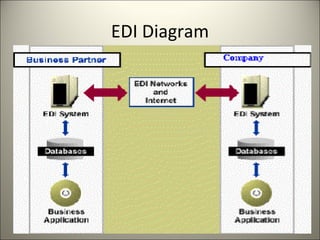
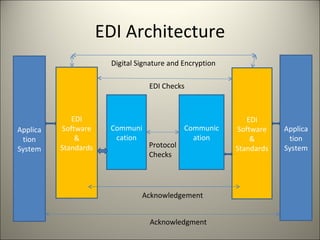
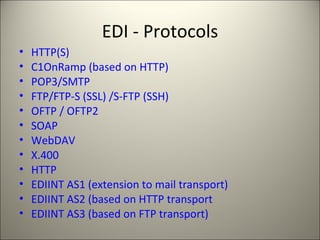
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) allows businesses to electronically exchange structured data through agreed message standards transmitted between computer systems, replacing paper documents. EDI originated in the 1960s for transport industry data transmission and standards were developed by organizations like ANSI and UN/ECE. EDIFACT is now the global EDI standard defining formats for many industries. Common EDI protocols include HTTP, FTP, AS1/AS2/AS3, and earlier versions used X.400. EDI has improved efficiency by reducing time, errors and costs compared to earlier physical document transfer systems.