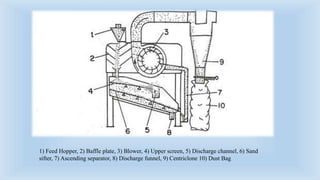
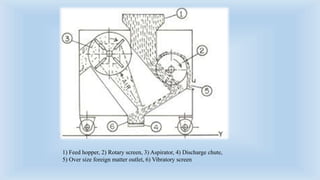
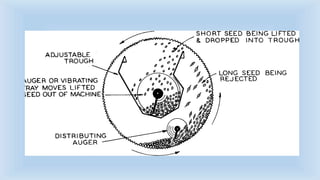
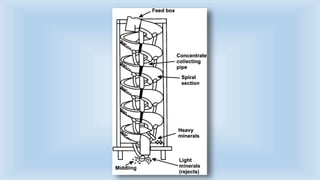
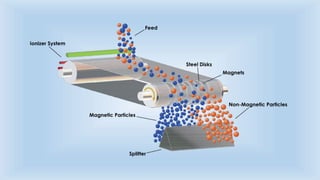
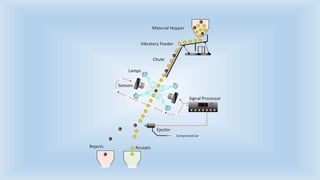
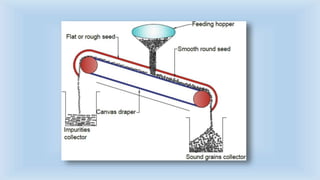
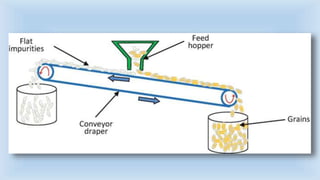
The document outlines various cleaning and grading technologies utilized in post-harvest processing for agricultural products, detailing principles and specific types of equipment such as air screen cleaners, magnetic separators, and color sorters. It explains how these technologies operate to separate and classify grains based on size, shape, and other qualities for enhanced efficiency in agricultural processes. The effectiveness of each method, including the importance of proper screen function, is also discussed.