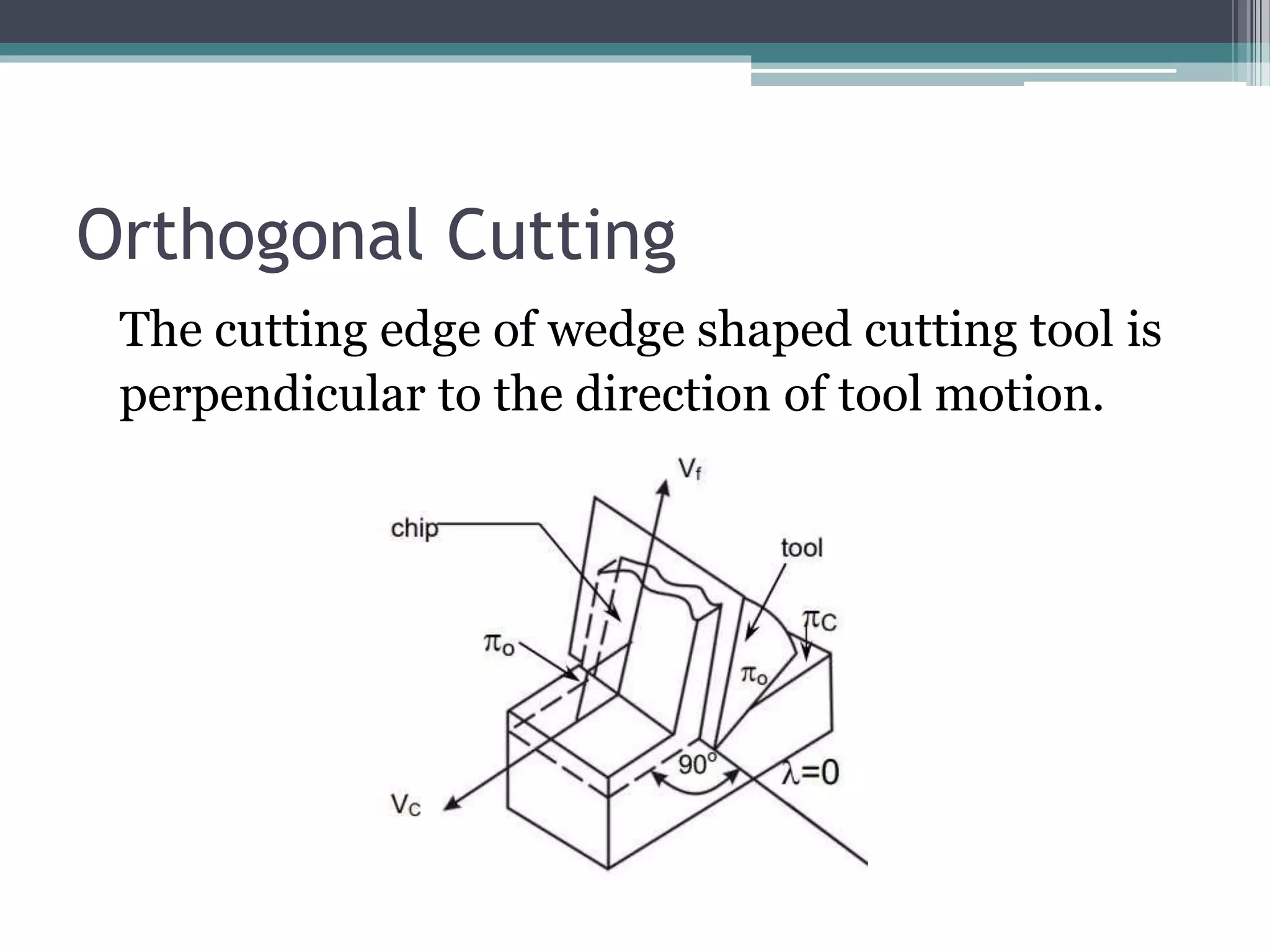
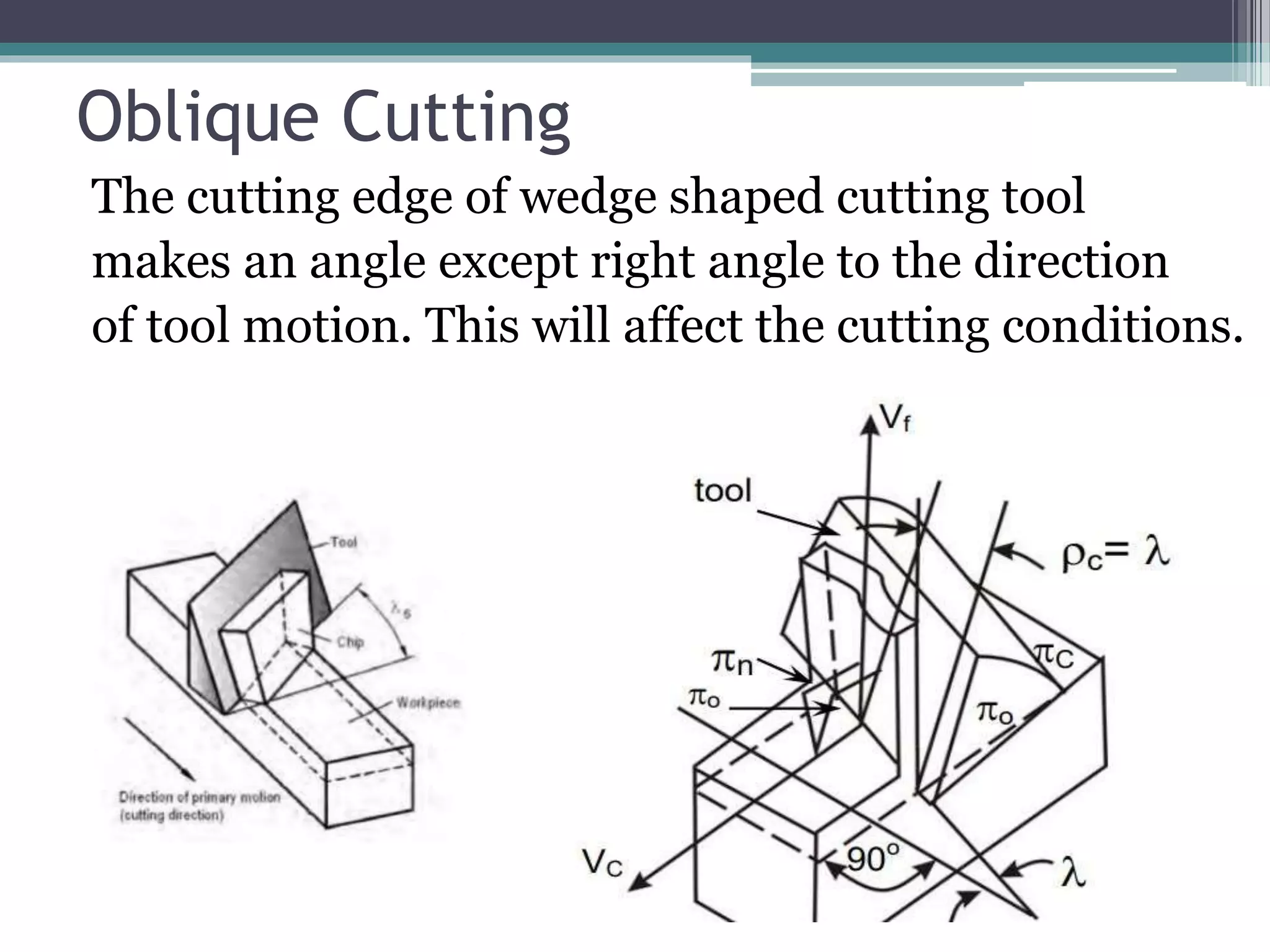
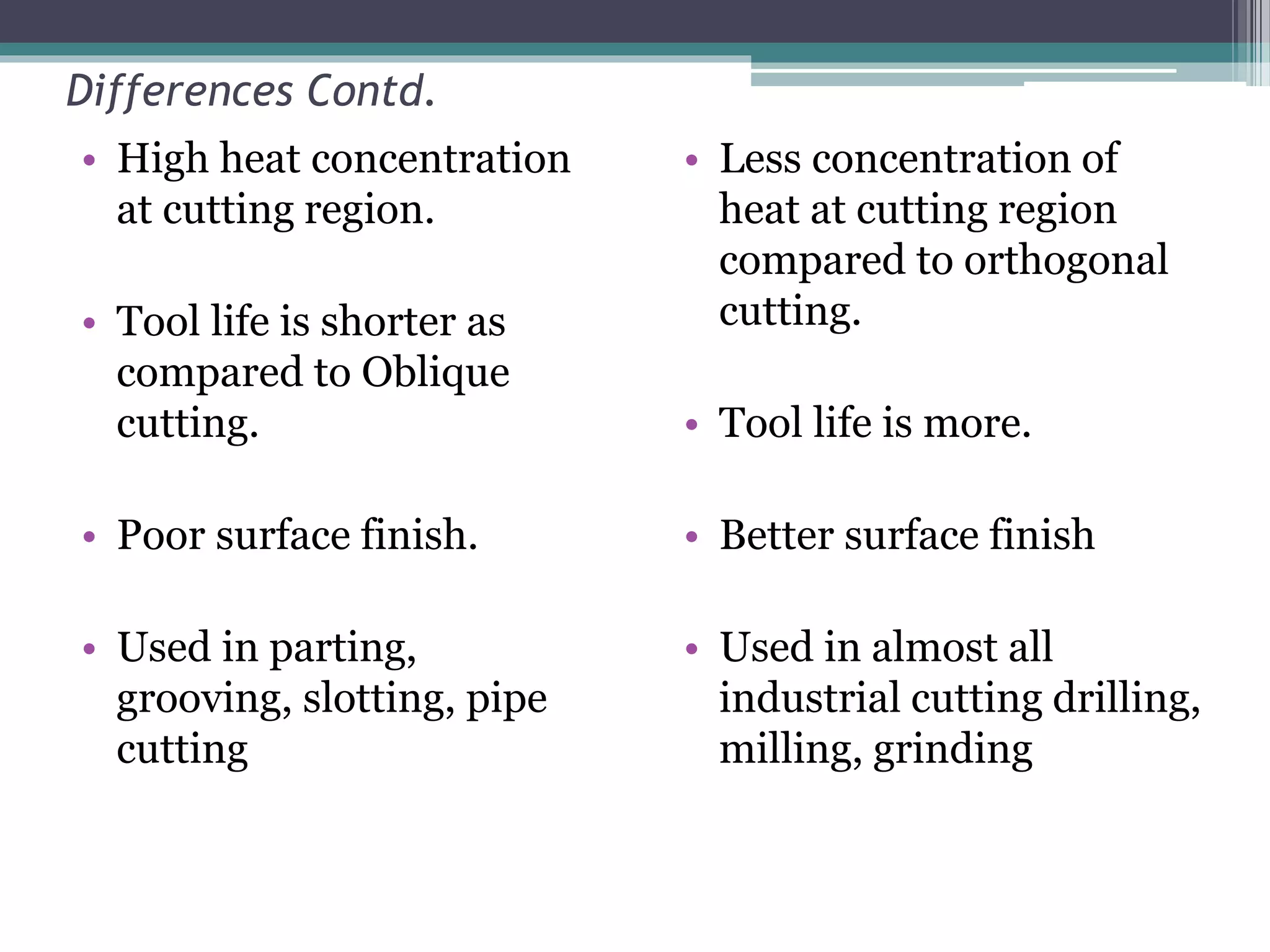
Metal cutting involves removing unwanted material from a workpiece. In orthogonal cutting, the cutting tool edge is perpendicular to the direction of motion, so chip flow is perpendicular to the cutting edge. In oblique cutting, the cutting tool edge is at an angle to the direction of motion, so chip flow is sideways. Orthogonal cutting results in higher heat concentration, shorter tool life, and poorer surface finish than oblique cutting. Oblique cutting is used for most industrial processes like drilling and milling.