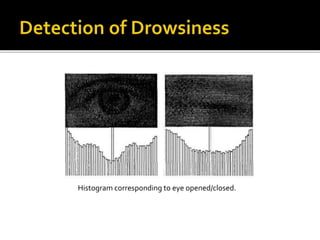
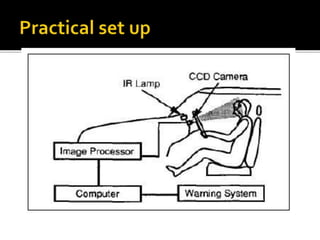
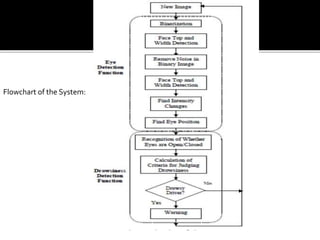
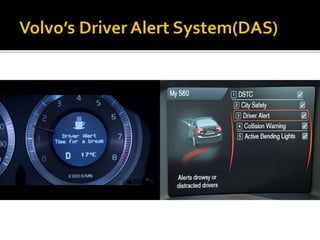
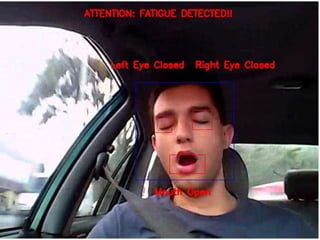
The document discusses the significant danger of driver fatigue in heavy vehicles, highlighting that 52% of heavy truck single-vehicle accidents are fatigue-related, leading to numerous injuries and fatalities annually. It outlines a proposed system to monitor driver drowsiness through real-time eye tracking and facial symmetry analysis, implemented by major automotive companies to enhance driver alertness. The system alerts drivers if signs of fatigue are detected and recommends breaks to prevent accidents.




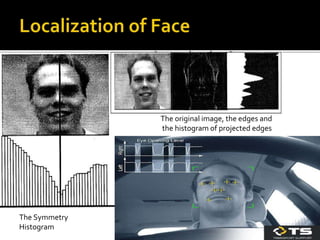
![ Since the Face is symmetric, a symmetry-based
approach. It was found that it is enough to use a sub
sampled, gray-scale version of the image. A
symmetry-value is then computed for every pixel-
column in the reduced image.
If the image is represented as I(x, y) then the
symmetry value for a pixel-column is given by :
S(x) = ∑∑ [abs I ((x,y-w)-(x,y+w))].
S(x) is computed for X € [k,size-k] where k is the
maximum distance from the pixel-column that
symmetry is measured, and x size is
the width of the image.The x corresponding to the
lowest value of S(x) is the center of the face.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/driverfatiguedetectionsystem-151209144618-lva1-app6891/85/Driver-fatigue-detection-system-5-320.jpg)