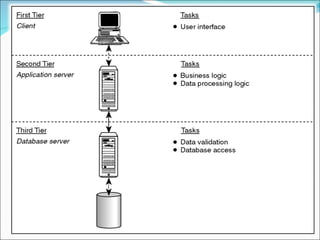
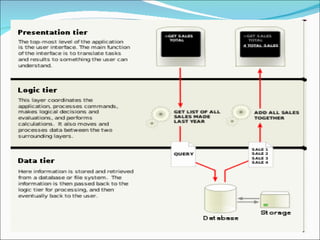
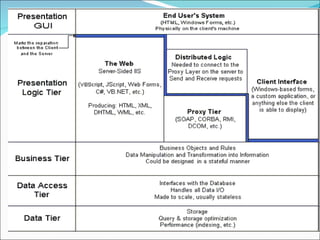
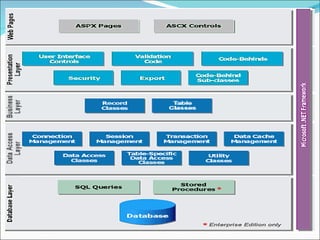
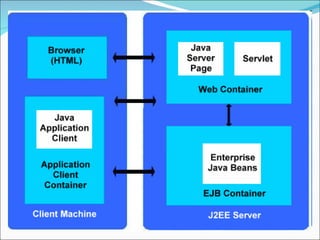
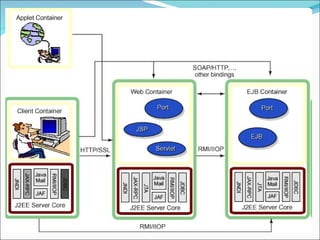
A 2-tier architecture involves clients communicating directly with servers that hold both the application and data tiers. A 3-tier architecture separates these functions into distinct tiers - clients interact with an application server tier that provides requested resources by accessing a separate data server tier. This separation of concerns allows for improved scalability, portability, and maintainability compared to a 2-tier architecture. Common web, application and database servers are discussed.