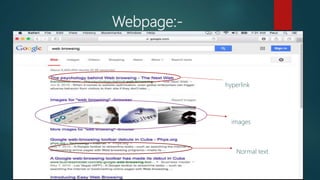
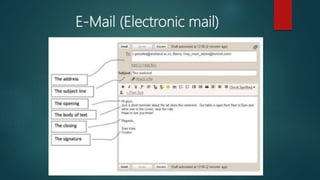
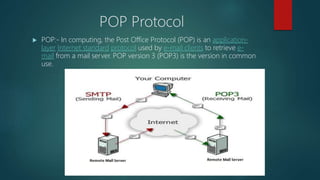
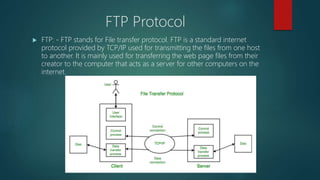
This document provides an overview of basic internet and mobile technologies. It defines key terms like internet, webpage, web server, blog, email, file transfer protocols, search engines, video conferencing and e-learning. Requirements for internet connection include a computer, network interface card, modem and internet service provider. Common webpage elements are hyperlinks, images and text. Static and dynamic webpages are described. [END SUMMARY]