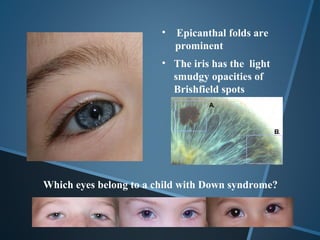
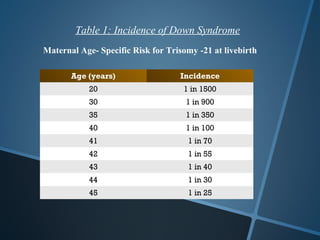
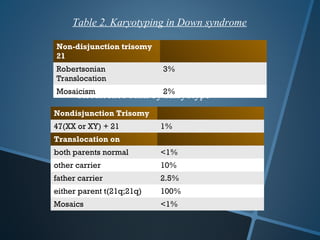
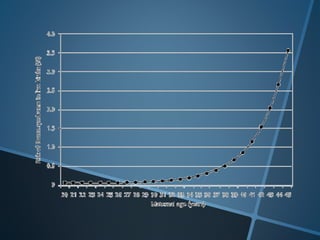
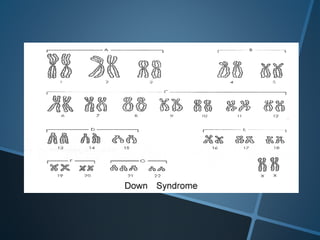
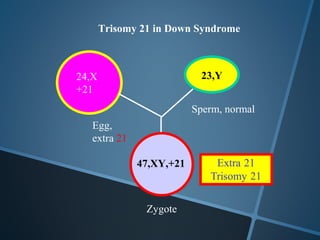
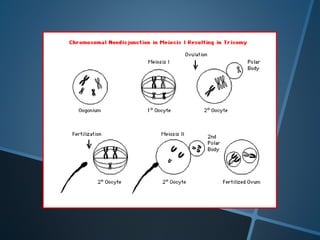
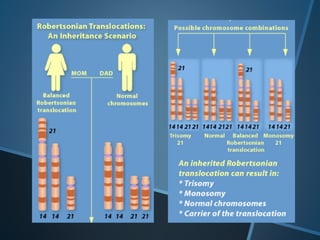
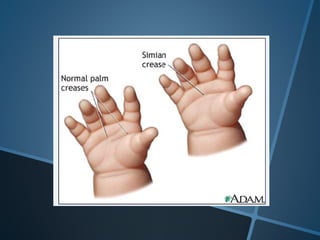
John Langdon Down was a British physician who first described Down syndrome in 1866 and recognized it as a distinct medical condition; he proposed that it results from reversion to ancestral traits seen in other races. Down syndrome, also known as trisomy 21, occurs when there is an extra chromosome 21 present and results in cognitive impairment and physical characteristics including a flat facial profile, upward slanting eyes, and a short neck. The risk of Down syndrome increases with maternal age and proper prenatal screening and testing can help diagnose the condition before birth.







![Newborn
• cardiac defects (50% ): AVSD [most
common], VSD, ASD, TOF or PDA
• gastrointestinal (12%): duodenal atresia
[commonest], tracheo-oesophageal
fistula, anorectal malformation, pyloric
stenosis and Hirshsprung disease.
• vision: congenital cataracts (3%),
glaucoma.
• hypotonia & joint laxity
• feeding problems. Usually
Resolve in few weeks.
• congenital hypothyroidism (1%)
• congenital dislocation of the hips](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/downsyndrome-120907114234-phpapp01/85/Down-syndrome-by-Dr-Rubzzz-17-320.jpg)