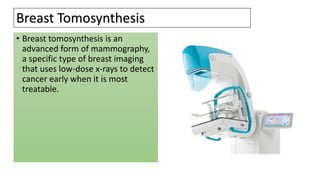
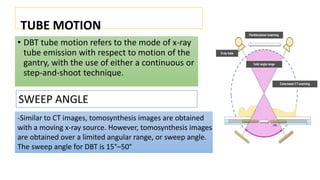
Breast tomosynthesis is an advanced form of mammography that uses low-dose x-rays and 3D reconstruction to create three-dimensional images of the breast. Multiple x-ray images are taken over a limited sweep angle and digitally reconstructed into slices to view tissue at different depths within the breast. This allows for detection of smaller tumors and greater accuracy in diagnosis compared to traditional mammography. While exposure to radiation is a risk, the benefits include improved cancer detection rates and fewer unnecessary biopsies.