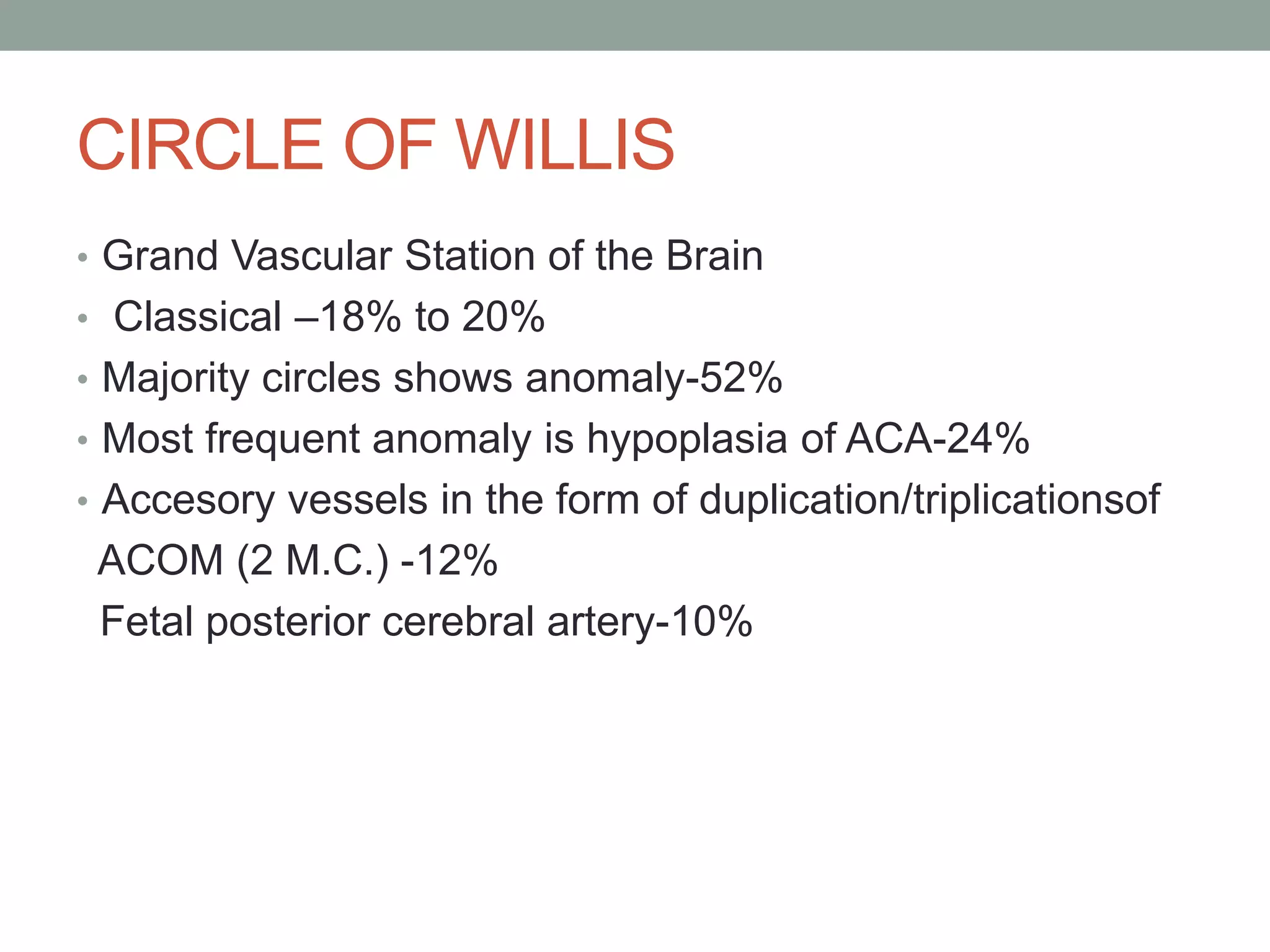
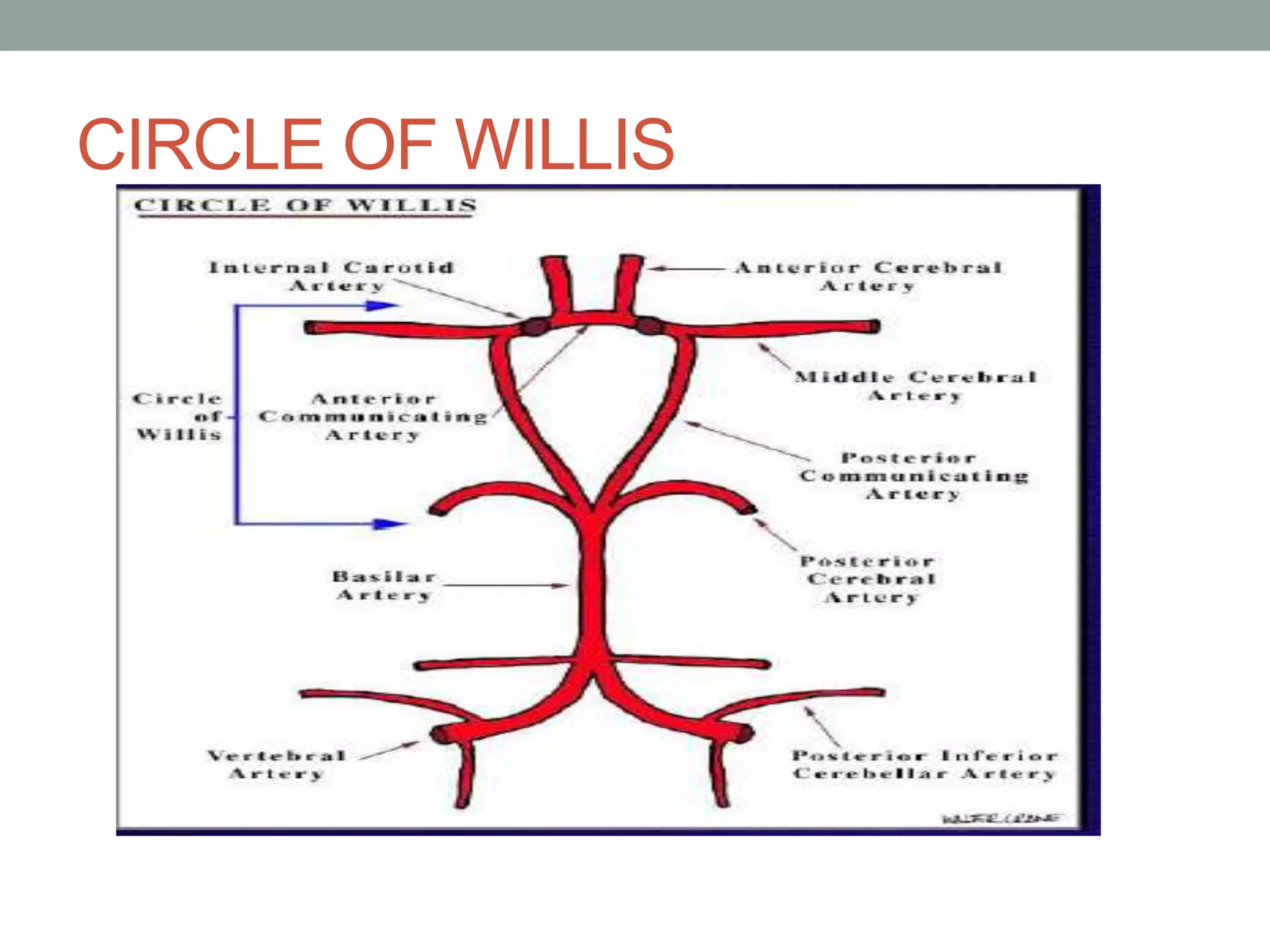
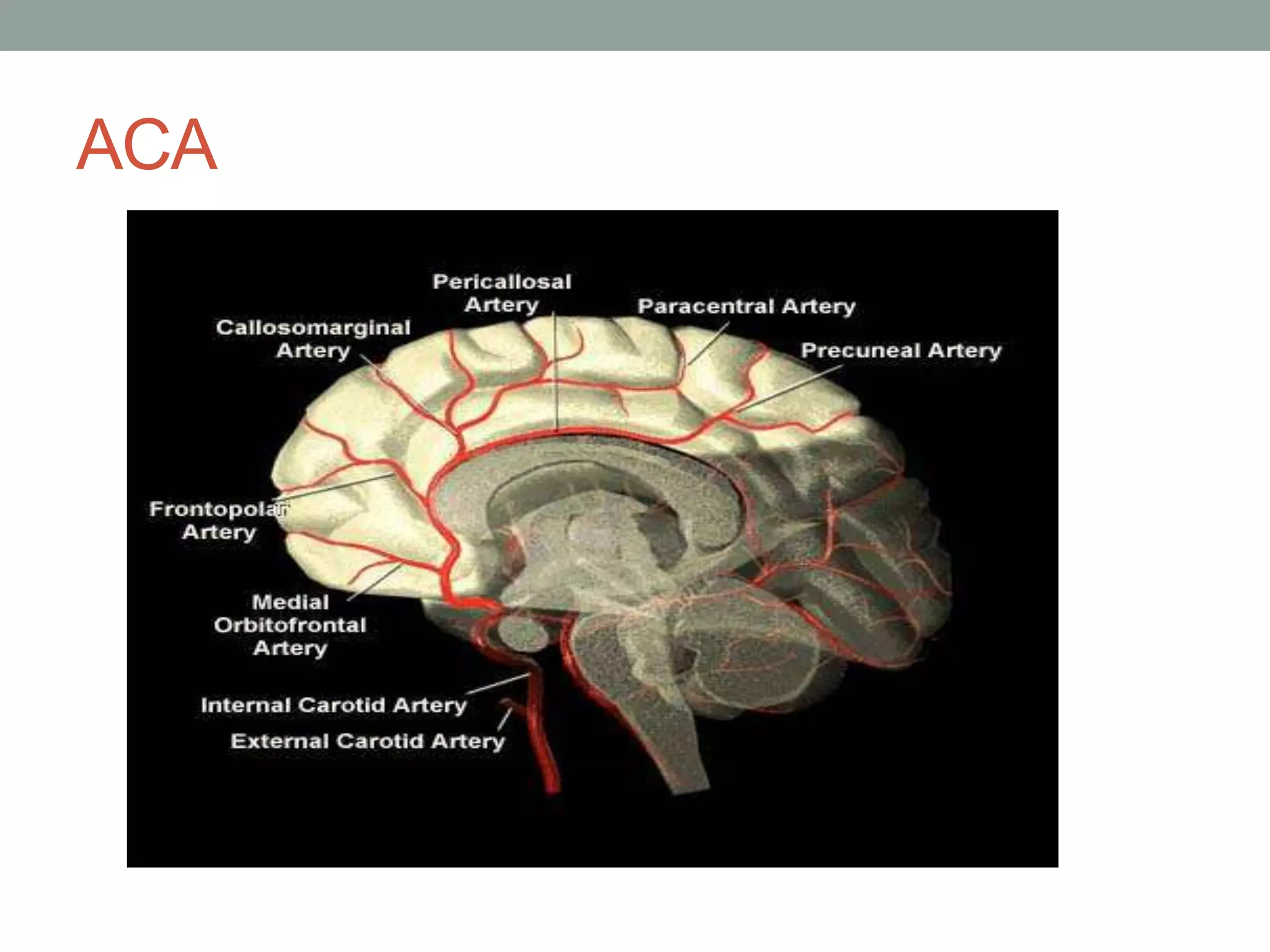
