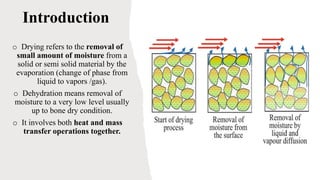
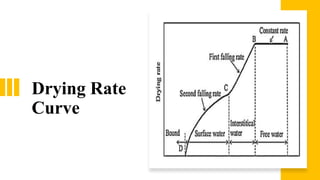
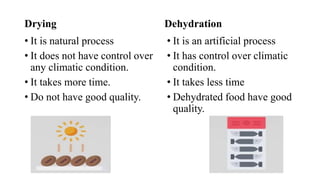
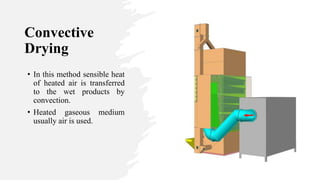
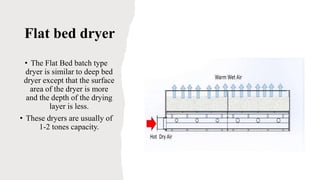
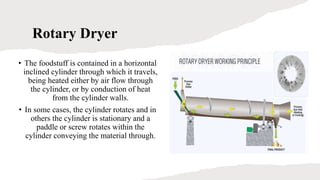
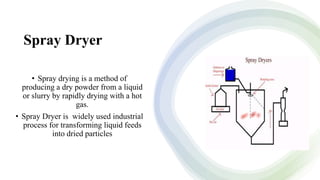
The document discusses drying and dehydration processes, detailing their definitions, differences, and importance in food engineering. It covers various drying methods, including natural and artificial techniques, and explains different types of dryers used in agriculture. The information emphasizes the significance of effective drying for quality preservation and microbial spoilage reduction.