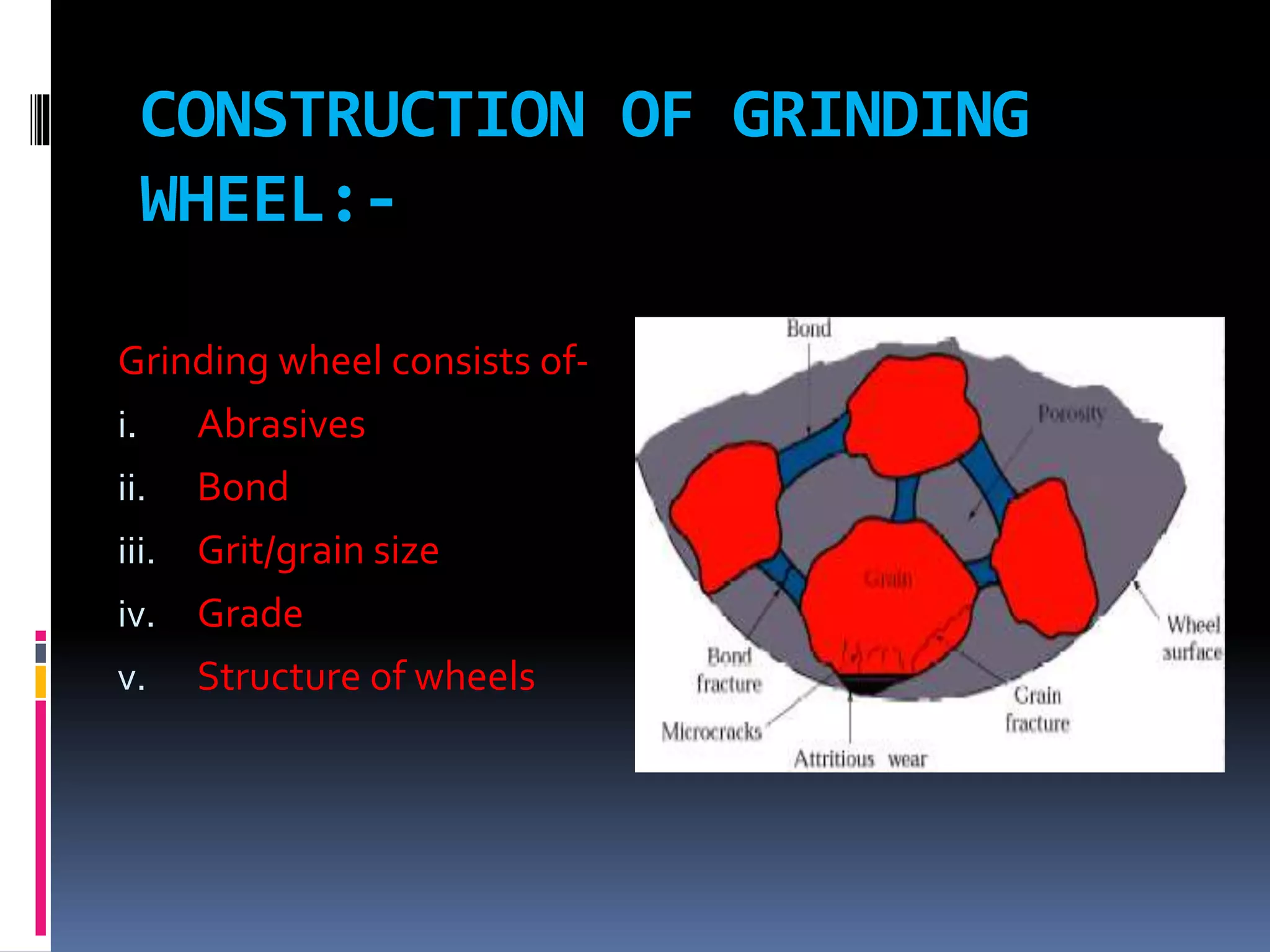
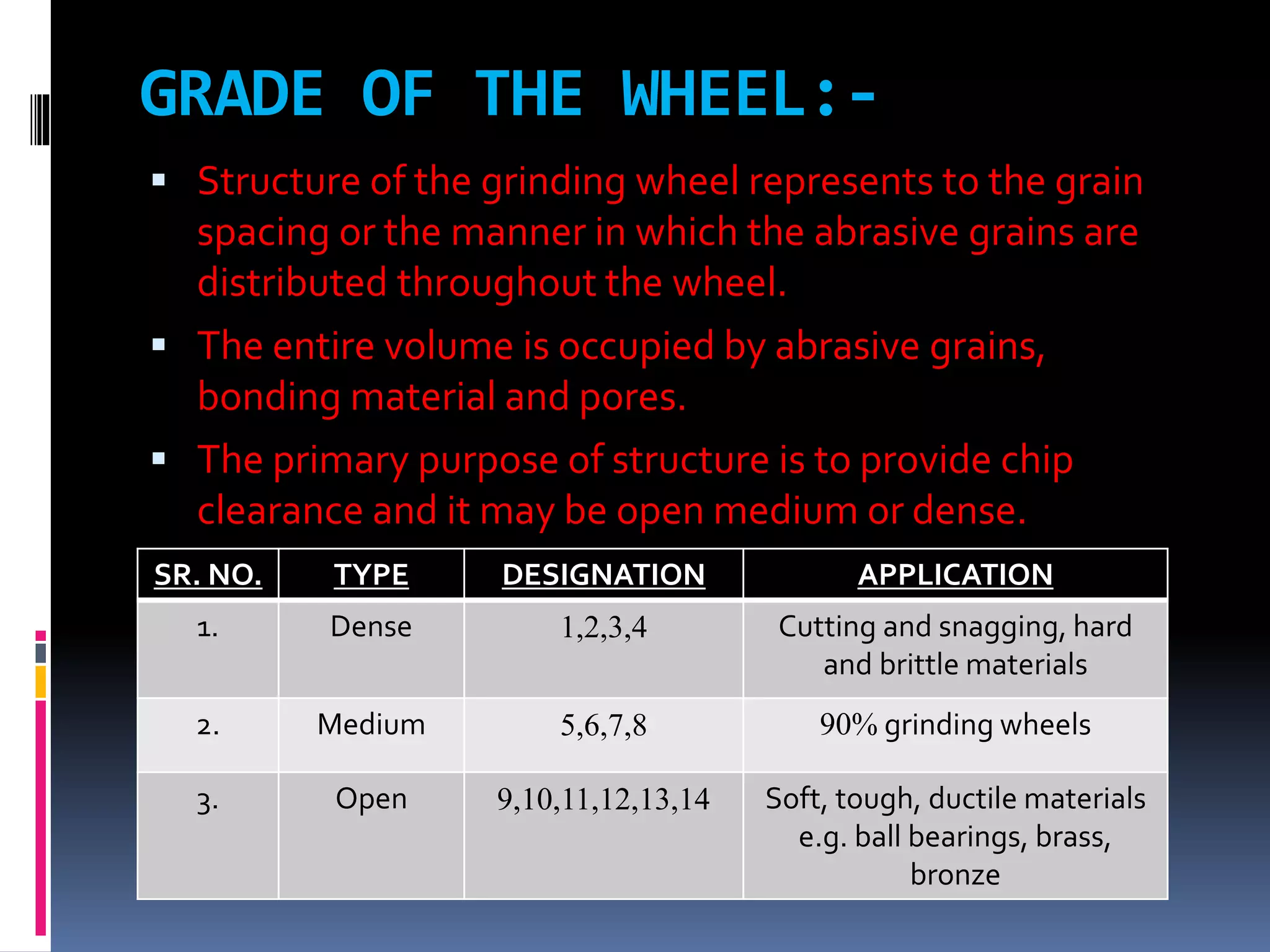
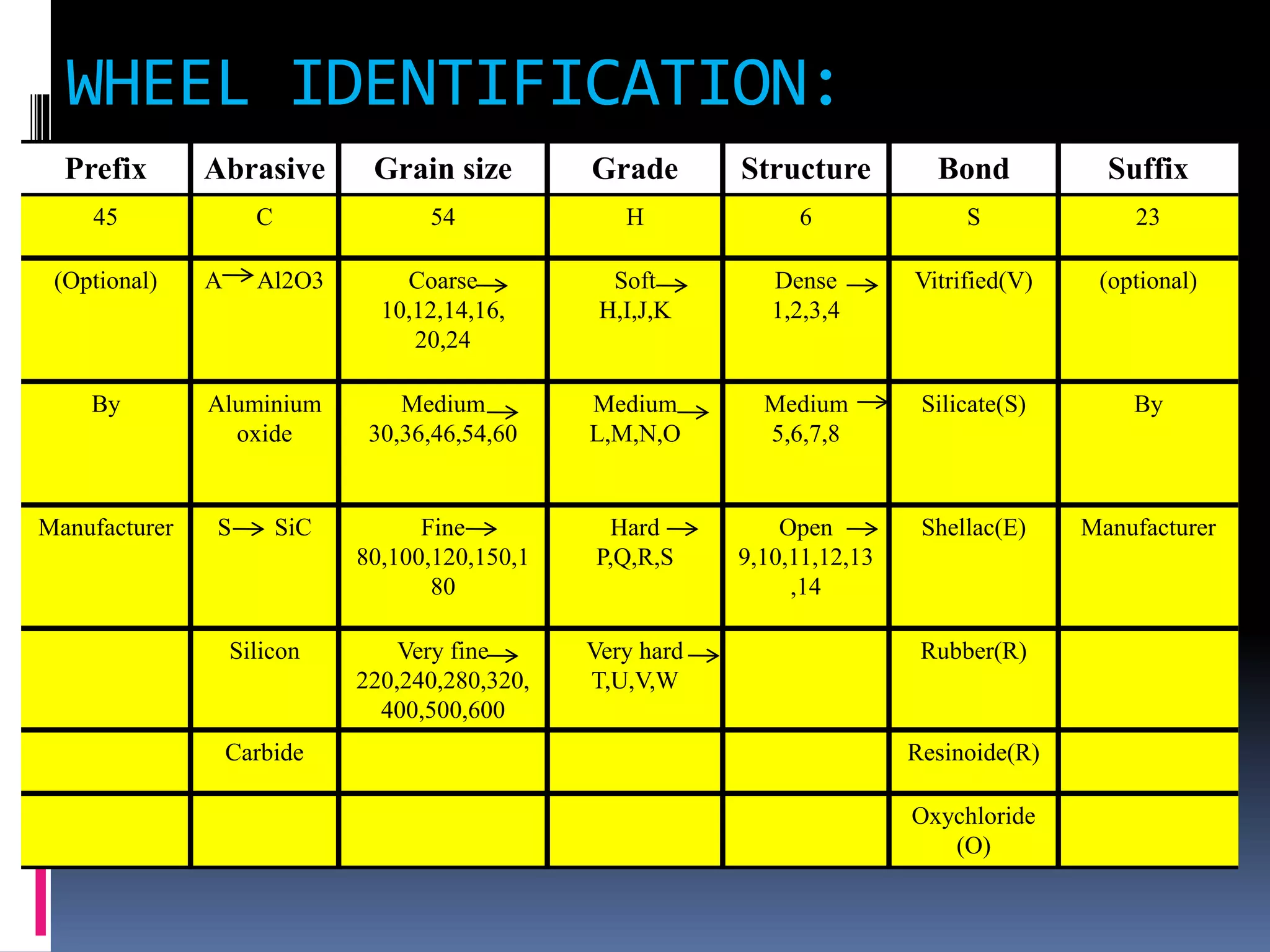
The document discusses the specifications and construction of grinding wheels. It states that a grinding wheel consists of abrasive grains and a bond that holds the grains together. The abrasive grains can be natural or synthetic and come in various sizes that determine stock removal rate and surface finish. The bond type and wheel structure also influence the grinding process. Proper wheel selection depends on factors like the material, operation, and required surface quality.