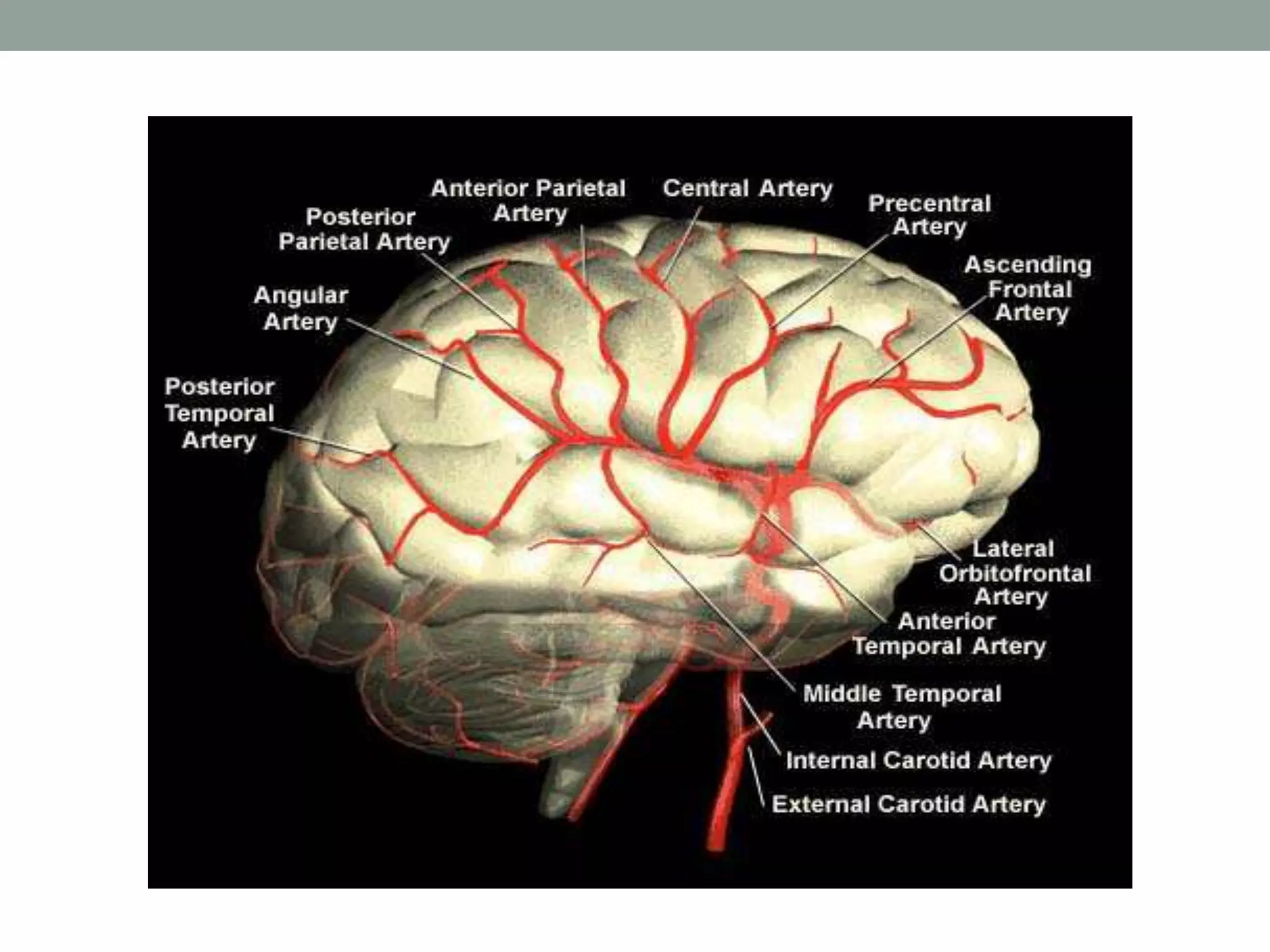
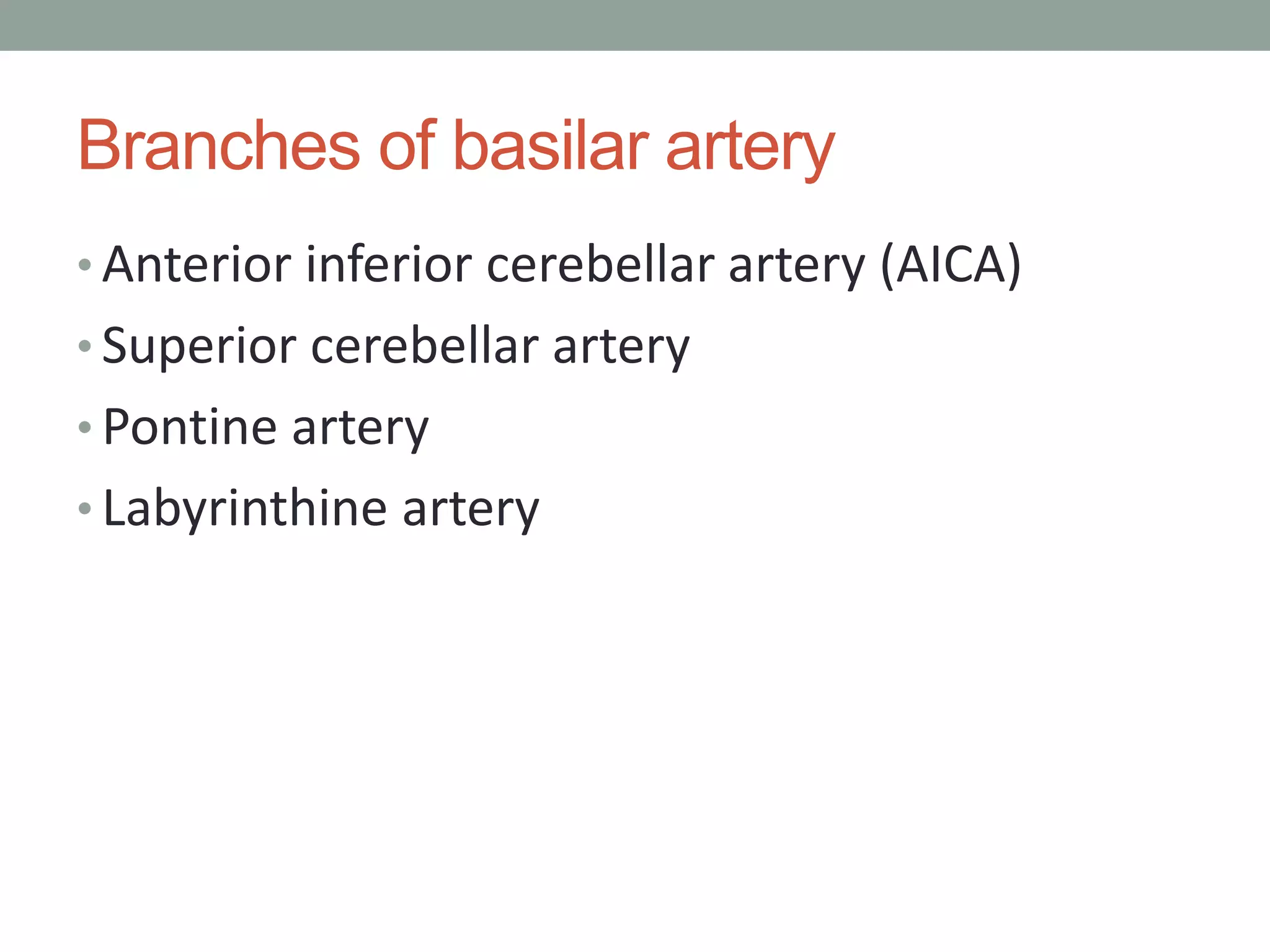
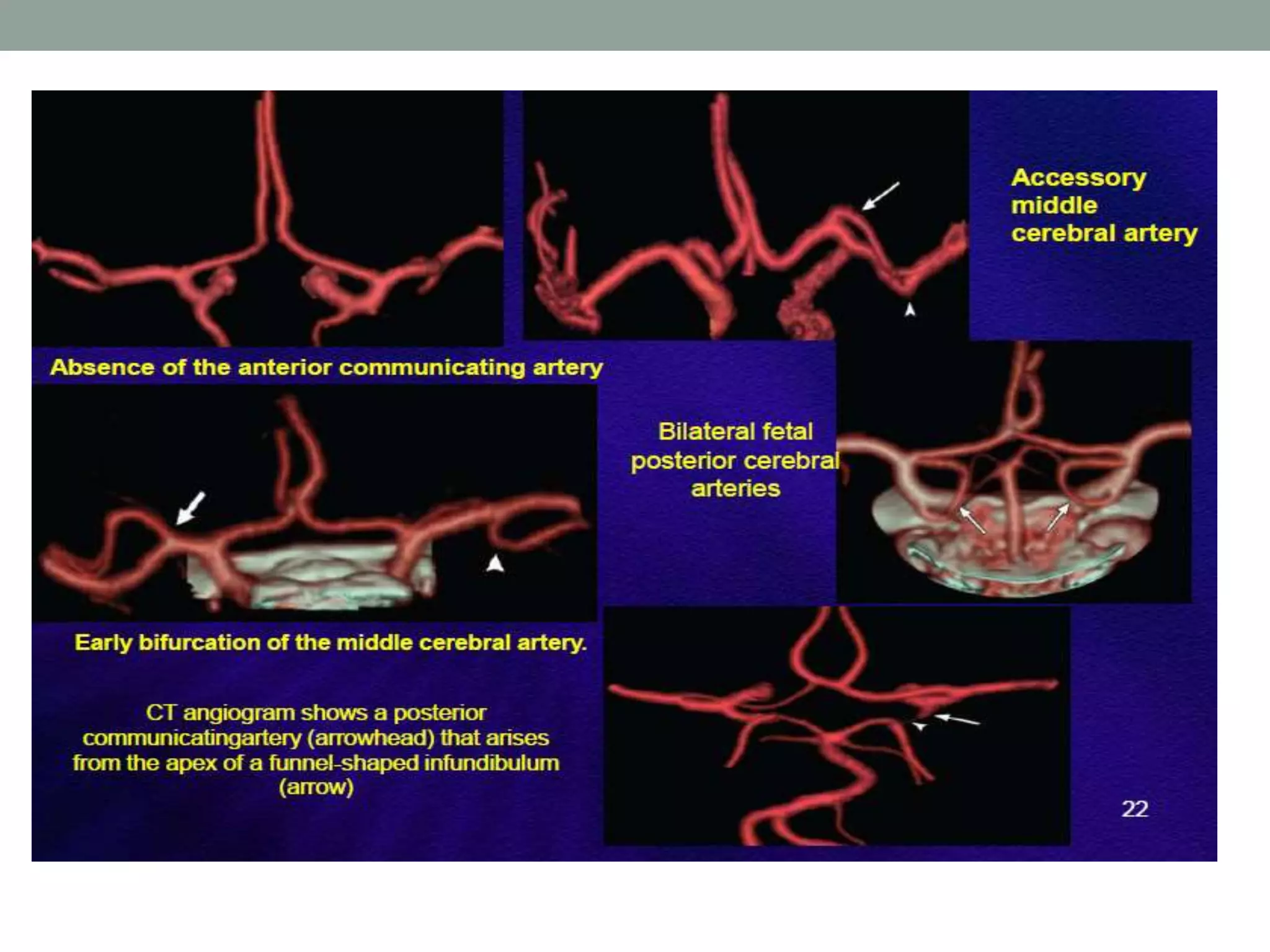
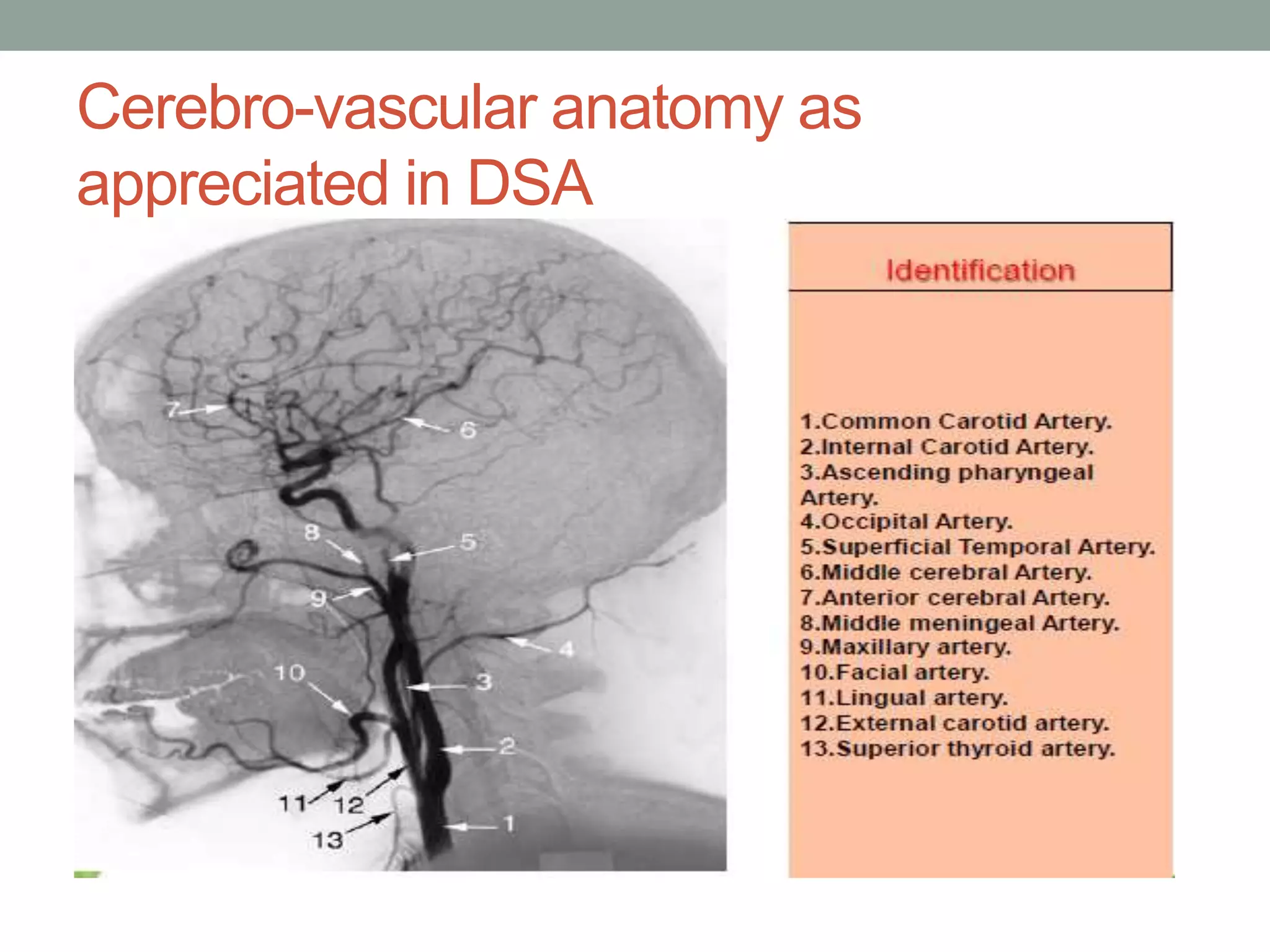
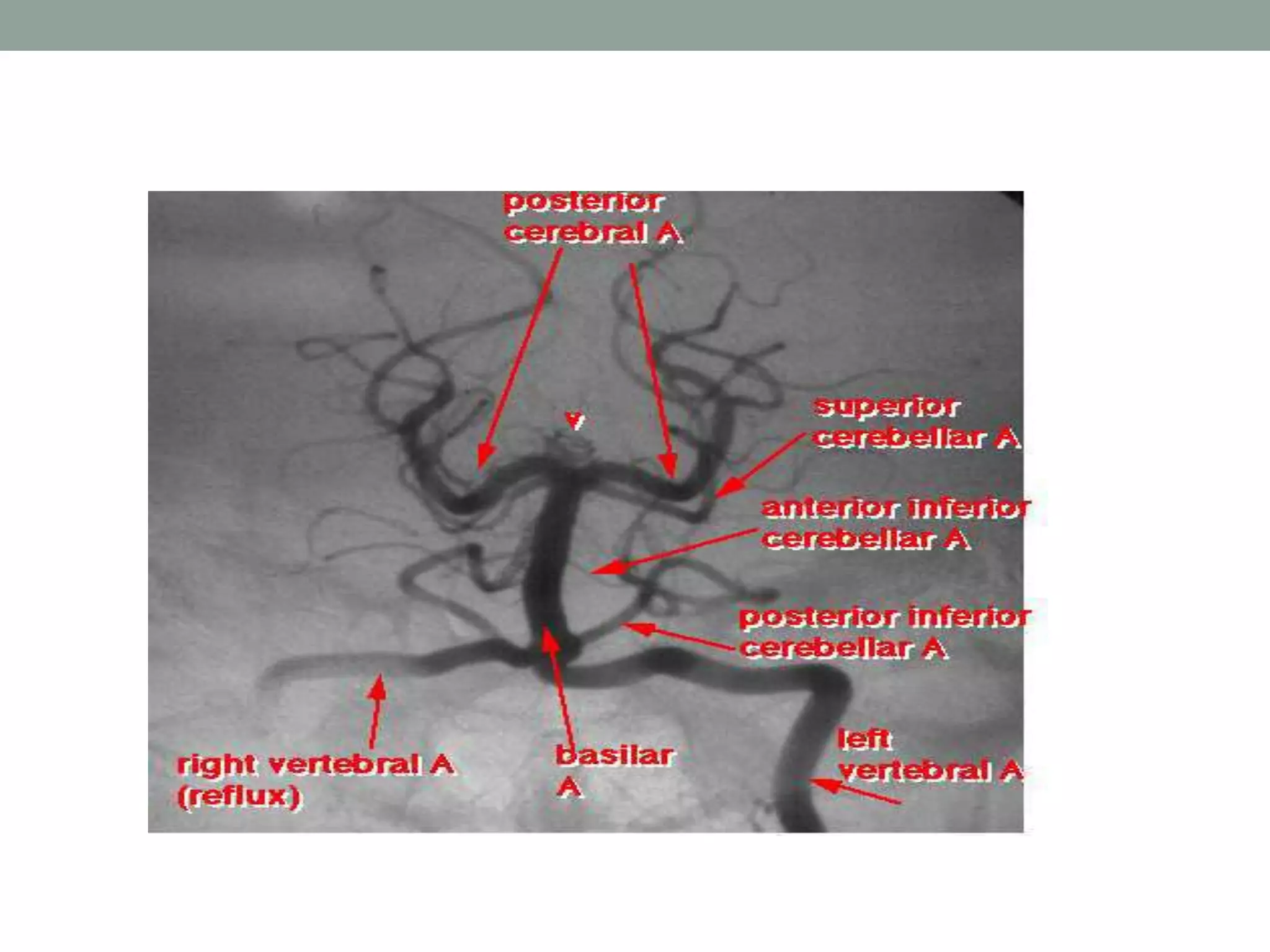
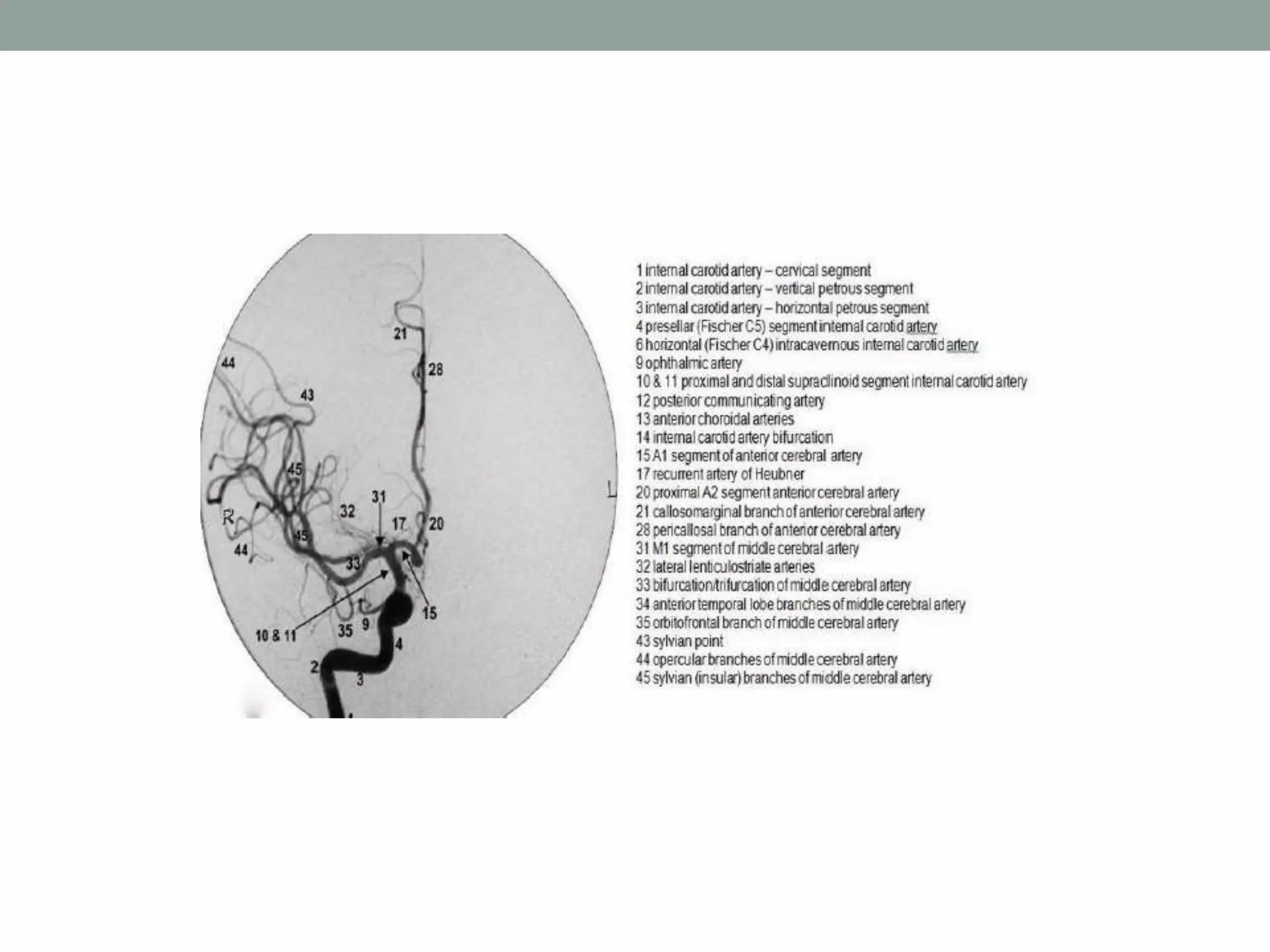
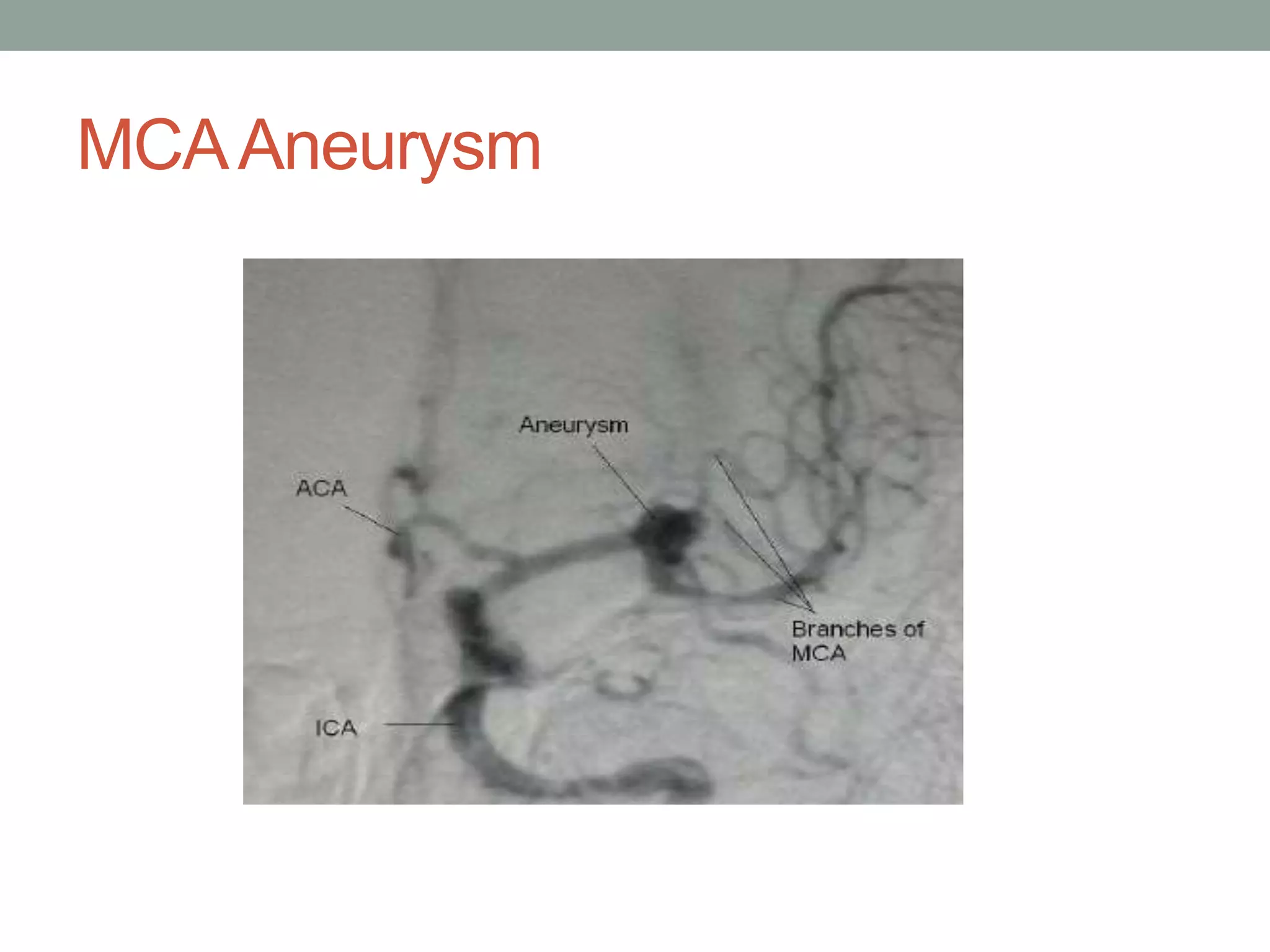
Digital subtraction angiography (DSA) is the gold standard for evaluating the cerebral vasculature. It involves injecting iodinated contrast material into arteries and using subtraction techniques to visualize vessels. The normal anatomy includes the circle of Willis and branches of major arteries. Variants are common. DSA is used to diagnose conditions like aneurysms and arteriovenous malformations. Newer digital systems provide 3D reconstruction and less radiation exposure compared to older techniques. DSA remains an important tool for interventional procedures and treatment planning of complex vascular lesions of the brain.